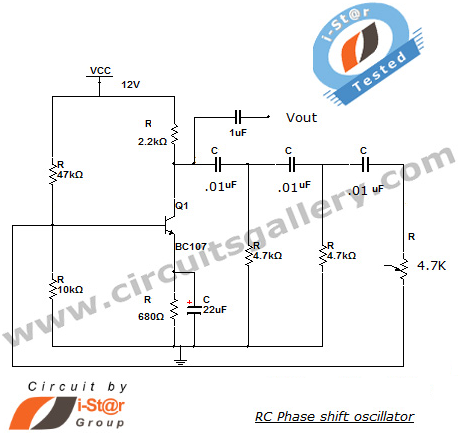
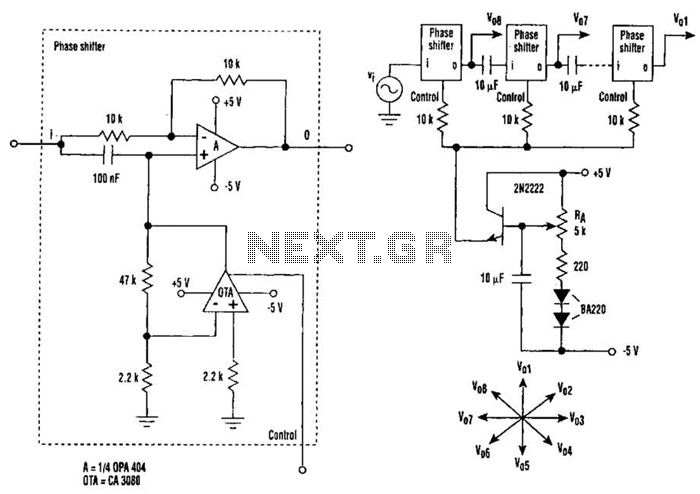
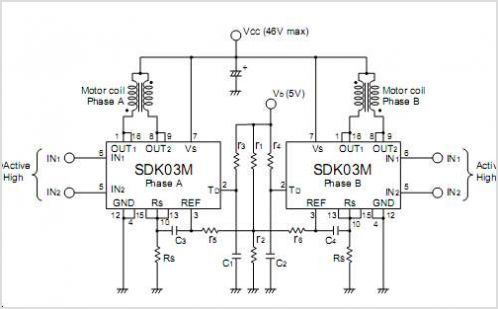
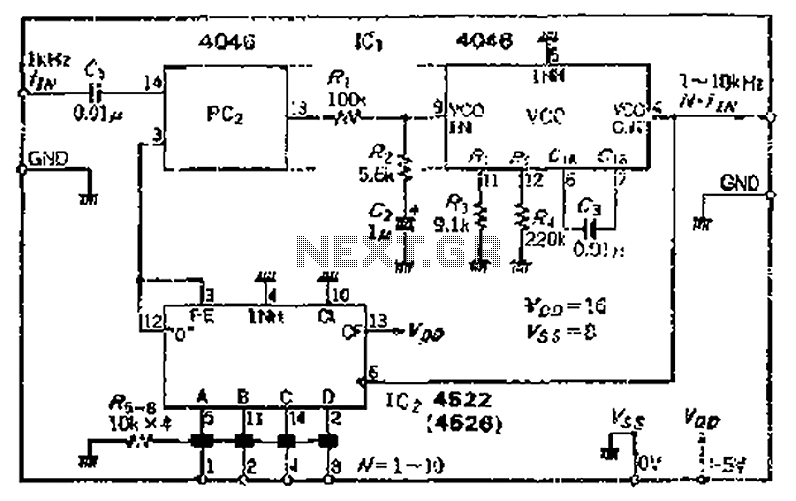
Measuring phase difference
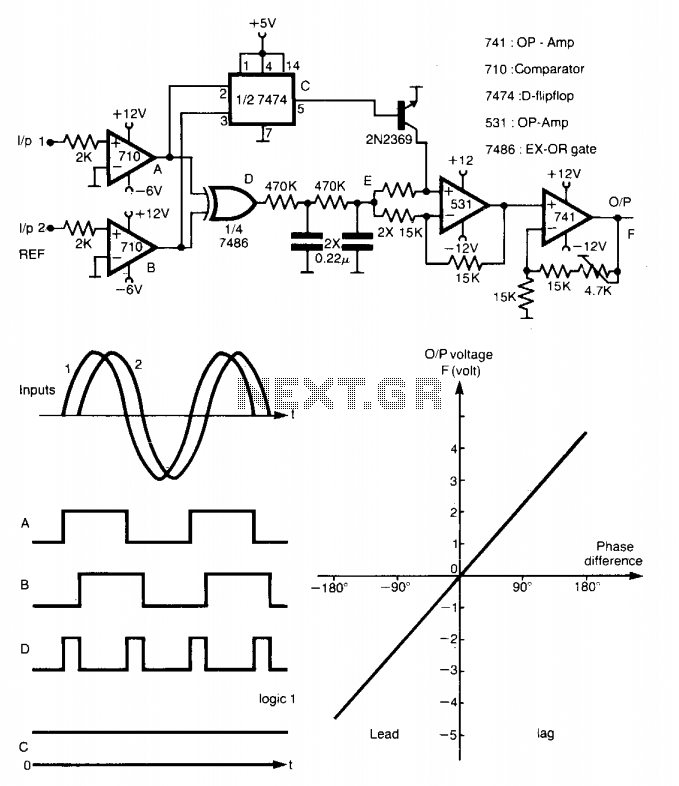
This method is capable of measuring the phase between 0 to ±180°. The generated square waves A and B are fed to a D flip-flop, which produces an output C equal to logic 1 when input A leads input B, and equal to logic 0 in the case of lagging. When C = logic 0, the output of the amplifier F will be positive and proportional to the average value of the output of the EX-OR. When C = logic 1, F will be negative and also proportional by the same factor. Hence, the output of the meter is positive in the case of lagging and negative for leading.
The circuit is tested for sinusoidal inputs and indicates a linearity within 1%. Measurements are unaffected by the frequency of the inputs up to 75 kHz.
The described circuit employs a method for phase measurement that is both effective and precise. The primary components include square wave generators, a D flip-flop, an EX-OR gate, and an amplifier. The square waves, designated as A and B, are generated to represent two distinct signals whose phase relationship is to be analyzed. The D flip-flop serves as a critical element in determining the leading or lagging nature of the input signals. It outputs logic 1 when signal A leads signal B and logic 0 when the opposite occurs.
The output from the D flip-flop, labeled as C, is fed into an amplifier, which is responsible for producing a proportional output based on the phase difference between the two input signals. When C is at logic 0, indicating that input A is lagging behind input B, the amplifier's output F is positive. Conversely, when C is at logic 1, indicating that input A is leading input B, the output F becomes negative. This dual-output mechanism allows for clear differentiation between leading and lagging phases, facilitating accurate phase measurement.
The circuit has been rigorously tested with sinusoidal inputs, demonstrating a linearity of within 1%. This indicates that the circuit maintains consistent performance across a range of input conditions. Additionally, the design is robust against variations in frequency, sustaining accurate measurements for input frequencies up to 75 kHz. This capability makes the circuit suitable for various applications in electronic measurement and control systems, where precise phase information is critical.This method is capable of measuring phase between 0 to ±180°. The generated square waves A and are fed to a D flip-flop which gives an output C equal to logic 1 when input 1 leads input 2 and equal to logic 0 in case of lagging. When C = logic 0, the output of the amplifier F will be positive proportional to the average value of the output of the EX-OR.
When C = logic 1, F will be negative and also proportional to by the same factor. Hence, the output of the meter is positive in case of lagging and negative for leading. The circuit is tested for sinusoidal inputs and indicates a linearity within 1%. Measurements are unaffected by the frequency of the inputs up to 75 kHz.
The circuit is tested for sinusoidal inputs and indicates a linearity within 1%. Measurements are unaffected by the frequency of the inputs up to 75 kHz.
The described circuit employs a method for phase measurement that is both effective and precise. The primary components include square wave generators, a D flip-flop, an EX-OR gate, and an amplifier. The square waves, designated as A and B, are generated to represent two distinct signals whose phase relationship is to be analyzed. The D flip-flop serves as a critical element in determining the leading or lagging nature of the input signals. It outputs logic 1 when signal A leads signal B and logic 0 when the opposite occurs.
The output from the D flip-flop, labeled as C, is fed into an amplifier, which is responsible for producing a proportional output based on the phase difference between the two input signals. When C is at logic 0, indicating that input A is lagging behind input B, the amplifier's output F is positive. Conversely, when C is at logic 1, indicating that input A is leading input B, the output F becomes negative. This dual-output mechanism allows for clear differentiation between leading and lagging phases, facilitating accurate phase measurement.
The circuit has been rigorously tested with sinusoidal inputs, demonstrating a linearity of within 1%. This indicates that the circuit maintains consistent performance across a range of input conditions. Additionally, the design is robust against variations in frequency, sustaining accurate measurements for input frequencies up to 75 kHz. This capability makes the circuit suitable for various applications in electronic measurement and control systems, where precise phase information is critical.This method is capable of measuring phase between 0 to ±180°. The generated square waves A and are fed to a D flip-flop which gives an output C equal to logic 1 when input 1 leads input 2 and equal to logic 0 in case of lagging. When C = logic 0, the output of the amplifier F will be positive proportional to the average value of the output of the EX-OR.
When C = logic 1, F will be negative and also proportional to by the same factor. Hence, the output of the meter is positive in case of lagging and negative for leading. The circuit is tested for sinusoidal inputs and indicates a linearity within 1%. Measurements are unaffected by the frequency of the inputs up to 75 kHz.