fm wireless microphone schematic
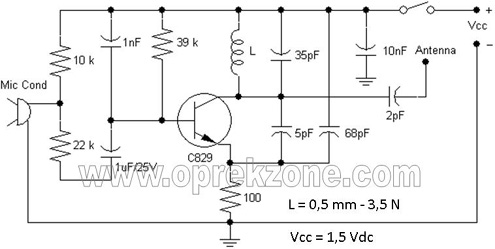
FM Wireless Microphone Schematic. In some applications, using a microphone cable can be quite challenging, necessitating the use of a cordless microphone, commonly referred to as a wireless microphone. This document presents a wireless microphone circuit schematic that utilizes a single transistor. The circuit operates on the FM band and is powered by 1.5-volt batteries. The design incorporates a single bipolar transistor, specifically the 2SC829, along with a few passive components. All capacitors are made from ceramic materials, and the resistors are rated at 1/4 watt to optimize the performance of the FM wireless microphone circuit. A single 1.5 V DC battery serves as the power supply. The antenna consists of a 0.75-meter copper wire, which can be fabricated on a printed circuit board (PCB). The circuit can be designed on a compact PCB measuring 0.8 x 5 cm, making it small enough to fit into the handle of the microphone. The inductor is constructed using enamel-coated wire with a diameter of 0.5 mm and consists of 3.5 turns. The operating frequency of the FM wireless microphone can be adjusted by stretching or tightening the wire coil of the inductor. The effective range of this wireless microphone can exceed 10 meters in a line-of-sight (LOS) condition, or without obstructions to the FM radio receiver.
The FM wireless microphone circuit is an efficient solution for applications where mobility is essential. The choice of the 2SC829 transistor is crucial, as it provides adequate amplification while operating at low voltage, which is ideal for battery-powered devices. The use of ceramic capacitors ensures stability and reliability in the circuit, especially in the high-frequency FM range.
The PCB layout, at a compact size of 0.8 x 5 cm, allows for easy integration into various microphone designs, ensuring that the circuitry does not add significant bulk. The antenna design, using a 0.75-meter copper wire, is optimized for both size and performance, allowing the microphone to maintain a good signal quality within its effective range.
The inductor's construction is also a vital aspect of the circuit’s performance. The enamel-coated wire not only provides insulation but also helps in maintaining the integrity of the coil's inductance. By adjusting the number of turns and the physical tension of the coil, users can fine-tune the operating frequency to match the desired FM band.
In summary, this FM wireless microphone schematic presents a practical and compact solution for wireless audio transmission, making it suitable for various applications, from public speaking to musical performances, where freedom of movement is a priority. The design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency, ensuring that users can easily replicate and utilize the circuit in their projects.FM Wireless Microphone Schematic. In some applications, the use of the microphone cable is sometimes very difficultly. So use a cordless microphone is needed. Microphone as it is often referred to as wireless microphones (cordless microphone). Here I share wireless microphone circuit schematics using one transistor. Constructed using one bipolar t ransistors and work on the FM band. Resources of the wireless FM microphone circuit is derived from the 1, 5 Volt batteries. Constructed using a single transistor 2SC829 and a few passive components. All capacitors using ceramic materials and resistors using the 1/4 watt to save a FM wireless microphone schematic circuit. Used a single 1. 5 Vdc of battery for power supply. Antenna can be used with a cable 0. 75 meters of length use copper lines made on pcb. The following sightings : Circuit of wireless fm microphone can be made on the of 0. 8 x 5 cm size pcb, so small enough to put on the handle body of microphone. Inductor built it using email wire diameter size of 0. 5 mm by 3. 5 turns. Setting the work frequency of fm wireless microphone made with stretch and tighten the wire coil inductor.
Effective range of wireless microphone above can reach 10 meters in the state of LOS (Line Off Sight) or without obstruction to the FM radio receiver. 🔗 External reference
The FM wireless microphone circuit is an efficient solution for applications where mobility is essential. The choice of the 2SC829 transistor is crucial, as it provides adequate amplification while operating at low voltage, which is ideal for battery-powered devices. The use of ceramic capacitors ensures stability and reliability in the circuit, especially in the high-frequency FM range.
The PCB layout, at a compact size of 0.8 x 5 cm, allows for easy integration into various microphone designs, ensuring that the circuitry does not add significant bulk. The antenna design, using a 0.75-meter copper wire, is optimized for both size and performance, allowing the microphone to maintain a good signal quality within its effective range.
The inductor's construction is also a vital aspect of the circuit’s performance. The enamel-coated wire not only provides insulation but also helps in maintaining the integrity of the coil's inductance. By adjusting the number of turns and the physical tension of the coil, users can fine-tune the operating frequency to match the desired FM band.
In summary, this FM wireless microphone schematic presents a practical and compact solution for wireless audio transmission, making it suitable for various applications, from public speaking to musical performances, where freedom of movement is a priority. The design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency, ensuring that users can easily replicate and utilize the circuit in their projects.FM Wireless Microphone Schematic. In some applications, the use of the microphone cable is sometimes very difficultly. So use a cordless microphone is needed. Microphone as it is often referred to as wireless microphones (cordless microphone). Here I share wireless microphone circuit schematics using one transistor. Constructed using one bipolar t ransistors and work on the FM band. Resources of the wireless FM microphone circuit is derived from the 1, 5 Volt batteries. Constructed using a single transistor 2SC829 and a few passive components. All capacitors using ceramic materials and resistors using the 1/4 watt to save a FM wireless microphone schematic circuit. Used a single 1. 5 Vdc of battery for power supply. Antenna can be used with a cable 0. 75 meters of length use copper lines made on pcb. The following sightings : Circuit of wireless fm microphone can be made on the of 0. 8 x 5 cm size pcb, so small enough to put on the handle body of microphone. Inductor built it using email wire diameter size of 0. 5 mm by 3. 5 turns. Setting the work frequency of fm wireless microphone made with stretch and tighten the wire coil inductor.
Effective range of wireless microphone above can reach 10 meters in the state of LOS (Line Off Sight) or without obstruction to the FM radio receiver. 🔗 External reference