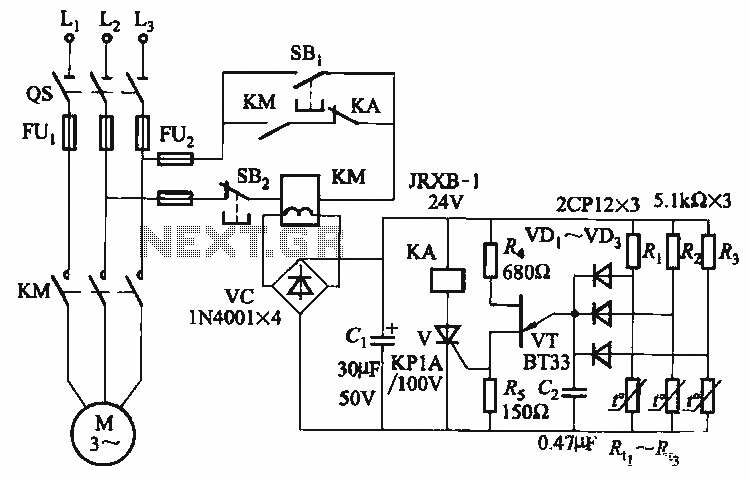
Modem/Fax Protector For Two Computers Circuit
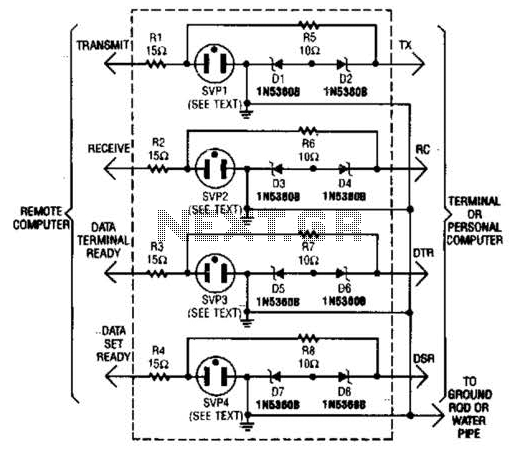
This modem/fax protector can be utilized in telephone-line connections between a PC or a terminal and a remote computer. In this circuit, the surge voltage protectors (SVPs) are rated at 230 V. Additionally, a proper grounding is essential for optimal performance.
The modem/fax protector circuit is designed to safeguard sensitive electronic equipment from voltage spikes and surges that may occur over telephone lines. It serves as a protective barrier between the connected devices and potential electrical disturbances, which can arise from lightning strikes, power fluctuations, or other anomalies in the electrical supply.
The circuit typically includes surge voltage protectors (SVPs) rated at 230 V, which are strategically placed to intercept and divert excessive voltage away from the devices. These SVPs operate by clamping the voltage to a safe level, thereby preventing damage to the modem or fax machine. The choice of a 230 V rating indicates that the protector is suitable for use in regions with standard voltage levels, ensuring compatibility with local electrical systems.
For effective operation, the circuit requires a robust grounding system. A good ground connection facilitates the dissipation of excess voltage into the earth, minimizing the risk of damage to connected equipment. The grounding path should be low-resistance and properly installed to ensure that it effectively diverts surges away from the electronic devices.
In designing the schematic for this modem/fax protector circuit, it is important to include the following components: the surge voltage protectors, connectors for telephone line inputs and outputs, and a grounding terminal. The layout should ensure that the SVPs are positioned close to the input connections to maximize their protective capabilities. Additionally, clear labeling of all connections and components will aid in the installation and maintenance of the circuit.
Overall, this modem/fax protector circuit is a crucial component in protecting telecommunications equipment, ensuring reliable performance and longevity in the presence of electrical disturbances. This modem/fax protector can be used in telephone-line connections between a PC or a terminal and a distant computer. In this circuit, the SVPs (surge voltage protectors) are rated at 230 V. A good ground is a must for effective operation.
The modem/fax protector circuit is designed to safeguard sensitive electronic equipment from voltage spikes and surges that may occur over telephone lines. It serves as a protective barrier between the connected devices and potential electrical disturbances, which can arise from lightning strikes, power fluctuations, or other anomalies in the electrical supply.
The circuit typically includes surge voltage protectors (SVPs) rated at 230 V, which are strategically placed to intercept and divert excessive voltage away from the devices. These SVPs operate by clamping the voltage to a safe level, thereby preventing damage to the modem or fax machine. The choice of a 230 V rating indicates that the protector is suitable for use in regions with standard voltage levels, ensuring compatibility with local electrical systems.
For effective operation, the circuit requires a robust grounding system. A good ground connection facilitates the dissipation of excess voltage into the earth, minimizing the risk of damage to connected equipment. The grounding path should be low-resistance and properly installed to ensure that it effectively diverts surges away from the electronic devices.
In designing the schematic for this modem/fax protector circuit, it is important to include the following components: the surge voltage protectors, connectors for telephone line inputs and outputs, and a grounding terminal. The layout should ensure that the SVPs are positioned close to the input connections to maximize their protective capabilities. Additionally, clear labeling of all connections and components will aid in the installation and maintenance of the circuit.
Overall, this modem/fax protector circuit is a crucial component in protecting telecommunications equipment, ensuring reliable performance and longevity in the presence of electrical disturbances. This modem/fax protector can be used in telephone-line connections between a PC or a terminal and a distant computer. In this circuit, the SVPs (surge voltage protectors) are rated at 230 V. A good ground is a must for effective operation.