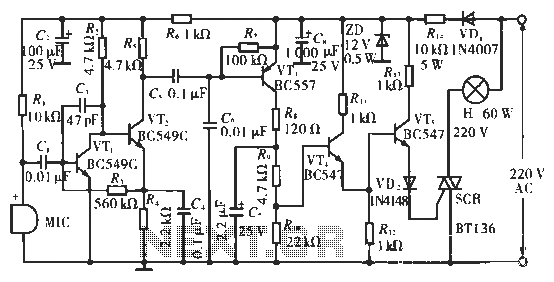
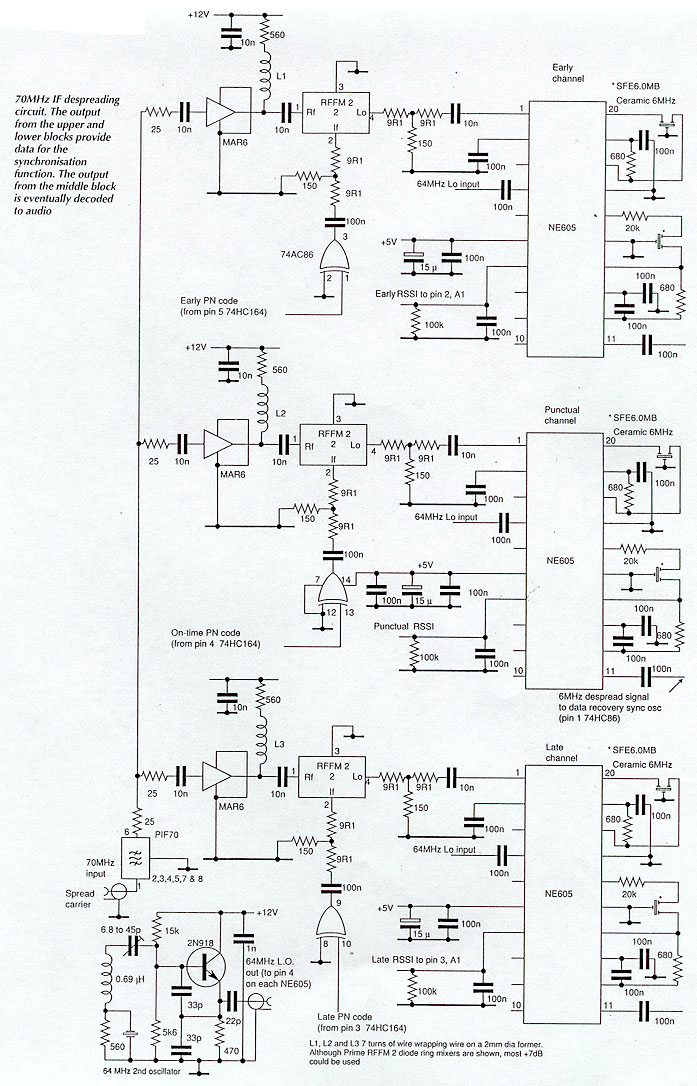
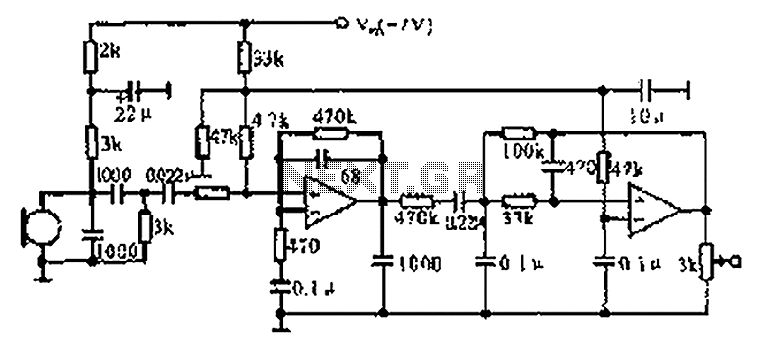
Mini Voice Operated RelayCircuit
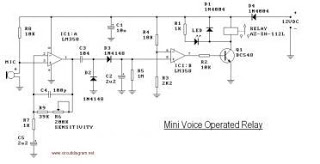
This circuit diagram represents a voice-operated relay. It functions similarly to a sound-activated switch circuit, which activates or deactivates the switch based on sound input. The output switch of this circuit operates through a relay.
The voice-operated relay circuit typically consists of a microphone, an amplifier, a comparator, and a relay module. The microphone captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified to ensure they are strong enough for further processing.
The amplified signal is fed into a comparator circuit, which compares the input signal against a predefined threshold level. When the sound exceeds this threshold, the comparator output changes state, signaling the relay to activate. This activation allows the relay to close its contacts, thereby connecting the output to the power source or load.
The relay is a crucial component in this circuit, as it provides electrical isolation between the low-power sound detection circuit and the high-power load. It ensures that the circuit can safely control devices that require higher voltages or currents without risking damage to the sound detection components.
Additionally, the circuit may include a delay mechanism to prevent false triggering from transient sounds or noise. This can be implemented using a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) timing circuit or a more sophisticated microcontroller-based approach, depending on the desired complexity and reliability of the system.
Overall, the voice-operated relay circuit is an effective solution for applications requiring sound-based control, such as automated lighting systems, remote switching, or interactive installations.This is the circuit diagram of a voice operated relay. It similar with sound activation switch circuit which will turn on and turn off (connect and disconnect) the switch depending on the sound input. The output switch of this circuit is act by a relay. 🔗 External reference
The voice-operated relay circuit typically consists of a microphone, an amplifier, a comparator, and a relay module. The microphone captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These signals are then amplified to ensure they are strong enough for further processing.
The amplified signal is fed into a comparator circuit, which compares the input signal against a predefined threshold level. When the sound exceeds this threshold, the comparator output changes state, signaling the relay to activate. This activation allows the relay to close its contacts, thereby connecting the output to the power source or load.
The relay is a crucial component in this circuit, as it provides electrical isolation between the low-power sound detection circuit and the high-power load. It ensures that the circuit can safely control devices that require higher voltages or currents without risking damage to the sound detection components.
Additionally, the circuit may include a delay mechanism to prevent false triggering from transient sounds or noise. This can be implemented using a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) timing circuit or a more sophisticated microcontroller-based approach, depending on the desired complexity and reliability of the system.
Overall, the voice-operated relay circuit is an effective solution for applications requiring sound-based control, such as automated lighting systems, remote switching, or interactive installations.This is the circuit diagram of a voice operated relay. It similar with sound activation switch circuit which will turn on and turn off (connect and disconnect) the switch depending on the sound input. The output switch of this circuit is act by a relay. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713