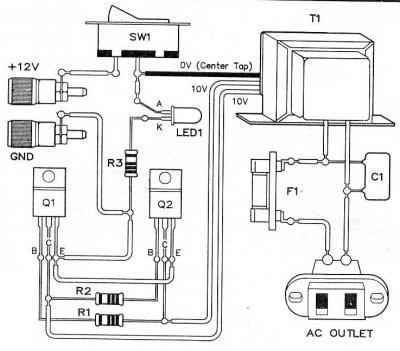
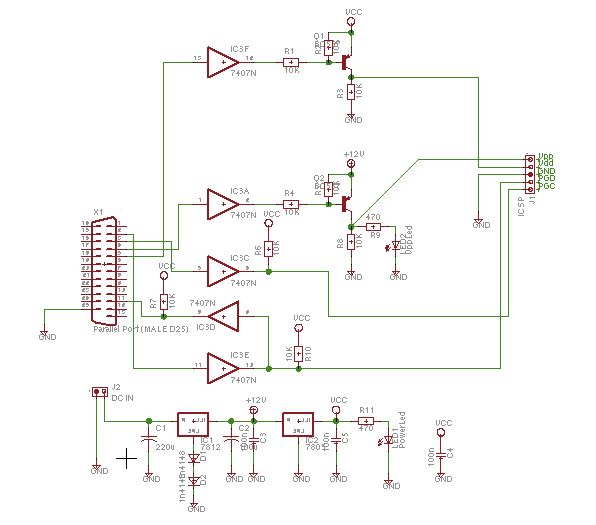
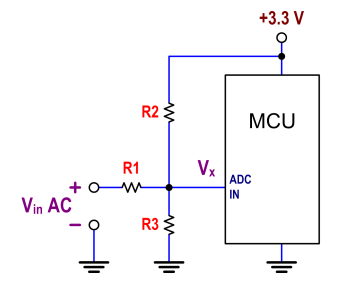
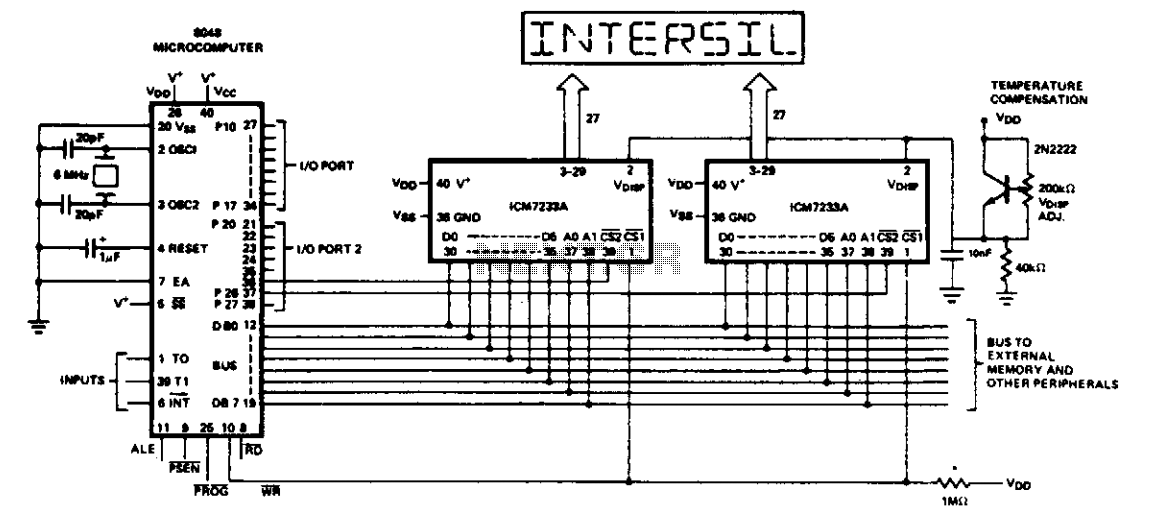
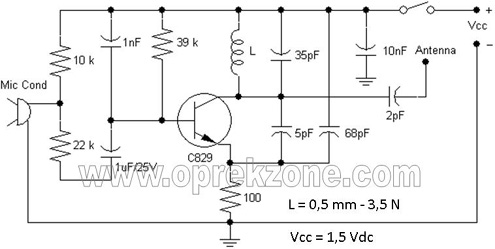
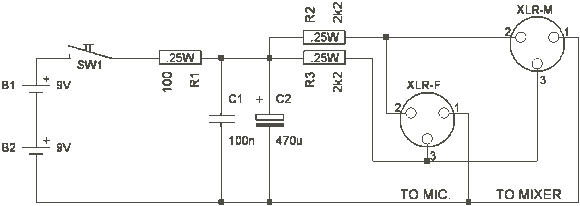
Mic Pre-Amp with Clipping
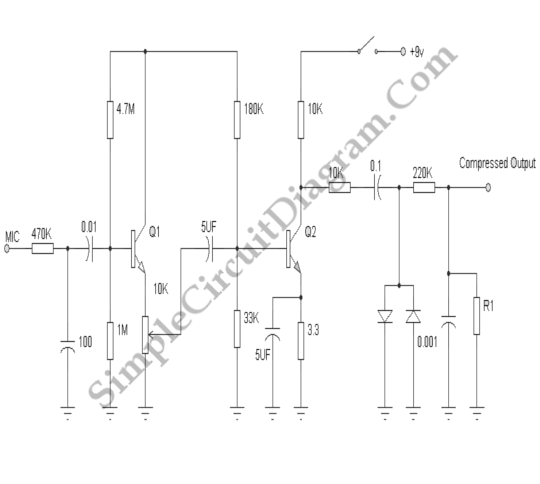
Signal clipping is typically avoided in most applications; however, there are specific instances in audio processing where clipping is intentionally utilized for beneficial effects.
Signal clipping is a phenomenon that occurs when an audio signal exceeds the maximum amplitude that a system can handle, resulting in the distortion of the waveform. In professional audio processing, clipping can be used creatively to enhance sound characteristics. For example, in electric guitar amplifiers, clipping is often employed to produce a "crunchy" sound that is desirable in rock music. This is achieved by intentionally driving the amplifier to its limits, causing the peaks of the waveform to flatten, which adds harmonic content and sustain to the sound.
In digital audio processing, clipping can also be used as a technique to increase perceived loudness without increasing the average level of the audio signal. By applying a soft clipping algorithm, the signal can be shaped in a way that adds warmth and richness, making it more engaging to the listener. This approach is commonly implemented in various audio effects processors and plugins.
Moreover, while clipping can enhance certain audio characteristics, it is essential to use it judiciously. Excessive clipping can lead to unwanted artifacts and a loss of audio fidelity. Therefore, understanding the context in which clipping is applied, as well as the desired outcome, is crucial for achieving the best results in audio engineering. Proper monitoring and metering during the mixing and mastering stages can help ensure that clipping is used effectively without compromising the overall sound quality.Signal clipping is usually avoided in most application, but we can find some useful examples where clipping is intentionally employed in audio processing. One.. 🔗 External reference
Signal clipping is a phenomenon that occurs when an audio signal exceeds the maximum amplitude that a system can handle, resulting in the distortion of the waveform. In professional audio processing, clipping can be used creatively to enhance sound characteristics. For example, in electric guitar amplifiers, clipping is often employed to produce a "crunchy" sound that is desirable in rock music. This is achieved by intentionally driving the amplifier to its limits, causing the peaks of the waveform to flatten, which adds harmonic content and sustain to the sound.
In digital audio processing, clipping can also be used as a technique to increase perceived loudness without increasing the average level of the audio signal. By applying a soft clipping algorithm, the signal can be shaped in a way that adds warmth and richness, making it more engaging to the listener. This approach is commonly implemented in various audio effects processors and plugins.
Moreover, while clipping can enhance certain audio characteristics, it is essential to use it judiciously. Excessive clipping can lead to unwanted artifacts and a loss of audio fidelity. Therefore, understanding the context in which clipping is applied, as well as the desired outcome, is crucial for achieving the best results in audio engineering. Proper monitoring and metering during the mixing and mastering stages can help ensure that clipping is used effectively without compromising the overall sound quality.Signal clipping is usually avoided in most application, but we can find some useful examples where clipping is intentionally employed in audio processing. One.. 🔗 External reference