Miniature DC Motor Speed Control circuit
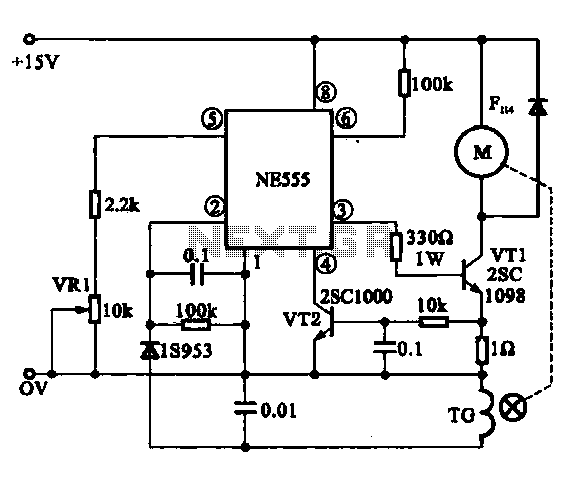
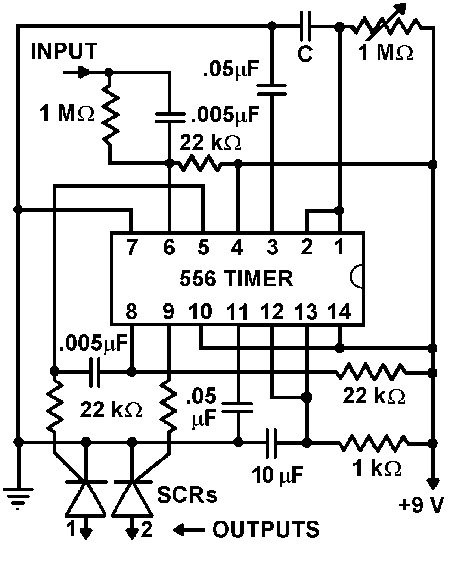
The Miniature DC Motor Speed Control circuit is designed to maintain a steady speed for micro motors, as illustrated in Figure 8-32. The circuit utilizes a voltage feedback mechanism suitable for applications such as tape recording machines that employ miniature DC motors. The driving circuit incorporates an NE 555 timer, which generates output switching pulses through the transistor VT1 to control the motor's rotation. The NE 555 timer receives a negative feedback signal input, allowing for steady speed regulation. An external potentiometer, VR1, enables fine adjustments to the motor speed. Additionally, Figure (b) presents a speed feedback motor drive circuit that includes a speed signal generator (TG). This generator filters the speed signal through a rectifier, converting it into a DC voltage that is fed back to the NE 555 timer. The NE 555 then tests and compares the voltage, producing a variable control signal at the output to maintain the desired motor speed.
The Miniature DC Motor Speed Control circuit operates by employing a combination of feedback mechanisms and control components to ensure consistent motor performance. The NE 555 timer serves as the central control unit, functioning in astable or monostable mode depending on the application requirements. In this configuration, the timer generates a series of pulses that dictate the switching of the transistor VT1, which in turn energizes the motor.
The feedback loop is critical for maintaining the desired speed. The voltage feedback from the motor is processed by the NE 555 timer, which compares the actual motor speed to the setpoint defined by the potentiometer VR1. By fine-tuning VR1, the user can adjust the threshold at which the NE 555 timer activates the transistor, thereby increasing or decreasing the motor speed as needed.
In the case of the speed feedback motor drive circuit depicted in Figure (b), the integration of a speed signal generator (TG) enhances the control mechanism. The TG outputs a signal that corresponds to the actual speed of the motor. This signal is rectified and converted to a DC voltage, which provides real-time feedback to the NE 555 timer. The timer continuously monitors this feedback and adjusts its output accordingly to ensure that the motor operates at a steady speed, compensating for any variations in load or supply voltage.
Overall, this circuit design is particularly useful in applications where precise speed control of miniature DC motors is essential, offering both simplicity and effectiveness in maintaining operational stability.Miniature DC Motor Speed Control circuit b Having a steady speed function micro motor drive circuit steady speed Miniature DC motor control circuit shown in Figure 8-32. Ring (a) shows the voltage feedback mode is for tape recording machine miniature DC motor drive circuit, which uses NE 555 when the base integrated circuit VT1 transistor output switching pulses through the drive motor rotation turn. NE 555 feet for the negative feedback signal input. Through the feedback loop to achieve steady speed control, feet external potentiometer VR1, can speed into fine adjustment.
Figure (b) shows the use of speed feedback motor drive circuit, which is provided to the motor speed signal generator TG, a speed signal filtered by the rectifier into a DC voltage is fed back to the @ NE 555 feet, the NE 555 testing and comparison, then by foot output a variable control signal, so as to achieve the purpose of steady speed.
The Miniature DC Motor Speed Control circuit operates by employing a combination of feedback mechanisms and control components to ensure consistent motor performance. The NE 555 timer serves as the central control unit, functioning in astable or monostable mode depending on the application requirements. In this configuration, the timer generates a series of pulses that dictate the switching of the transistor VT1, which in turn energizes the motor.
The feedback loop is critical for maintaining the desired speed. The voltage feedback from the motor is processed by the NE 555 timer, which compares the actual motor speed to the setpoint defined by the potentiometer VR1. By fine-tuning VR1, the user can adjust the threshold at which the NE 555 timer activates the transistor, thereby increasing or decreasing the motor speed as needed.
In the case of the speed feedback motor drive circuit depicted in Figure (b), the integration of a speed signal generator (TG) enhances the control mechanism. The TG outputs a signal that corresponds to the actual speed of the motor. This signal is rectified and converted to a DC voltage, which provides real-time feedback to the NE 555 timer. The timer continuously monitors this feedback and adjusts its output accordingly to ensure that the motor operates at a steady speed, compensating for any variations in load or supply voltage.
Overall, this circuit design is particularly useful in applications where precise speed control of miniature DC motors is essential, offering both simplicity and effectiveness in maintaining operational stability.Miniature DC Motor Speed Control circuit b Having a steady speed function micro motor drive circuit steady speed Miniature DC motor control circuit shown in Figure 8-32. Ring (a) shows the voltage feedback mode is for tape recording machine miniature DC motor drive circuit, which uses NE 555 when the base integrated circuit VT1 transistor output switching pulses through the drive motor rotation turn. NE 555 feet for the negative feedback signal input. Through the feedback loop to achieve steady speed control, feet external potentiometer VR1, can speed into fine adjustment.
Figure (b) shows the use of speed feedback motor drive circuit, which is provided to the motor speed signal generator TG, a speed signal filtered by the rectifier into a DC voltage is fed back to the @ NE 555 feet, the NE 555 testing and comparison, then by foot output a variable control signal, so as to achieve the purpose of steady speed.