Memory doorbell circuit
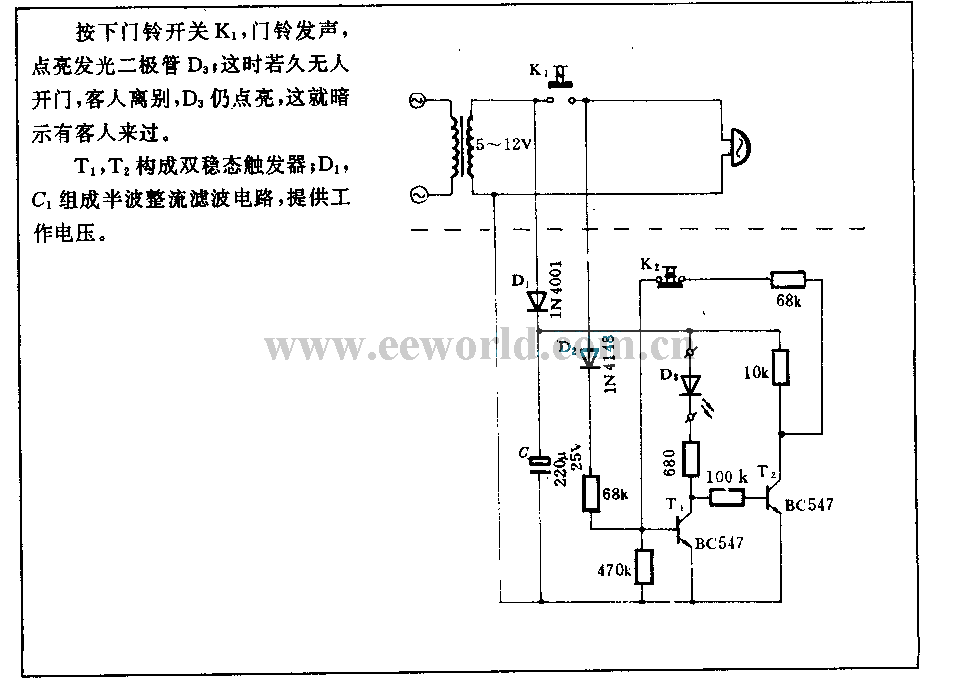
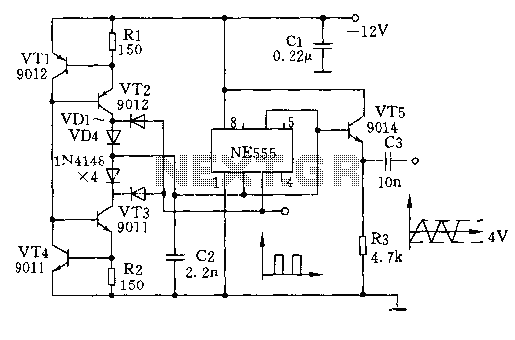
When the doorbell switch K1 is pressed, the doorbell rings and LED D3 lights up. If there is no one to answer the door, guests will leave, but D3 remains illuminated, indicating that visitors have arrived. The circuit includes a flip-flop made up of transistors T1 and T2. Additionally, D1 and C1 form a half-wave rectification filter circuit to provide the necessary operating voltage.
The described circuit functions as a visitor alert system that combines auditory and visual notifications. Upon pressing the doorbell switch K1, an electrical signal is generated, which activates the doorbell sound module. Simultaneously, LED D3 is illuminated, providing a visual cue that the doorbell has been activated.
In the event that no one answers the door, LED D3 continues to stay lit, serving as a reminder of the visitors who have come and left. This feature is particularly useful in scenarios where the homeowner may not have heard the doorbell.
The flip-flop circuit, composed of transistors T1 and T2, plays a crucial role in maintaining the state of LED D3. This configuration allows the LED to remain on even after the doorbell switch is released, effectively latching the state of the circuit until it is reset.
The half-wave rectification filter circuit, formed by diode D1 and capacitor C1, converts the AC voltage from the power supply into a usable DC voltage for the rest of the circuit. This ensures stable operation of the components, particularly the flip-flop and the LED, by smoothing out any fluctuations in the power supply.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient and serves a practical purpose in enhancing home security and visitor management, providing both sound and visual alerts to the homeowner.Pressed doorbell switch K1, the doorbell phonation, lighted up LED D3; if there are nobody to open the door, guests leave, D3 still on, this means there were guests came. Flip-flop is composed of T1, T2; D1, C1 form half wave rectification filter circuit, to support work voltage..
🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a visitor alert system that combines auditory and visual notifications. Upon pressing the doorbell switch K1, an electrical signal is generated, which activates the doorbell sound module. Simultaneously, LED D3 is illuminated, providing a visual cue that the doorbell has been activated.
In the event that no one answers the door, LED D3 continues to stay lit, serving as a reminder of the visitors who have come and left. This feature is particularly useful in scenarios where the homeowner may not have heard the doorbell.
The flip-flop circuit, composed of transistors T1 and T2, plays a crucial role in maintaining the state of LED D3. This configuration allows the LED to remain on even after the doorbell switch is released, effectively latching the state of the circuit until it is reset.
The half-wave rectification filter circuit, formed by diode D1 and capacitor C1, converts the AC voltage from the power supply into a usable DC voltage for the rest of the circuit. This ensures stable operation of the components, particularly the flip-flop and the LED, by smoothing out any fluctuations in the power supply.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient and serves a practical purpose in enhancing home security and visitor management, providing both sound and visual alerts to the homeowner.Pressed doorbell switch K1, the doorbell phonation, lighted up LED D3; if there are nobody to open the door, guests leave, D3 still on, this means there were guests came. Flip-flop is composed of T1, T2; D1, C1 form half wave rectification filter circuit, to support work voltage..
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713