Modulation monitor
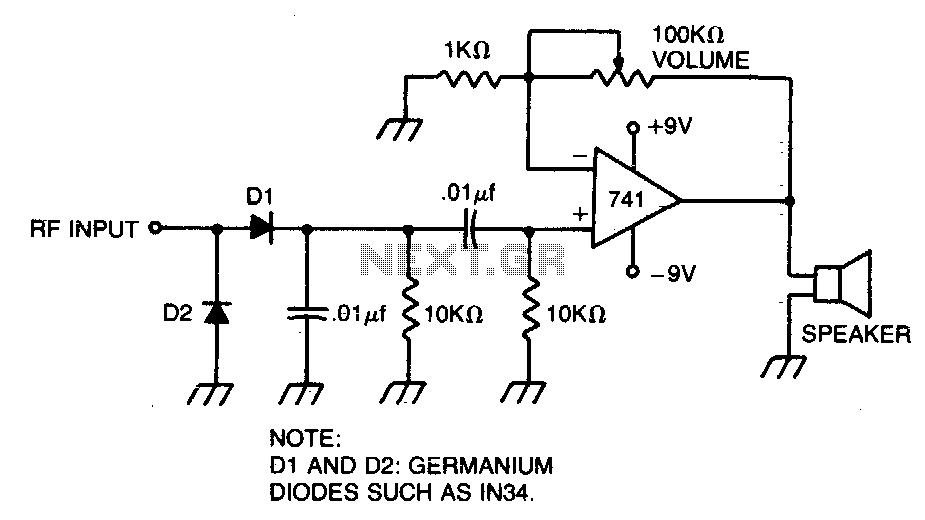
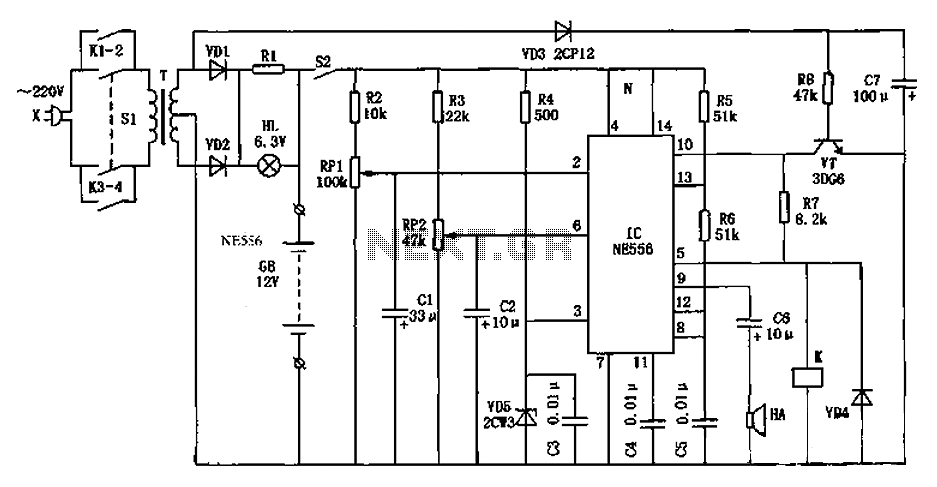
A broad-tuned receiver demodulates the RF signal picked up by a loosely coupled wire placed near the transmitting antenna.
The broad-tuned receiver operates by utilizing a loosely coupled wire antenna, which is strategically positioned in proximity to the transmitting antenna. This setup allows the receiver to capture a wide range of radio frequency (RF) signals effectively. The loosely coupled wire acts as an inductive element, enabling the receiver to demodulate various RF signals without the need for precise tuning to a specific frequency.
In a typical configuration, the broad-tuned receiver includes components such as an RF amplifier, a demodulator, and audio output circuitry. The RF amplifier enhances the weak RF signals received by the wire antenna, ensuring that they are strong enough for subsequent processing. The demodulator then extracts the original information signal from the modulated RF carrier wave, converting it into a baseband audio signal or another form suitable for further use.
The design of the receiver may incorporate various filtering techniques to minimize noise and interference, thus improving the clarity of the demodulated signal. Additionally, the output stage may include audio amplification to drive speakers or headphones, allowing for audible reproduction of the received signals.
Overall, the broad-tuned receiver is an efficient solution for applications requiring the reception of diverse RF signals in environments where precise frequency tuning is not feasible. It is particularly useful in scenarios such as amateur radio, emergency communication systems, and educational demonstrations in the field of electronics.Broad-tuned receiver demodulates the RF signal picked up by a ioosely coupled wire placed near the transmitting antenna. 🔗 External reference
The broad-tuned receiver operates by utilizing a loosely coupled wire antenna, which is strategically positioned in proximity to the transmitting antenna. This setup allows the receiver to capture a wide range of radio frequency (RF) signals effectively. The loosely coupled wire acts as an inductive element, enabling the receiver to demodulate various RF signals without the need for precise tuning to a specific frequency.
In a typical configuration, the broad-tuned receiver includes components such as an RF amplifier, a demodulator, and audio output circuitry. The RF amplifier enhances the weak RF signals received by the wire antenna, ensuring that they are strong enough for subsequent processing. The demodulator then extracts the original information signal from the modulated RF carrier wave, converting it into a baseband audio signal or another form suitable for further use.
The design of the receiver may incorporate various filtering techniques to minimize noise and interference, thus improving the clarity of the demodulated signal. Additionally, the output stage may include audio amplification to drive speakers or headphones, allowing for audible reproduction of the received signals.
Overall, the broad-tuned receiver is an efficient solution for applications requiring the reception of diverse RF signals in environments where precise frequency tuning is not feasible. It is particularly useful in scenarios such as amateur radio, emergency communication systems, and educational demonstrations in the field of electronics.Broad-tuned receiver demodulates the RF signal picked up by a ioosely coupled wire placed near the transmitting antenna. 🔗 External reference