Mosfet Heating Circuits
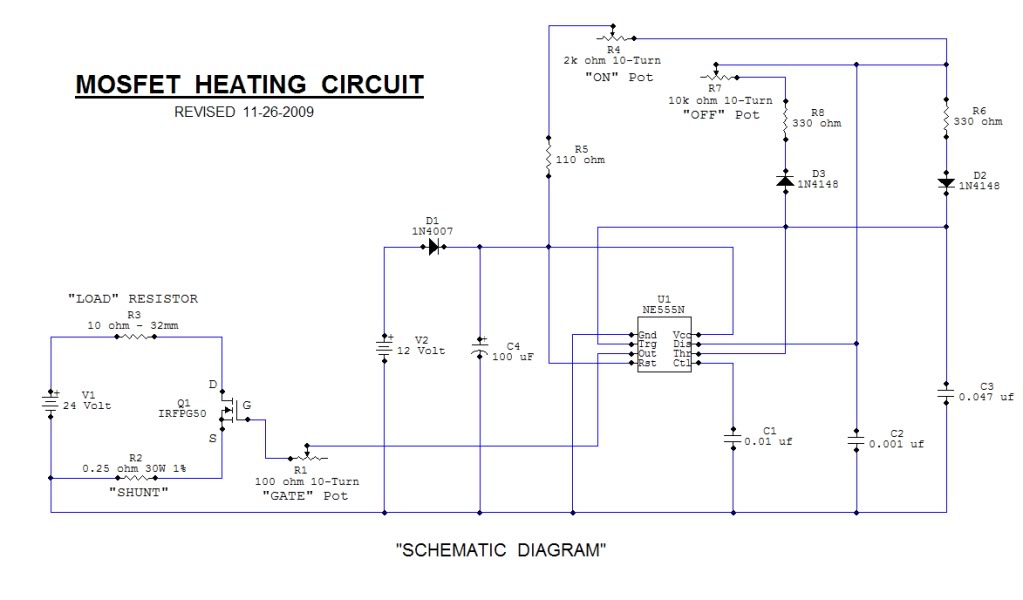
This open-source thread focuses on the development of a "MOSFET Heating Circuit," which is a modified version of an existing design.
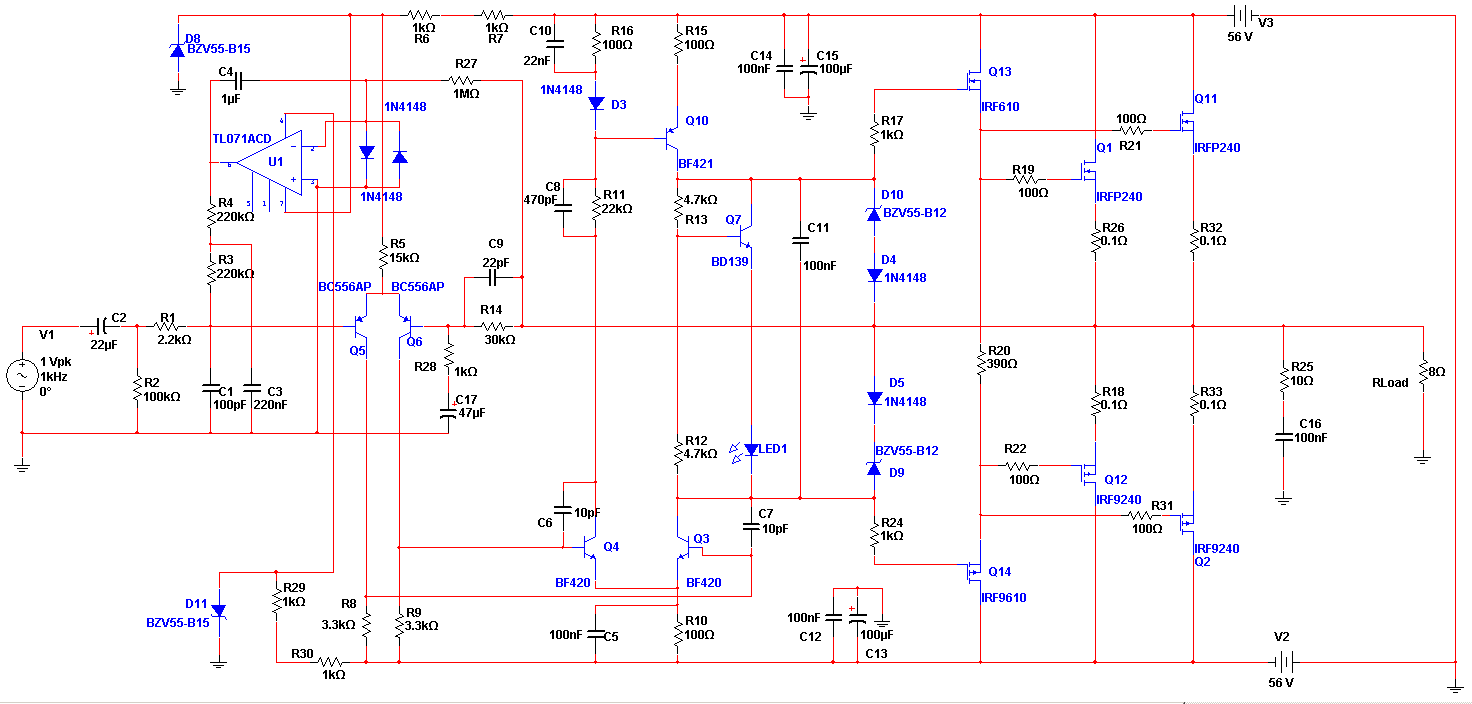
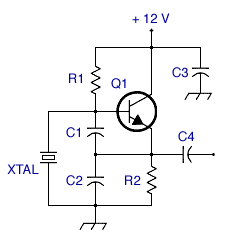
The MOSFET Heating Circuit is designed to efficiently manage and control heating elements using MOSFET technology. MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) are preferred in heating applications due to their high efficiency and fast switching capabilities. The circuit typically consists of a power supply, a MOSFET, a microcontroller or control circuit, and the heating element itself.
In this schematic, the power supply provides the necessary voltage to the circuit, which is often in the range of 12V to 24V, depending on the heating element specifications. The MOSFET acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current to the heating element based on the input signal from the microcontroller. The microcontroller can be programmed to adjust the duty cycle of the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, allowing for precise temperature control.
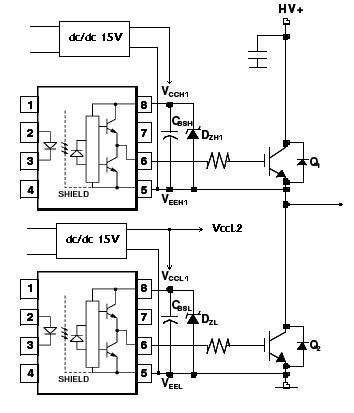
Additional components may include resistors for gate drive circuitry, capacitors for filtering, and diodes for flyback protection if inductive loads are used. A heat sink may be necessary for the MOSFET to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring reliable performance.
Safety features such as thermal cutoffs or fuses can be integrated into the design to prevent overheating and potential damage to the circuit. Overall, this MOSFET Heating Circuit represents an effective solution for applications requiring controlled heating, such as in 3D printers, soldering tools, or temperature-sensitive processes.This Open Source thread is for the advancement of a ""Mosfet Heating Circuit"" one that is a modified replication of one.. 🔗 External reference
The MOSFET Heating Circuit is designed to efficiently manage and control heating elements using MOSFET technology. MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) are preferred in heating applications due to their high efficiency and fast switching capabilities. The circuit typically consists of a power supply, a MOSFET, a microcontroller or control circuit, and the heating element itself.
In this schematic, the power supply provides the necessary voltage to the circuit, which is often in the range of 12V to 24V, depending on the heating element specifications. The MOSFET acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current to the heating element based on the input signal from the microcontroller. The microcontroller can be programmed to adjust the duty cycle of the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, allowing for precise temperature control.
Additional components may include resistors for gate drive circuitry, capacitors for filtering, and diodes for flyback protection if inductive loads are used. A heat sink may be necessary for the MOSFET to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring reliable performance.
Safety features such as thermal cutoffs or fuses can be integrated into the design to prevent overheating and potential damage to the circuit. Overall, this MOSFET Heating Circuit represents an effective solution for applications requiring controlled heating, such as in 3D printers, soldering tools, or temperature-sensitive processes.This Open Source thread is for the advancement of a ""Mosfet Heating Circuit"" one that is a modified replication of one.. 🔗 External reference