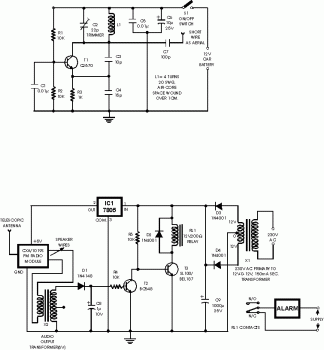
MOSFET based step-up joule thief circuit
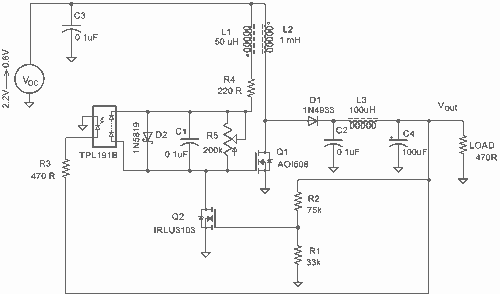
It employs a low threshold MOSFET and two coupled coils to function as a joule thief. An additional MOSFET is utilized for regulation.
The circuit operates as a joule thief, which is a type of DC-DC converter designed to extract energy from a low-voltage power source, such as a single AA battery or depleted batteries. The low threshold MOSFET serves as the primary switching element, allowing it to turn on at lower voltages, making it suitable for maximizing energy extraction from the source.
The two coupled coils, typically configured as a transformer, play a crucial role in energy transfer. When the MOSFET is activated, current flows through one coil, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the second coil, which can be significantly higher than the input voltage. The energy stored in the magnetic field is released when the MOSFET turns off, providing a boost in voltage to power the load.
The second MOSFET in the circuit functions as a regulator, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. By controlling the duty cycle of the primary MOSFET, the regulator can adjust the energy transfer to the load, optimizing efficiency and preventing overvoltage conditions.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient for low-power applications, allowing for the utilization of energy from sources that would otherwise be considered unusable. It is commonly employed in applications such as LED drivers, low-power sensors, and other devices requiring energy harvesting from low-voltage sources.It uses a low threshold MOSFET and two coupled coils to operate as a joule thief. A second MOSFET is used to regulate the 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates as a joule thief, which is a type of DC-DC converter designed to extract energy from a low-voltage power source, such as a single AA battery or depleted batteries. The low threshold MOSFET serves as the primary switching element, allowing it to turn on at lower voltages, making it suitable for maximizing energy extraction from the source.
The two coupled coils, typically configured as a transformer, play a crucial role in energy transfer. When the MOSFET is activated, current flows through one coil, generating a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the second coil, which can be significantly higher than the input voltage. The energy stored in the magnetic field is released when the MOSFET turns off, providing a boost in voltage to power the load.
The second MOSFET in the circuit functions as a regulator, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. By controlling the duty cycle of the primary MOSFET, the regulator can adjust the energy transfer to the load, optimizing efficiency and preventing overvoltage conditions.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient for low-power applications, allowing for the utilization of energy from sources that would otherwise be considered unusable. It is commonly employed in applications such as LED drivers, low-power sensors, and other devices requiring energy harvesting from low-voltage sources.It uses a low threshold MOSFET and two coupled coils to operate as a joule thief. A second MOSFET is used to regulate the 🔗 External reference