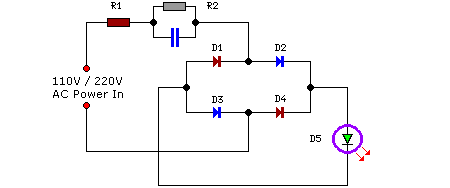
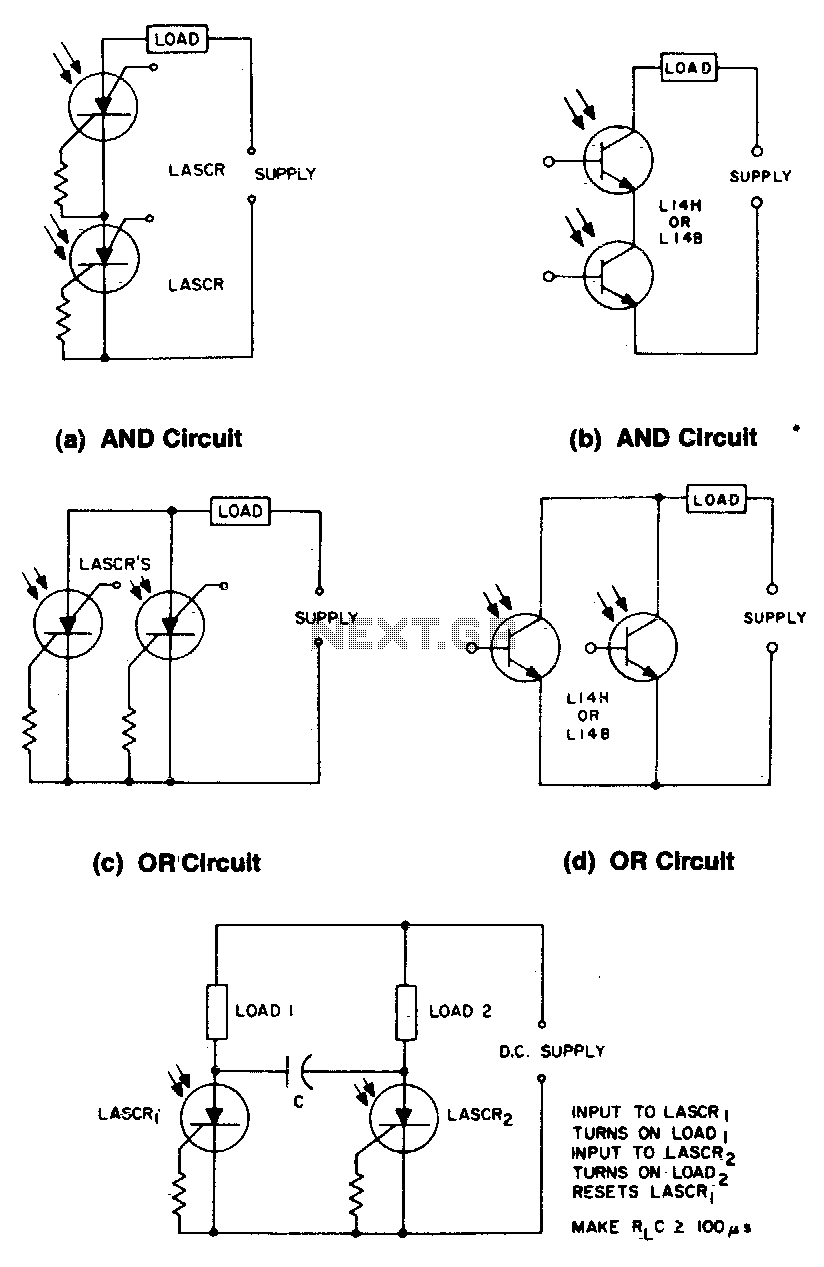
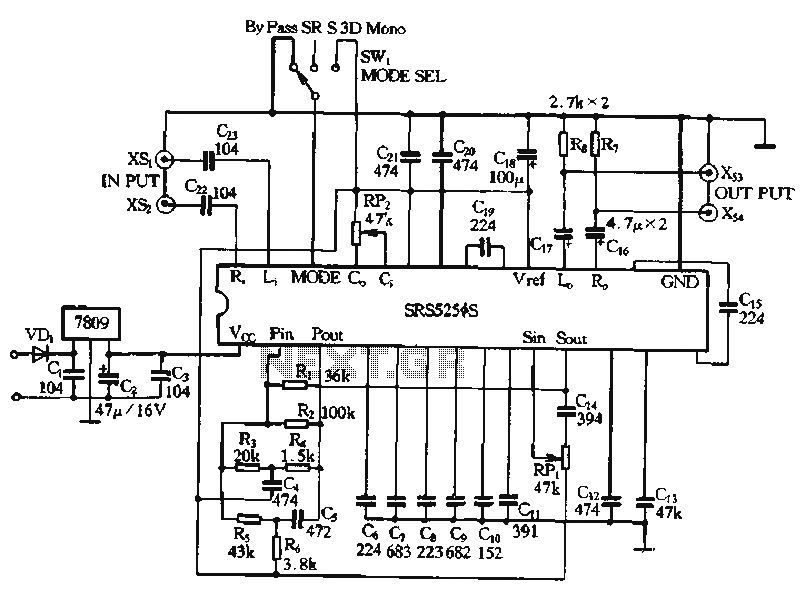
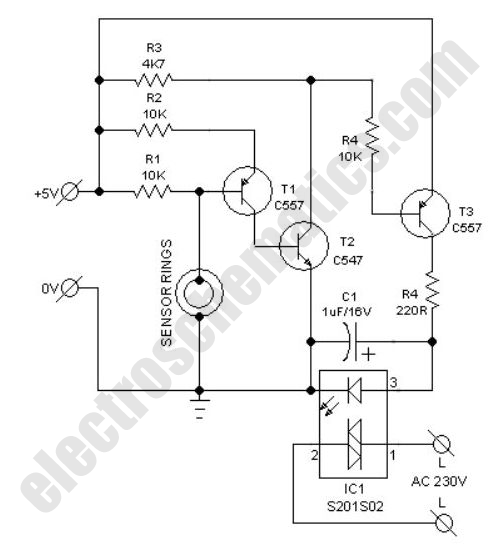
Modular Class A Buffer preamplifier circuit
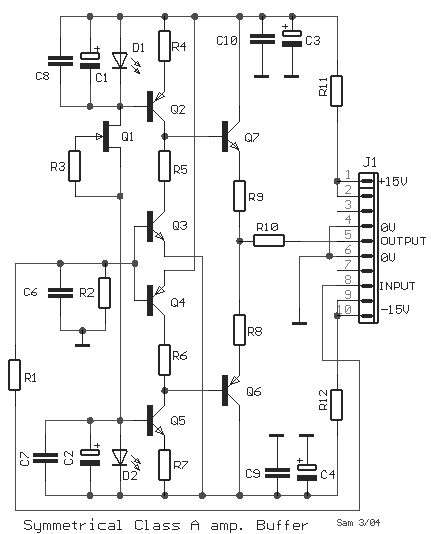
A unit that is often very useful for isolating two stages in sound circuits. This circuit incorporates an amplification unit with a gain of X1. It employs only local negative feedback rather than total negative feedback, resulting in very low distortion levels. Careful matching is required for the types of transistors and the resistor used between them.
This circuit is designed to function as a two-stage amplifier, providing isolation between stages to prevent signal interference and maintain audio fidelity. The amplification unit operates with a gain of X1, ensuring that the input signal is preserved without excessive amplification, which could introduce distortion. The use of local negative feedback is critical in this design, as it minimizes distortion while maintaining a stable gain.
The selection of transistors is crucial for optimal performance. Transistors must be matched not only in terms of their electrical characteristics but also in terms of their thermal stability. Variations in transistor parameters can lead to imbalances that affect the circuit's overall performance. Additionally, the resistor placed between the transistors must be chosen carefully to ensure that the biasing conditions are met, allowing for linear operation of the transistors and minimizing the risk of distortion.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various audio processing scenarios, such as in mixing consoles, effects units, or any situation where signal integrity is paramount. The careful design and component selection contribute to a robust audio path that can handle a variety of input signals while maintaining clarity and reducing unwanted artifacts.A unit which is often very useful, if we need to isolate, in sound circuits, two stage between them. Then we can use this circuit which has an amplified unit, which gain X1, we do not use total negative feedback, only local, with the result that distortion remains at a very low level. Matching must be done with great care to the types of transistors, resistor between them.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to function as a two-stage amplifier, providing isolation between stages to prevent signal interference and maintain audio fidelity. The amplification unit operates with a gain of X1, ensuring that the input signal is preserved without excessive amplification, which could introduce distortion. The use of local negative feedback is critical in this design, as it minimizes distortion while maintaining a stable gain.
The selection of transistors is crucial for optimal performance. Transistors must be matched not only in terms of their electrical characteristics but also in terms of their thermal stability. Variations in transistor parameters can lead to imbalances that affect the circuit's overall performance. Additionally, the resistor placed between the transistors must be chosen carefully to ensure that the biasing conditions are met, allowing for linear operation of the transistors and minimizing the risk of distortion.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various audio processing scenarios, such as in mixing consoles, effects units, or any situation where signal integrity is paramount. The careful design and component selection contribute to a robust audio path that can handle a variety of input signals while maintaining clarity and reducing unwanted artifacts.A unit which is often very useful, if we need to isolate, in sound circuits, two stage between them. Then we can use this circuit which has an amplified unit, which gain X1, we do not use total negative feedback, only local, with the result that distortion remains at a very low level. Matching must be done with great care to the types of transistors, resistor between them.. 🔗 External reference