Mini LOGGER V1.0 Block Diagram
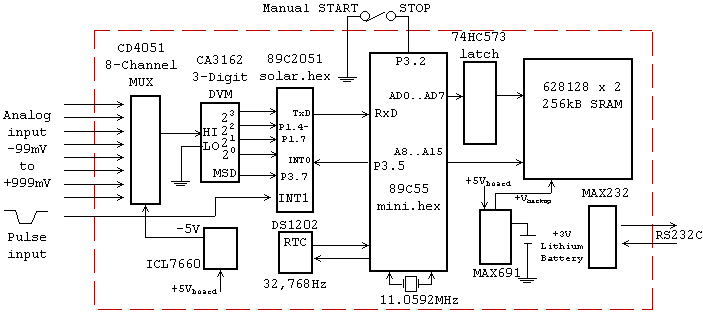
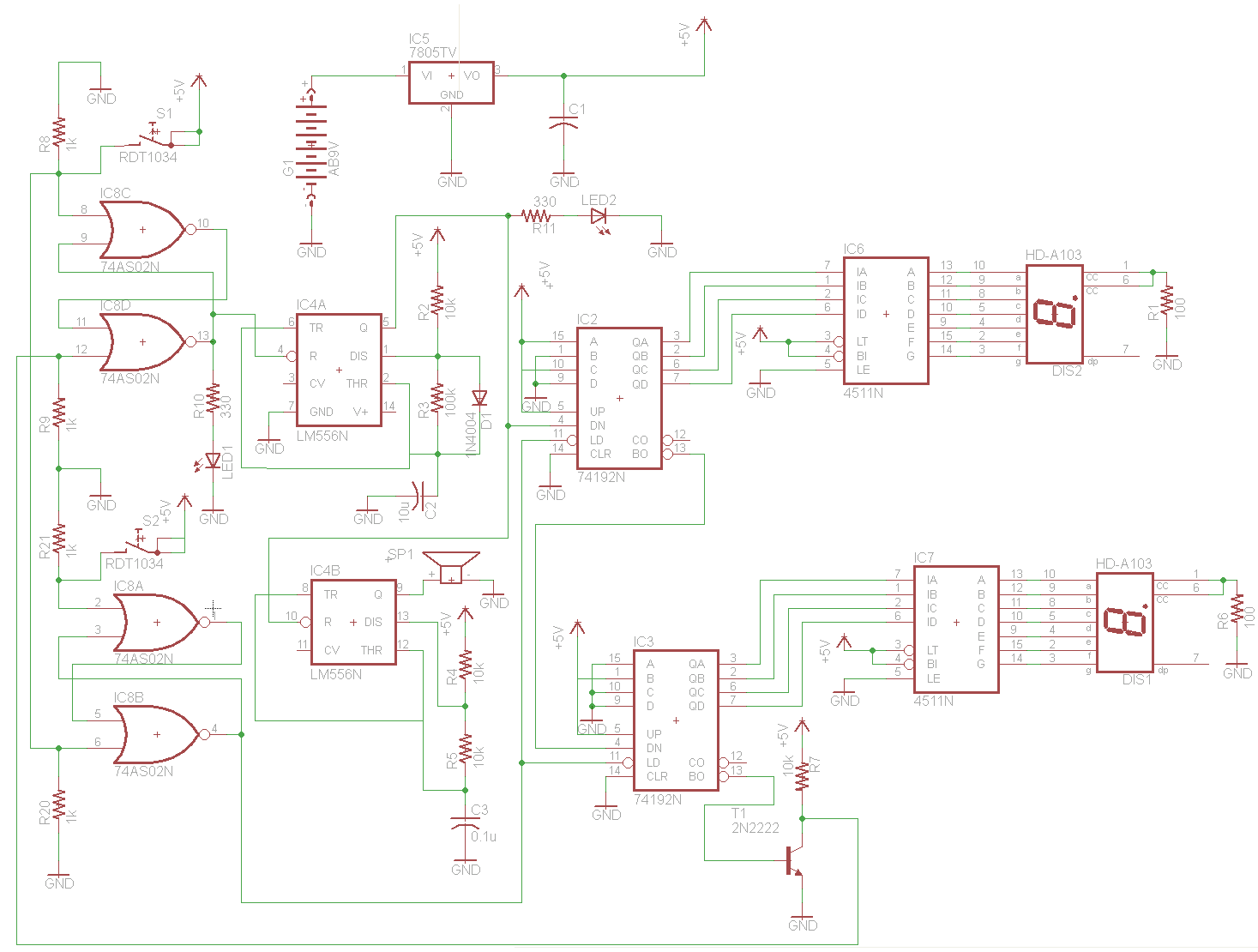
A simplified block diagram of the MiniLOGGER is presented. The CMOS analog multiplexer, 4051, provides output for an 8-channel single-ended input to the analog-to-digital converter chip, CA3162, which operates in free-running mode. The digital output is a 4-bit BCD format, starting with the Most Significant Digit (MSD), followed by the Next Significant Digit (NSD) and the Least Significant Digit (LSD). The pulse period for the MSD is 2 ms. The 89C2051 microcontroller runs the firmware solar3.hex, which manages the 8-channel readings and responds to an external pulse. Upon receiving the INT0 signal, the microcontroller transmits the digital value in ASCII format through the TxD pin. The 89C55 microcontroller reads this record, time-stamped by the DS1202, and stores it in SRAM. Additionally, it saves the DATE/TIME and includes commas for channel separation. A supervisory and power supply chip, MAX691, is used for battery backup to the SRAM and real-time clock (RTC), while the MAX232 serves as an RS232 converter and the ICL7660 functions as a negative voltage converter.
The MiniLOGGER circuit integrates several key components to facilitate its function as a multi-channel data logger. The CMOS analog multiplexer (4051) allows for the selection of one of eight input channels, which are processed as single-ended signals. These signals are then fed into the CA3162 analog-to-digital converter, which is set to operate in free-running mode. The converter outputs a 4-bit Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) representation of the digital signal, beginning with the Most Significant Digit (MSD) and followed by the Next Significant Digit (NSD) and Least Significant Digit (LSD). The output pulse period for the MSD is specified at 2 milliseconds, ensuring timely data conversion.
The microcontroller, 89C2051, executes the firmware solar3.hex, which orchestrates the reading of the eight channels and manages external pulse reception. When triggered by an INT0 signal, the microcontroller sends the converted digital values via the TxD pin in ASCII format, enabling easy communication with other devices. The 89C55 microcontroller is responsible for reading the data records, which are time-stamped using the DS1202 real-time clock. This data is stored in SRAM and includes date and time information, with channel values separated by commas for clarity.
To enhance the reliability of the MiniLOGGER, a supervisory and power supply chip, MAX691, is integrated to provide battery backup for the SRAM and RTC, ensuring that critical data is retained during power outages. The MAX232 chip is included to facilitate RS232 communication, allowing for connectivity with standard serial devices. Lastly, the ICL7660 negative voltage converter is utilized to generate the necessary negative voltage levels required for certain components in the circuit, ensuring proper operation across the entire system. This comprehensive design enables the MiniLOGGER to function effectively as a robust data acquisition system.A simplified block diagram of the MiniLOGGER is shown in Figure 1. The CMOS analog multiplexer, 4051 provides the output for 8-channel single-end input to an analog-to-digital converter chip, CA3162. The CA3162 is connected in free running mode. The digital output is 4-bit BCD started with MSD, NSD, and LSD. The pulse period of MSD is 2ms. The 89C 2051 runs solar3. hex, the firmware that controls 8-channel reading and receives external pulse. When the chip was triggered by INT0 signal, it will send the digital value in ASCII format through TxD pin; The 89C55 reads such record with time stamped read from DS1202 and saved into SRAM. Now it saves also DATE/TIME and provides comma for each channel separation. There`s also a supervisory and power supply chip, MAX691 for battery backup to SRAM and RTC, MAX232 for RS232 converter, and ICL7660 negative voltage converter.
🔗 External reference
The MiniLOGGER circuit integrates several key components to facilitate its function as a multi-channel data logger. The CMOS analog multiplexer (4051) allows for the selection of one of eight input channels, which are processed as single-ended signals. These signals are then fed into the CA3162 analog-to-digital converter, which is set to operate in free-running mode. The converter outputs a 4-bit Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) representation of the digital signal, beginning with the Most Significant Digit (MSD) and followed by the Next Significant Digit (NSD) and Least Significant Digit (LSD). The output pulse period for the MSD is specified at 2 milliseconds, ensuring timely data conversion.
The microcontroller, 89C2051, executes the firmware solar3.hex, which orchestrates the reading of the eight channels and manages external pulse reception. When triggered by an INT0 signal, the microcontroller sends the converted digital values via the TxD pin in ASCII format, enabling easy communication with other devices. The 89C55 microcontroller is responsible for reading the data records, which are time-stamped using the DS1202 real-time clock. This data is stored in SRAM and includes date and time information, with channel values separated by commas for clarity.
To enhance the reliability of the MiniLOGGER, a supervisory and power supply chip, MAX691, is integrated to provide battery backup for the SRAM and RTC, ensuring that critical data is retained during power outages. The MAX232 chip is included to facilitate RS232 communication, allowing for connectivity with standard serial devices. Lastly, the ICL7660 negative voltage converter is utilized to generate the necessary negative voltage levels required for certain components in the circuit, ensuring proper operation across the entire system. This comprehensive design enables the MiniLOGGER to function effectively as a robust data acquisition system.A simplified block diagram of the MiniLOGGER is shown in Figure 1. The CMOS analog multiplexer, 4051 provides the output for 8-channel single-end input to an analog-to-digital converter chip, CA3162. The CA3162 is connected in free running mode. The digital output is 4-bit BCD started with MSD, NSD, and LSD. The pulse period of MSD is 2ms. The 89C 2051 runs solar3. hex, the firmware that controls 8-channel reading and receives external pulse. When the chip was triggered by INT0 signal, it will send the digital value in ASCII format through TxD pin; The 89C55 reads such record with time stamped read from DS1202 and saved into SRAM. Now it saves also DATE/TIME and provides comma for each channel separation. There`s also a supervisory and power supply chip, MAX691 for battery backup to SRAM and RTC, MAX232 for RS232 converter, and ICL7660 negative voltage converter.
🔗 External reference