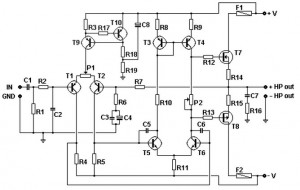
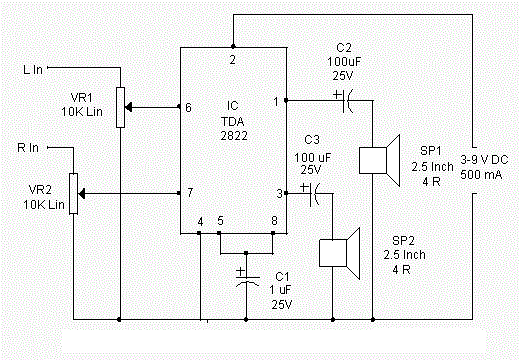
Mic Amplifier
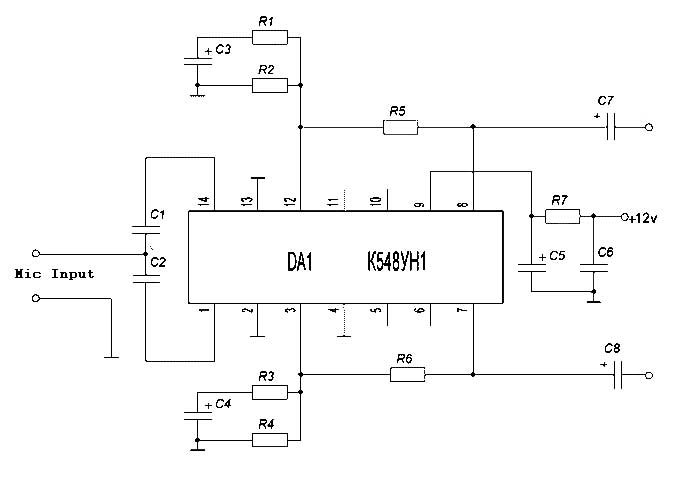
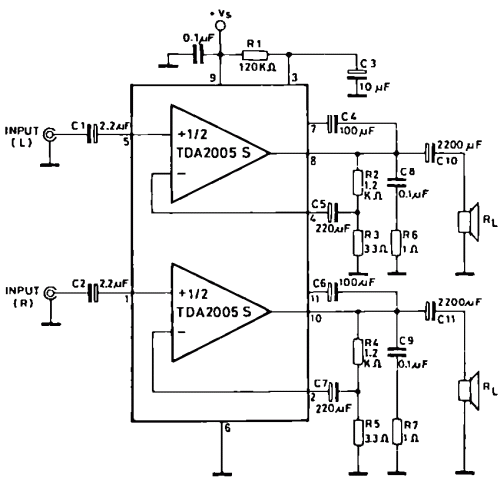
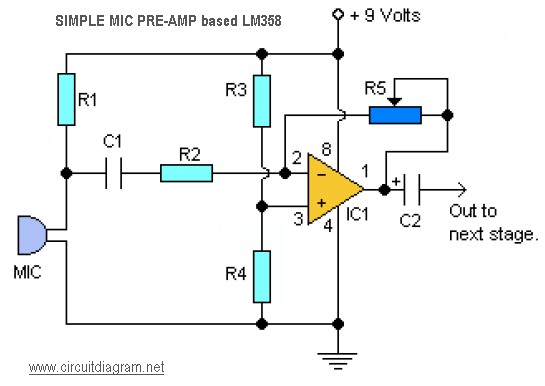
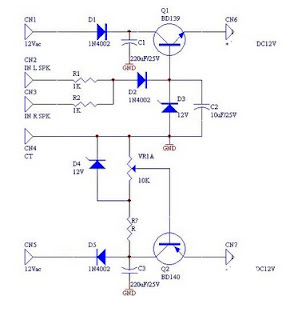
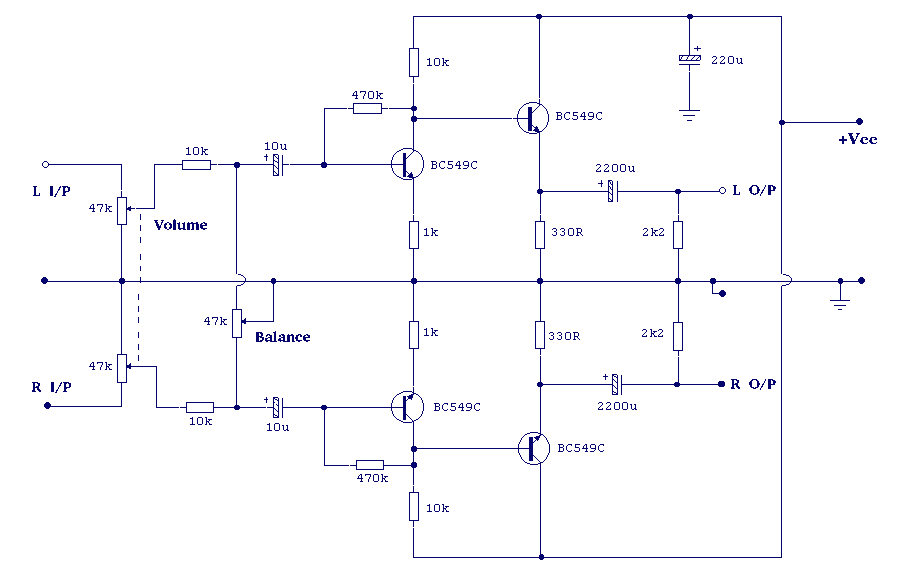
Microphone amplifier schematic diagram. This circuit has been tested with three microphones: one from SONY and two from Chinese manufacturers, and it operates successfully with all. When assembled correctly, the device functions immediately without the need for tuning.
The microphone amplifier circuit is designed to amplify audio signals from various types of microphones, ensuring clear and robust output suitable for further processing or amplification. The schematic typically includes essential components such as operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, capacitors, and sometimes transistors, depending on the desired gain and frequency response characteristics.
In this particular design, the op-amp serves as the core amplification element. The choice of op-amp is crucial; it should have low noise and high input impedance to avoid loading the microphone. The circuit may employ a single-supply or dual-supply configuration, depending on the op-amp specifications and the intended application.
Resistors are used to set the gain of the amplifier. The gain can be adjusted by changing the feedback resistor values, allowing for flexibility in amplification levels. Capacitors are typically included in the circuit to filter out unwanted frequencies and to stabilize the power supply, ensuring that the output signal remains clean and free from distortion.
The circuit also includes a power supply section, which may consist of a voltage regulator to provide a stable voltage to the op-amp. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power pins of the op-amp to minimize noise from the power supply.
Overall, this microphone amplifier schematic is versatile, capable of handling different microphone types, and is designed for immediate functionality upon assembly, making it an excellent choice for various audio applications.Mic Amplifier schematic diagram. This circuit has been tried on three microphones, one from SONY, and then two Chinese, everything works! With the correct assembly of the device starts to work immediately, and does not need tuning. 🔗 External reference
The microphone amplifier circuit is designed to amplify audio signals from various types of microphones, ensuring clear and robust output suitable for further processing or amplification. The schematic typically includes essential components such as operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, capacitors, and sometimes transistors, depending on the desired gain and frequency response characteristics.
In this particular design, the op-amp serves as the core amplification element. The choice of op-amp is crucial; it should have low noise and high input impedance to avoid loading the microphone. The circuit may employ a single-supply or dual-supply configuration, depending on the op-amp specifications and the intended application.
Resistors are used to set the gain of the amplifier. The gain can be adjusted by changing the feedback resistor values, allowing for flexibility in amplification levels. Capacitors are typically included in the circuit to filter out unwanted frequencies and to stabilize the power supply, ensuring that the output signal remains clean and free from distortion.
The circuit also includes a power supply section, which may consist of a voltage regulator to provide a stable voltage to the op-amp. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power pins of the op-amp to minimize noise from the power supply.
Overall, this microphone amplifier schematic is versatile, capable of handling different microphone types, and is designed for immediate functionality upon assembly, making it an excellent choice for various audio applications.Mic Amplifier schematic diagram. This circuit has been tried on three microphones, one from SONY, and then two Chinese, everything works! With the correct assembly of the device starts to work immediately, and does not need tuning. 🔗 External reference