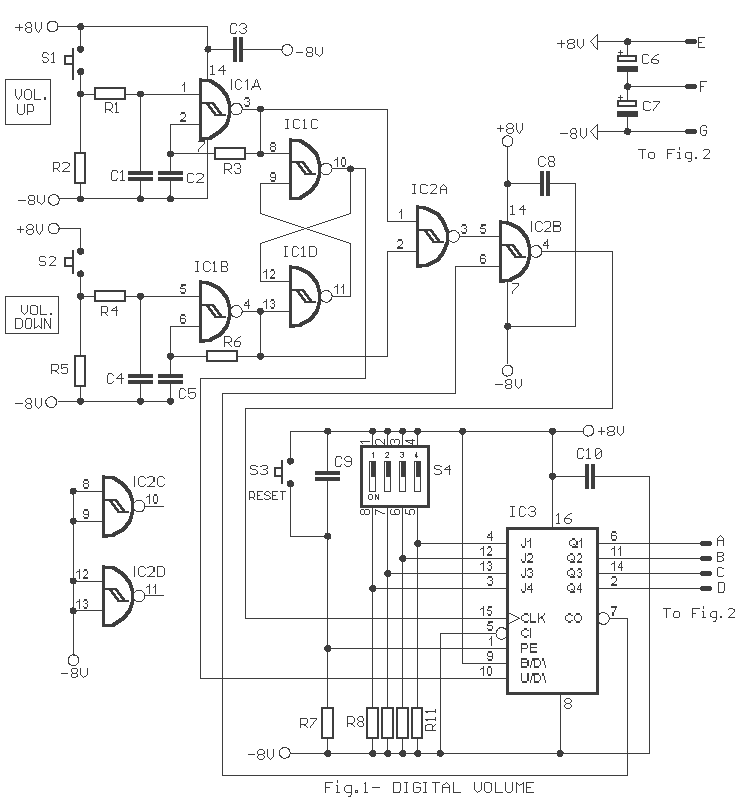
Microphone preamplifier with TLC251
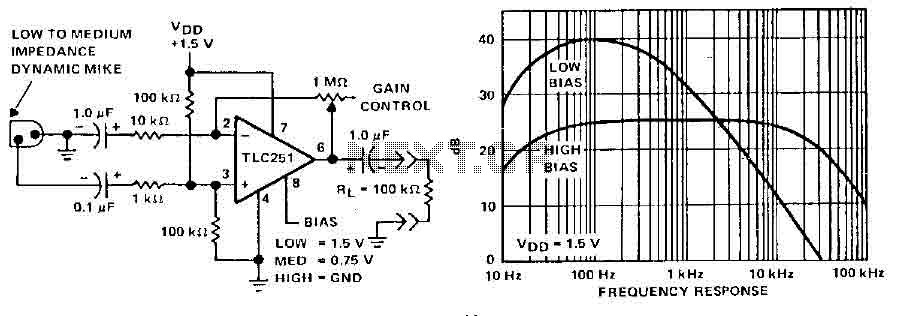
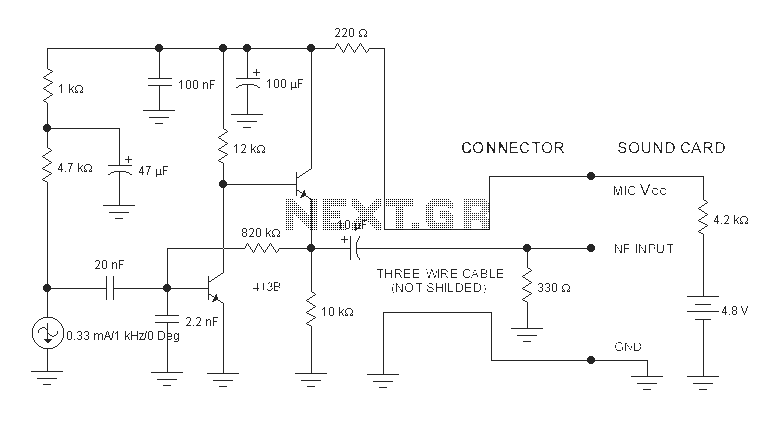
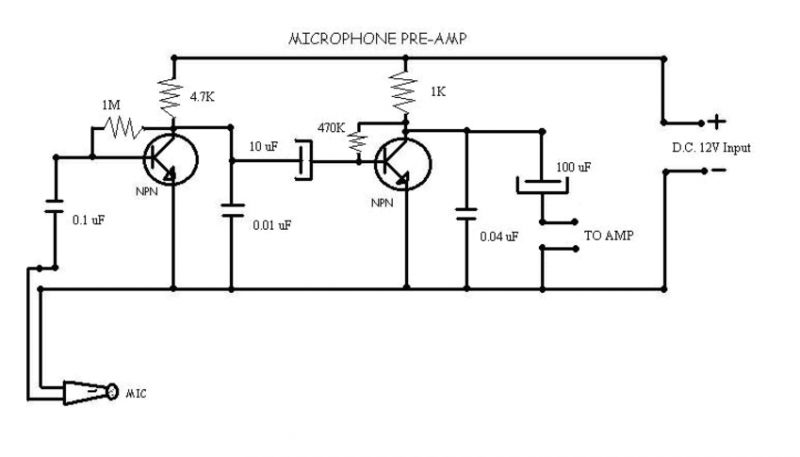
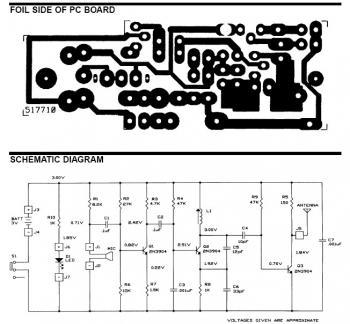
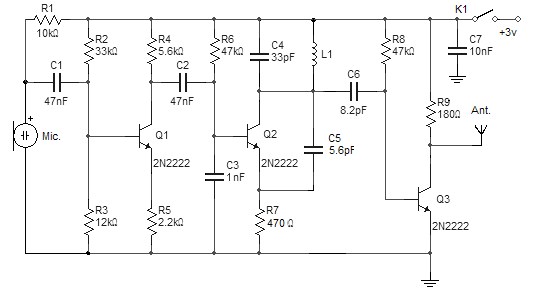
A microphone preamplifier utilizing a CMOS operational amplifier powered by its own battery is compact enough to fit within a small microphone casing. The amplifier functions with a 1.5V battery and exhibits low supply currents. This preamplifier operates at very low power while maintaining a reasonable frequency response. The TLC251, operating at a low bias of 1.5V, consumes a supply current of only 10 µA and has a frequency response of 3 dB ranging from 27 Hz to 4.8 kHz. With an 8-pin ground configuration, designated as the polarization state, the high limit increases above 25 kHz. The supply current is only 30 pA under these conditions.
The described microphone preamplifier is designed for applications where space and power efficiency are critical. The use of a CMOS operational amplifier, specifically the TLC251, ensures that the device operates with minimal power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The operational amplifier's low supply current of 10 µA at 1.5V is particularly advantageous for portable applications, allowing for extended battery life.
The frequency response of the preamplifier is critical for audio applications, with the specified 3 dB bandwidth from 27 Hz to 4.8 kHz ensuring that the device can accurately capture a wide range of audio signals. The low-frequency cutoff at 27 Hz allows for the reproduction of deep bass sounds, while the upper limit of 4.8 kHz ensures clarity in voice and instrument reproduction. The mention of a high limit increase above 25 kHz indicates that the amplifier can handle higher frequencies, which may be beneficial for certain audio applications, although the primary response range is focused on the audible spectrum.
The 8-pin grounded configuration facilitates easy integration into various circuit designs, providing a stable reference point for the operational amplifier. The low supply current of 30 pA under specific conditions further emphasizes the efficiency of the design, making it suitable for applications requiring long-term operation without frequent battery replacement.
Overall, this microphone preamplifier represents a well-engineered solution for enhancing audio signal quality in compact and energy-efficient formats. Its specifications indicate a balance between performance and power consumption, making it an ideal choice for modern portable audio devices.A microphone preamplifier using: om CMOS op amp with its own battery, is small enough to be placed in a case of small microphone. The amplifier operates from a 1.5V battery cathode mercury low supply currents. This preamp will operate at very low power and maintain a reasonable frequency response as well. The TLC251 is operating in low bias (operating at 1.5 V) draws a supply current of only 10 and has a year - frequency response of 3 dB 27 Hz to 4.8 kHz.
With 8-pin grounded, which is designated as the polarization state high limit increases above 25 kHz. Supply current is only - 30 pA under these conditions.
The described microphone preamplifier is designed for applications where space and power efficiency are critical. The use of a CMOS operational amplifier, specifically the TLC251, ensures that the device operates with minimal power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The operational amplifier's low supply current of 10 µA at 1.5V is particularly advantageous for portable applications, allowing for extended battery life.
The frequency response of the preamplifier is critical for audio applications, with the specified 3 dB bandwidth from 27 Hz to 4.8 kHz ensuring that the device can accurately capture a wide range of audio signals. The low-frequency cutoff at 27 Hz allows for the reproduction of deep bass sounds, while the upper limit of 4.8 kHz ensures clarity in voice and instrument reproduction. The mention of a high limit increase above 25 kHz indicates that the amplifier can handle higher frequencies, which may be beneficial for certain audio applications, although the primary response range is focused on the audible spectrum.
The 8-pin grounded configuration facilitates easy integration into various circuit designs, providing a stable reference point for the operational amplifier. The low supply current of 30 pA under specific conditions further emphasizes the efficiency of the design, making it suitable for applications requiring long-term operation without frequent battery replacement.
Overall, this microphone preamplifier represents a well-engineered solution for enhancing audio signal quality in compact and energy-efficient formats. Its specifications indicate a balance between performance and power consumption, making it an ideal choice for modern portable audio devices.A microphone preamplifier using: om CMOS op amp with its own battery, is small enough to be placed in a case of small microphone. The amplifier operates from a 1.5V battery cathode mercury low supply currents. This preamp will operate at very low power and maintain a reasonable frequency response as well. The TLC251 is operating in low bias (operating at 1.5 V) draws a supply current of only 10 and has a year - frequency response of 3 dB 27 Hz to 4.8 kHz.
With 8-pin grounded, which is designated as the polarization state high limit increases above 25 kHz. Supply current is only - 30 pA under these conditions.