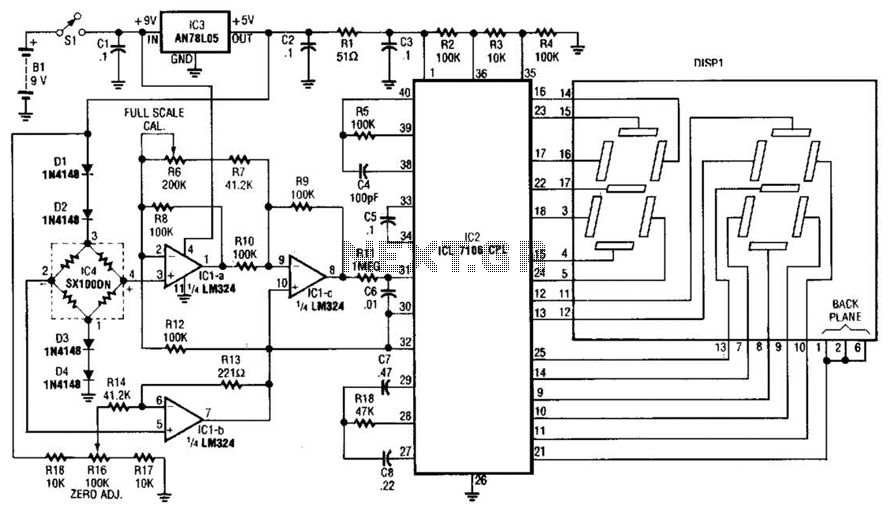
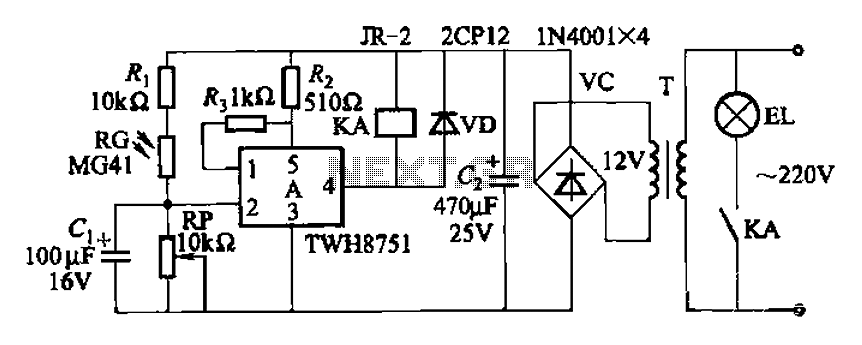
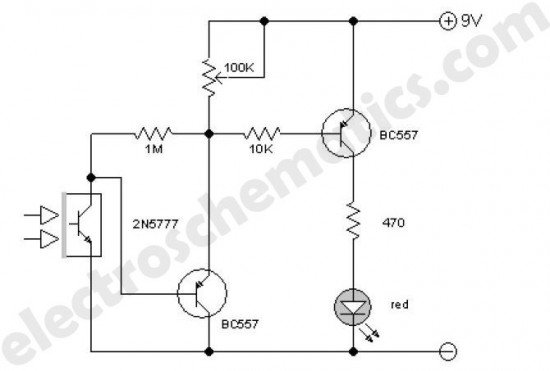
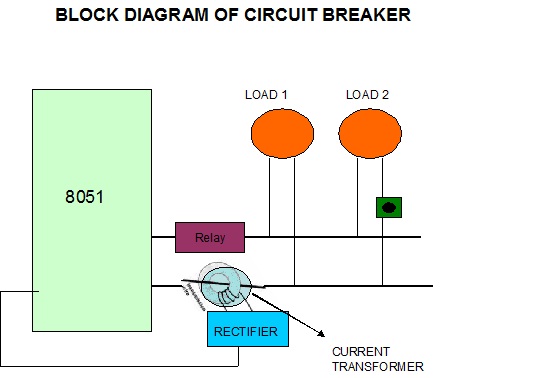
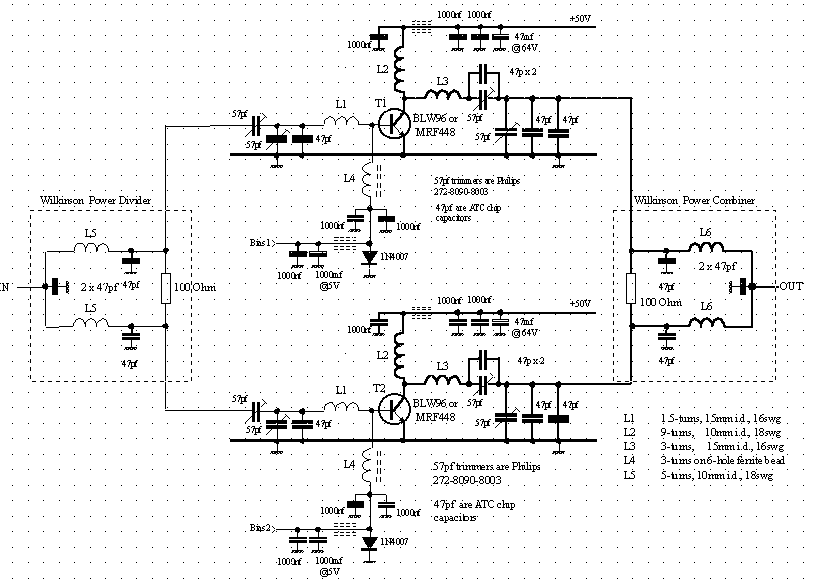
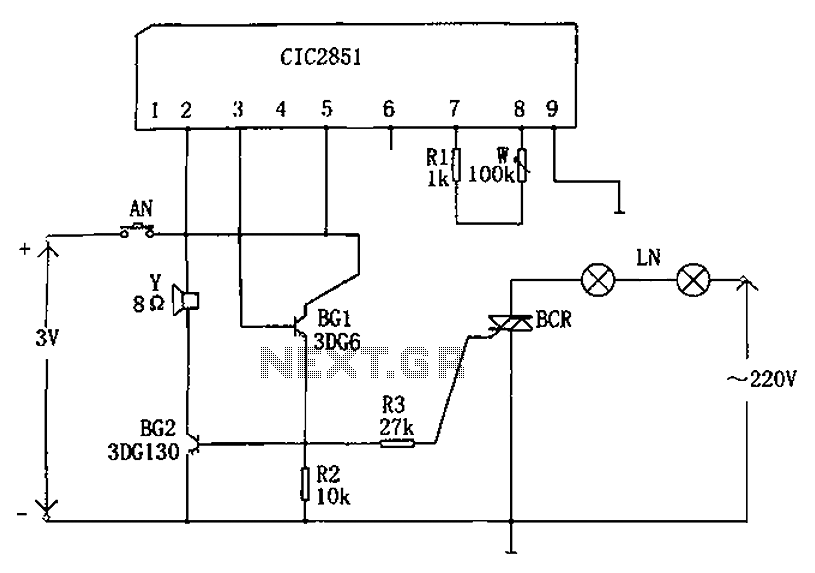
morse Circuit
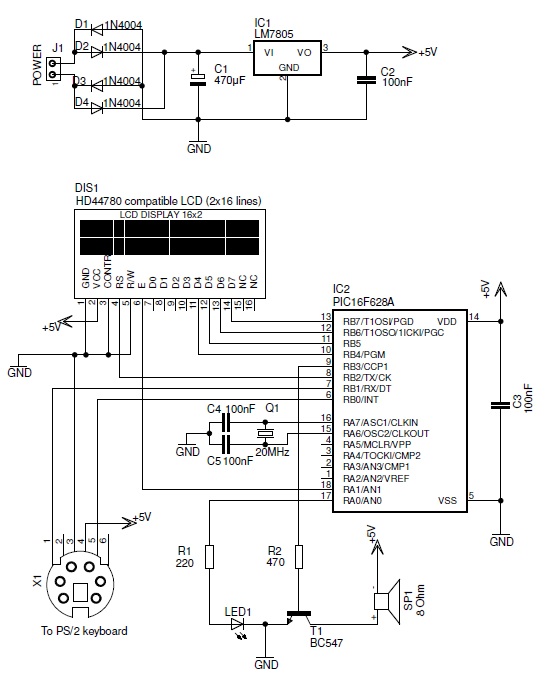
This PIC-based hardware circuit accepts texts from a PS/2 keyboard and converts it into a Morse code audio signal.
The described circuit utilizes a PIC microcontroller to interface with a PS/2 keyboard, allowing for the input of alphanumeric characters. The microcontroller processes the received data and translates each character into its corresponding Morse code representation. This conversion is achieved through a predefined mapping of characters to Morse code sequences, which consist of dots and dashes.
The output of the microcontroller is then used to generate an audio signal that represents the Morse code. This audio signal can be produced using a simple piezoelectric buzzer or speaker, which is driven by a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal from the microcontroller. The duration of the audio signals is carefully timed to reflect the lengths of the Morse code symbols: short beeps for dots, longer beeps for dashes, and silence for the spaces between symbols and letters.
The circuit may include additional components such as pull-up resistors for the keyboard interface and capacitors for signal smoothing. Power supply considerations must also be addressed, ensuring that the microcontroller and audio output device operate within their specified voltage and current ratings. Overall, this circuit serves as a practical demonstration of interfacing digital input devices with audio output, showcasing the versatility of microcontroller applications in communication systems.This PIC-based hardware circuit accepts texts from a PS/2 keyboard and converts it into a morse code audio signal.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a PIC microcontroller to interface with a PS/2 keyboard, allowing for the input of alphanumeric characters. The microcontroller processes the received data and translates each character into its corresponding Morse code representation. This conversion is achieved through a predefined mapping of characters to Morse code sequences, which consist of dots and dashes.
The output of the microcontroller is then used to generate an audio signal that represents the Morse code. This audio signal can be produced using a simple piezoelectric buzzer or speaker, which is driven by a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal from the microcontroller. The duration of the audio signals is carefully timed to reflect the lengths of the Morse code symbols: short beeps for dots, longer beeps for dashes, and silence for the spaces between symbols and letters.
The circuit may include additional components such as pull-up resistors for the keyboard interface and capacitors for signal smoothing. Power supply considerations must also be addressed, ensuring that the microcontroller and audio output device operate within their specified voltage and current ratings. Overall, this circuit serves as a practical demonstration of interfacing digital input devices with audio output, showcasing the versatility of microcontroller applications in communication systems.This PIC-based hardware circuit accepts texts from a PS/2 keyboard and converts it into a morse code audio signal.. 🔗 External reference