MOSFET-based Joule Thief steps up voltage
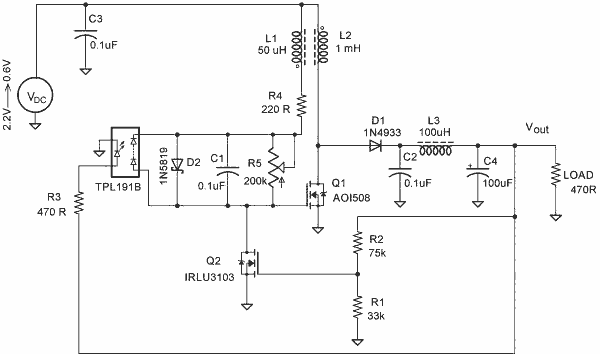
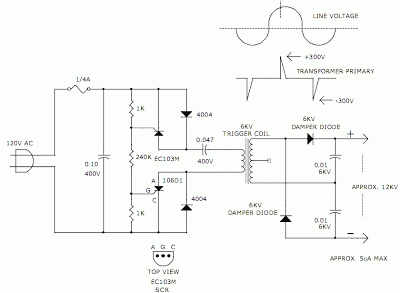
A simple blocking oscillator circuit can be utilized to increase voltage by leveraging the properties of coil inductance (V = L di/dt). Such a circuit is illustrated in Figure 1.
The blocking oscillator circuit is a type of oscillator that operates by inducing oscillations through positive feedback. It typically consists of a transistor, a coil (inductor), a capacitor, and a resistor. The fundamental operation relies on the rapid charging and discharging of the capacitor, which, in turn, influences the magnetic field in the inductor.
In this circuit, when the transistor is turned on, current begins to flow through the inductor, causing it to store energy in the form of a magnetic field. The inductor's property of resisting changes in current results in a gradual increase in current flow. Once the current reaches a certain threshold, the transistor enters saturation, and the magnetic field collapses rapidly. This sudden change in current induces a high voltage across the inductor, following the equation V = L di/dt.
The output voltage can be significantly higher than the input voltage due to this inductive kickback. The oscillation frequency of the circuit is determined by the values of the inductor and capacitor, as well as the characteristics of the transistor. The resistor serves to limit the current and stabilize the operation of the circuit.
The simplicity of the blocking oscillator circuit makes it suitable for various applications, including voltage converters, pulse generators, and signal modulation. It is important to ensure that the components are rated for the expected voltage and current levels to avoid damage and ensure reliable operation. Proper design considerations, such as component selection and layout, can enhance the performance and efficiency of the blocking oscillator circuit.A simple blocking oscillator circuit can be used to step up voltage using properties of coil inductance (V = L di/dt). Such a circuit is shown in Figure 1. 🔗 External reference
The blocking oscillator circuit is a type of oscillator that operates by inducing oscillations through positive feedback. It typically consists of a transistor, a coil (inductor), a capacitor, and a resistor. The fundamental operation relies on the rapid charging and discharging of the capacitor, which, in turn, influences the magnetic field in the inductor.
In this circuit, when the transistor is turned on, current begins to flow through the inductor, causing it to store energy in the form of a magnetic field. The inductor's property of resisting changes in current results in a gradual increase in current flow. Once the current reaches a certain threshold, the transistor enters saturation, and the magnetic field collapses rapidly. This sudden change in current induces a high voltage across the inductor, following the equation V = L di/dt.
The output voltage can be significantly higher than the input voltage due to this inductive kickback. The oscillation frequency of the circuit is determined by the values of the inductor and capacitor, as well as the characteristics of the transistor. The resistor serves to limit the current and stabilize the operation of the circuit.
The simplicity of the blocking oscillator circuit makes it suitable for various applications, including voltage converters, pulse generators, and signal modulation. It is important to ensure that the components are rated for the expected voltage and current levels to avoid damage and ensure reliable operation. Proper design considerations, such as component selection and layout, can enhance the performance and efficiency of the blocking oscillator circuit.A simple blocking oscillator circuit can be used to step up voltage using properties of coil inductance (V = L di/dt). Such a circuit is shown in Figure 1. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713