Op-Amp Circuit: Difference Amplifier
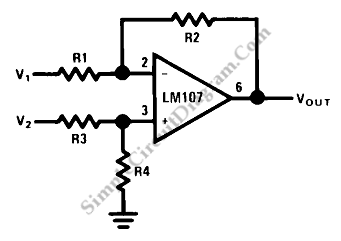
This circuit is a difference amplifier. It functions as an inverting amplifier that enables the subtraction of two voltages, effectively performing a summation.
The difference amplifier is a fundamental circuit configuration in analog electronics, primarily used for amplifying the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any common mode signals. This is particularly useful in applications where precise voltage measurements are required, such as in sensor signal conditioning and operational amplifiers.
The core components of a difference amplifier typically include four resistors and two operational amplifiers (op-amps). The resistors are arranged in a manner that sets the gain of the amplifier and determines the input impedance. The configuration can be represented using the following resistor values: R1 and R2 for the input stage, and R3 and R4 for the feedback stage. For ideal operation, the resistor values should be matched, meaning R1 = R3 and R2 = R4, which ensures that the circuit maintains a balanced response to differential inputs.
In operation, the voltage difference between the two input terminals (V1 and V2) is amplified by the circuit. The output voltage (Vout) can be expressed mathematically as:
Vout = (R2/R1) * (V2 - V1)
This equation highlights the role of the resistor ratios in determining the gain of the amplifier. When V1 and V2 are equal, the output voltage will be zero, demonstrating the ability of the difference amplifier to reject common mode signals.
The difference amplifier finds numerous applications, including data acquisition systems, instrumentation amplifiers, and in scenarios where noise reduction is critical. Its ability to amplify small differential signals in the presence of larger common mode voltages makes it an essential tool in precision measurement and control systems.This is a circuit of difference amplifier. This circuit is an inverting amplifier that allows the subtraction of two voltages and that is the summing.. 🔗 External reference
The difference amplifier is a fundamental circuit configuration in analog electronics, primarily used for amplifying the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any common mode signals. This is particularly useful in applications where precise voltage measurements are required, such as in sensor signal conditioning and operational amplifiers.
The core components of a difference amplifier typically include four resistors and two operational amplifiers (op-amps). The resistors are arranged in a manner that sets the gain of the amplifier and determines the input impedance. The configuration can be represented using the following resistor values: R1 and R2 for the input stage, and R3 and R4 for the feedback stage. For ideal operation, the resistor values should be matched, meaning R1 = R3 and R2 = R4, which ensures that the circuit maintains a balanced response to differential inputs.
In operation, the voltage difference between the two input terminals (V1 and V2) is amplified by the circuit. The output voltage (Vout) can be expressed mathematically as:
Vout = (R2/R1) * (V2 - V1)
This equation highlights the role of the resistor ratios in determining the gain of the amplifier. When V1 and V2 are equal, the output voltage will be zero, demonstrating the ability of the difference amplifier to reject common mode signals.
The difference amplifier finds numerous applications, including data acquisition systems, instrumentation amplifiers, and in scenarios where noise reduction is critical. Its ability to amplify small differential signals in the presence of larger common mode voltages makes it an essential tool in precision measurement and control systems.This is a circuit of difference amplifier. This circuit is an inverting amplifier that allows the subtraction of two voltages and that is the summing.. 🔗 External reference