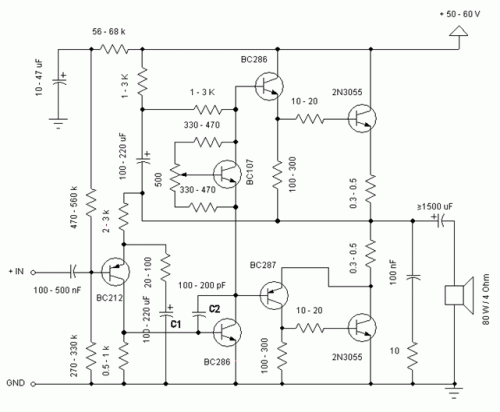
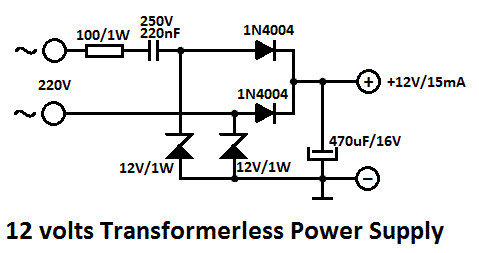
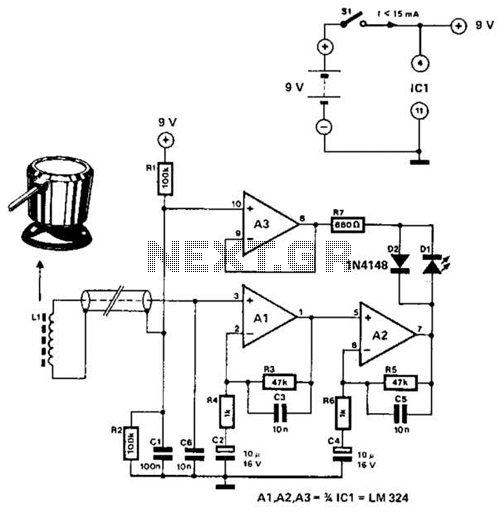
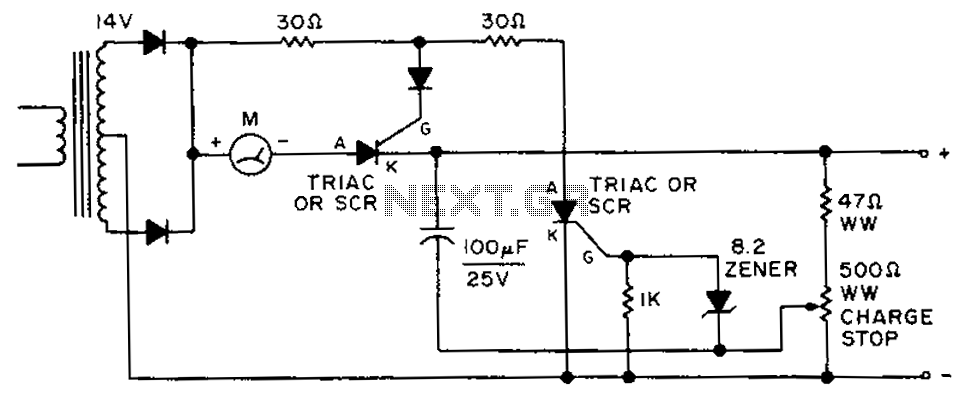
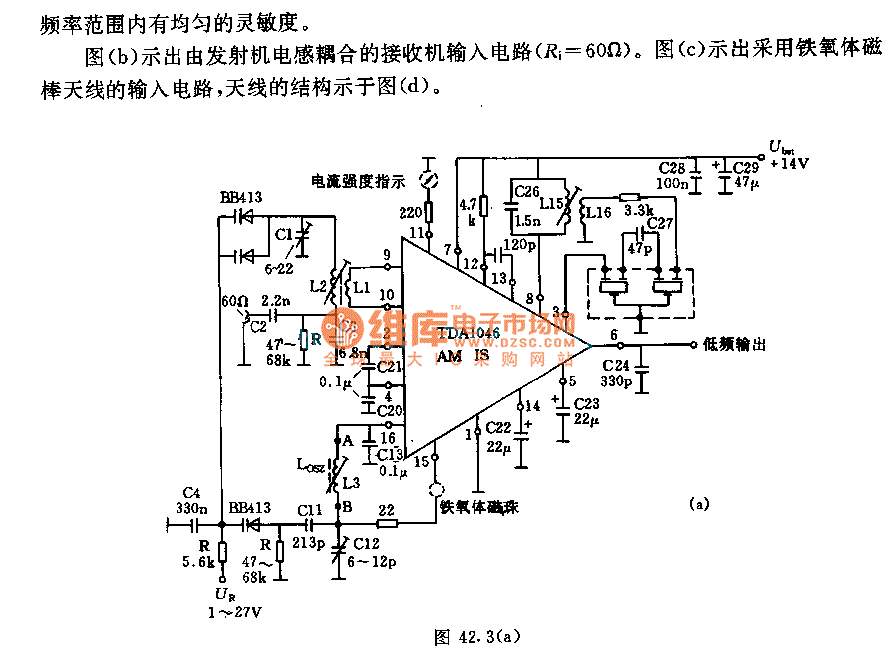
electronic circuit breaker
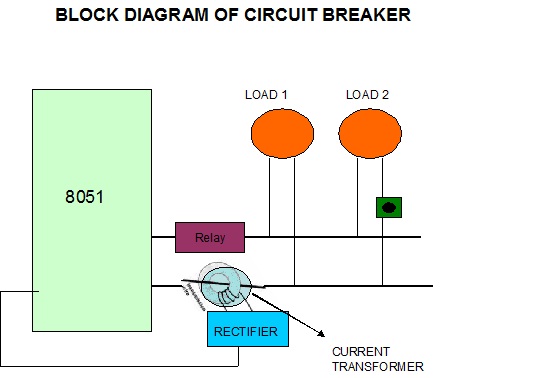
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, immediately discontinue electrical flow. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers come in various sizes, from small devices that protect individual household appliances to large switchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city. This device is essential for protecting any electrical appliance from breakdown caused by overcurrent (or voltage). The overall system of an electronic circuit breaker is more dynamic than other circuit breakers, as the current can be controlled according to the needs of the system. Understanding a new computer involves familiarizing oneself with the machine's capabilities, which can be achieved by studying the internal hardware design (device architecture) and examining the size, number, and dimensions of the registers. A microcontroller is a single chip that contains the processor (CPU), non-volatile memory for the program (ROM or flash), volatile memory for input and output (RAM), a clock, and an I/O control unit. Often referred to as a "computer on a chip," billions of microcontroller units (MCUs) are embedded each year in a wide range of products, from toys to appliances to automobiles. For instance, a single vehicle may utilize 70 or more microcontrollers. The AT89S52 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit microcontroller with 8K bytes of in-system programmable Flash memory. This device is manufactured using Atmel's high-density non-volatile memory technology and is compatible with the industry-standard 80C51 instruction set and pinout. The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional non-volatile memory programmer. By combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with in-system programmable Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel AT89S52 provides a powerful microcontroller that offers a highly flexible and cost-effective solution for many embedded control applications. The AT89S52 features include 8K bytes of Flash, 256 bytes of RAM, 32 I/O lines, a watchdog timer, two data pointers, three 16-bit timer/counters, a six-vector two-level interrupt architecture, a full duplex serial port, on-chip oscillator, and clock circuitry. Additionally, the AT89S52 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero frequency and supports two software-selectable power-saving modes. The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port, and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down mode retains the RAM contents but freezes the oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt. The hardware is driven by a set of program instructions, or software. Once familiar with both hardware and software, users can effectively apply the microcontroller to various problems. In this project, an external AC supply (220 V) is used as input; this high voltage is converted into 12 Volts AC by a step-down transformer. Voltage regulators and filters, along with a bridge rectifier, are then employed to convert the AC into DC voltage.
A circuit breaker is an essential component in electrical systems, safeguarding circuits against overloads and short circuits. Its automatic operation ensures that when a fault is detected, the circuit is interrupted, preventing potential damage to connected devices. The ability to reset circuit breakers makes them more convenient than fuses, which require replacement after a single use.
The integration of microcontrollers, such as the AT89S52, enhances the functionality of circuit breakers by enabling programmable control and monitoring capabilities. The AT89S52’s architecture allows for efficient processing and control of electrical parameters, making it suitable for applications requiring precise management of electrical flow. Its features, including multiple I/O lines and interrupt handling, facilitate the development of sophisticated control systems that can respond dynamically to changing electrical conditions.
In practical applications, the circuit breaker’s operation can be further enhanced by incorporating sensors and communication interfaces. This allows for remote monitoring and control, enabling users to receive alerts about circuit status and potential issues. The use of microcontrollers in conjunction with circuit breakers can lead to the development of smart electrical systems that optimize energy usage and improve safety.
The power supply design, utilizing a step-down transformer and subsequent rectification, is critical for powering microcontroller-based systems. The conversion from high voltage AC to low voltage DC is a fundamental aspect of ensuring that microcontrollers and other electronic components operate within their specified voltage ranges. The inclusion of voltage regulators and filters ensures stable and clean DC voltage, which is vital for the reliable operation of sensitive electronic circuitry.
In summary, the combination of circuit breakers and microcontrollers represents a significant advancement in electrical engineering, providing enhanced protection, control, and monitoring capabilities for a wide range of applications.A circuit breaker is an automatically-operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow.
Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then has to be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect an individual household appliance up to large switchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city. This device is very useful to protect any electrical appliance from breakdown caused by over current (or voltage).
The overall system of electronics circuit breaker is more dynamic than other circuit breaker as a current can be controlled according to the need of the system. When we have to learn about a new computer we have to familiarize about the machine capability we are using, and we can do it by studying the internal hardware design (devices architecture), and also to know about the size, number and the size of the registers.
A microcontroller is a single chip that contains the processor (the CPU), non-volatile memory for the program (ROM or flash), volatile memory for input and output (RAM), a clock and an I/O control unit. Also called a "computer on a chip, " billions of microcontroller units (MCUs) are embedded each year in a myriad of products from toys to appliances to automobiles.
For example, a single vehicle can use 70 or more microcontrollers. The following picture describes a general block diagram of microcontroller. 89s52: The AT89S52 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit microcontroller with 8K bytes of in-system programmable Flash memory. The device is manufactured using Atmel`s high-density nonvolatile memory technology and is compatible with the industry-standard 80C51 instruction set and pinout.
The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer. By combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with in-system programmable Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel`s AT89S52 is a powerful microcontroller which provides a highly-flexible and cost-effective solution to many embedded control applications.
The AT89S52 provides the following standard features: 8K bytes of Flash, 256 bytes of RAM, 32 I/O lines, Watchdog timer, two data pointers, three 16-bit timer/counters, a six-vector two-level interrupt architecture, a full duplex serial port, on-chip oscillator, and clock circuitry. In addition, the AT89S52 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes.
The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port, and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down mode saves the RAM con-tents but freezes the oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt.
The hardware is driven by a set of program instructions, or software. Once familiar with hardware and software, the user can then apply the microcontroller to the problems easily. In this project we are using external A. C supply (220 v) as input, this high voltage is converted into 12 Volts A. C by step down transformer, then we use voltage regulators and filters with bridge rectifier to convert the A.
C into D. C voltage. 🔗 External reference
A circuit breaker is an essential component in electrical systems, safeguarding circuits against overloads and short circuits. Its automatic operation ensures that when a fault is detected, the circuit is interrupted, preventing potential damage to connected devices. The ability to reset circuit breakers makes them more convenient than fuses, which require replacement after a single use.
The integration of microcontrollers, such as the AT89S52, enhances the functionality of circuit breakers by enabling programmable control and monitoring capabilities. The AT89S52’s architecture allows for efficient processing and control of electrical parameters, making it suitable for applications requiring precise management of electrical flow. Its features, including multiple I/O lines and interrupt handling, facilitate the development of sophisticated control systems that can respond dynamically to changing electrical conditions.
In practical applications, the circuit breaker’s operation can be further enhanced by incorporating sensors and communication interfaces. This allows for remote monitoring and control, enabling users to receive alerts about circuit status and potential issues. The use of microcontrollers in conjunction with circuit breakers can lead to the development of smart electrical systems that optimize energy usage and improve safety.
The power supply design, utilizing a step-down transformer and subsequent rectification, is critical for powering microcontroller-based systems. The conversion from high voltage AC to low voltage DC is a fundamental aspect of ensuring that microcontrollers and other electronic components operate within their specified voltage ranges. The inclusion of voltage regulators and filters ensures stable and clean DC voltage, which is vital for the reliable operation of sensitive electronic circuitry.
In summary, the combination of circuit breakers and microcontrollers represents a significant advancement in electrical engineering, providing enhanced protection, control, and monitoring capabilities for a wide range of applications.A circuit breaker is an automatically-operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and, by interrupting continuity, to immediately discontinue electrical flow.
Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then has to be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect an individual household appliance up to large switchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city. This device is very useful to protect any electrical appliance from breakdown caused by over current (or voltage).
The overall system of electronics circuit breaker is more dynamic than other circuit breaker as a current can be controlled according to the need of the system. When we have to learn about a new computer we have to familiarize about the machine capability we are using, and we can do it by studying the internal hardware design (devices architecture), and also to know about the size, number and the size of the registers.
A microcontroller is a single chip that contains the processor (the CPU), non-volatile memory for the program (ROM or flash), volatile memory for input and output (RAM), a clock and an I/O control unit. Also called a "computer on a chip, " billions of microcontroller units (MCUs) are embedded each year in a myriad of products from toys to appliances to automobiles.
For example, a single vehicle can use 70 or more microcontrollers. The following picture describes a general block diagram of microcontroller. 89s52: The AT89S52 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit microcontroller with 8K bytes of in-system programmable Flash memory. The device is manufactured using Atmel`s high-density nonvolatile memory technology and is compatible with the industry-standard 80C51 instruction set and pinout.
The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a conventional nonvolatile memory programmer. By combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with in-system programmable Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel`s AT89S52 is a powerful microcontroller which provides a highly-flexible and cost-effective solution to many embedded control applications.
The AT89S52 provides the following standard features: 8K bytes of Flash, 256 bytes of RAM, 32 I/O lines, Watchdog timer, two data pointers, three 16-bit timer/counters, a six-vector two-level interrupt architecture, a full duplex serial port, on-chip oscillator, and clock circuitry. In addition, the AT89S52 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes.
The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port, and interrupt system to continue functioning. The Power-down mode saves the RAM con-tents but freezes the oscillator, disabling all other chip functions until the next interrupt.
The hardware is driven by a set of program instructions, or software. Once familiar with hardware and software, the user can then apply the microcontroller to the problems easily. In this project we are using external A. C supply (220 v) as input, this high voltage is converted into 12 Volts A. C by step down transformer, then we use voltage regulators and filters with bridge rectifier to convert the A.
C into D. C voltage. 🔗 External reference