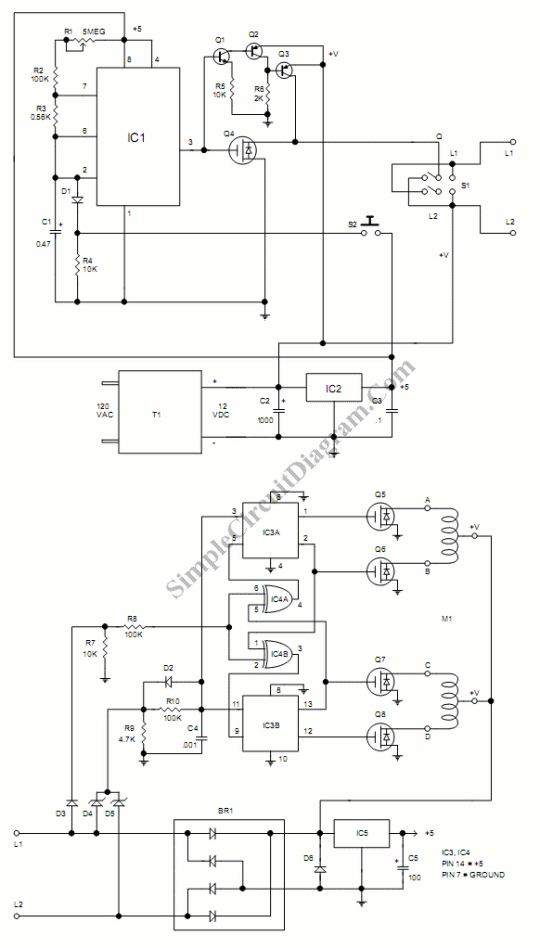
Motor Drivers
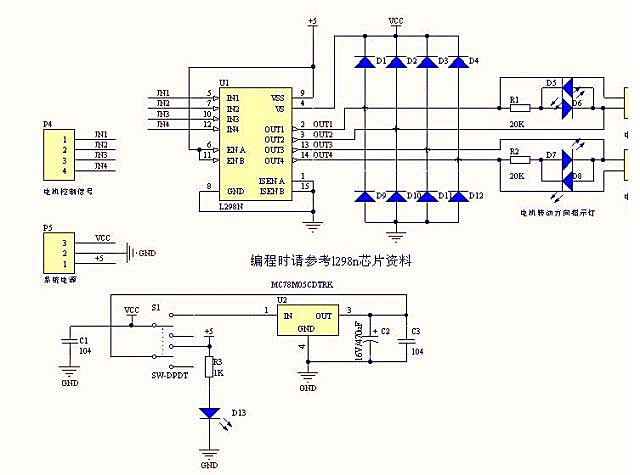
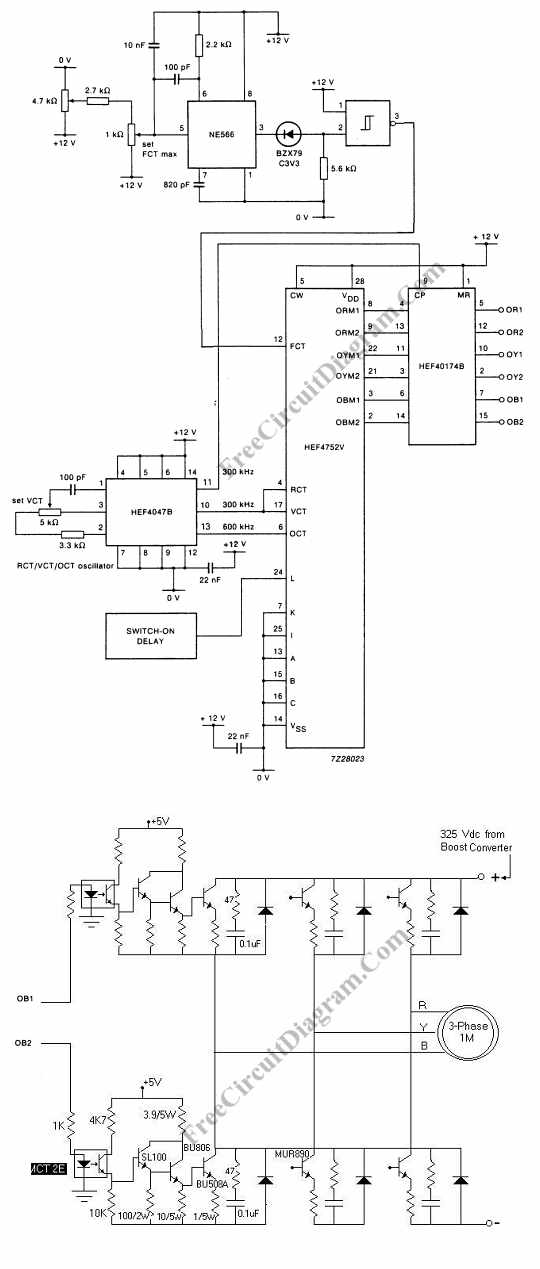
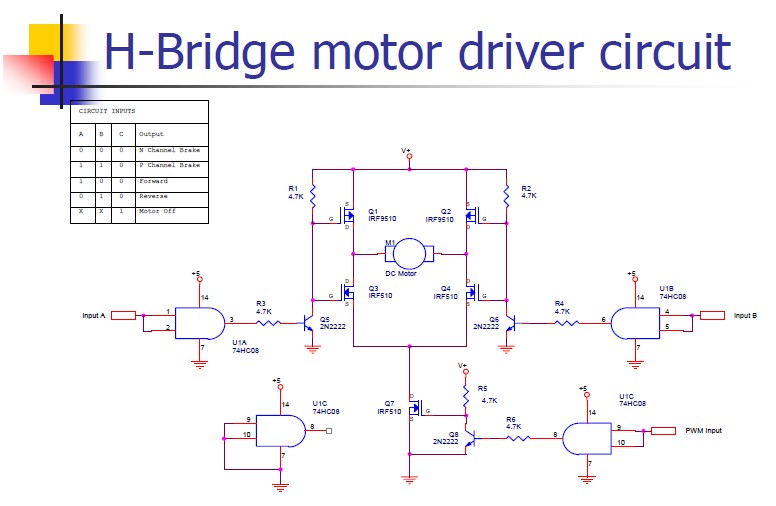
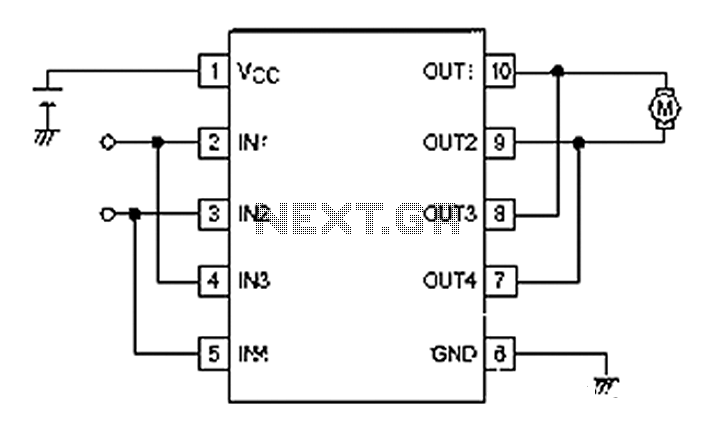
Arduino can drive various types of motors. However, the low-power signals from Arduino must control high-power circuits to operate the motors effectively. This document will provide examples of how Arduino can control different motor types and sizes. A motor driver typically consists of a circuit board with several electronic components, including a high-power motor driver chip or power transistors. These boards generally cost between $10 and $15. An example is the Arduino "Shield" that connects directly to an Arduino, which utilizes the L298N motor driver chip that will be discussed in detail later. The L298N Arduino Motor Driver Shield features a heat sink for the L298N chip, enabling it to handle higher currents. It is also a more cost-effective solution compared to shield versions and can often be mounted near the motors. Two DC motors can be connected to the outputs on the right side of the board. Arduino controls the inputs to connect the motor terminals to Ground or Vcc (Motor Power Supply), allowing voltage to be applied in either direction through the motors. Both terminals can also be connected to Ground to stop the motors. Measures are taken to manage "Back EMF" and "power supply noise," as described in the tutorial on DC motors. Eight diodes are connected from the motor outputs to ground and the motor power supply to limit or "snub" back EMF voltages that could otherwise damage the chip. The diodes on the right side are LEDs that illuminate when the motors are powered, indicating the direction of current flow. Additionally, a +5 volt regulator chip (MC78M05) provides +5 volts to the L298N chip.
The Arduino motor control system utilizes the L298N motor driver chip, which is designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors. The chip operates by receiving control signals from the Arduino, which dictate whether the motors should rotate forward, backward, or stop. The L298N can control two motors simultaneously, making it suitable for various applications including robotics and automation.
The circuit board layout typically includes input pins connected to the Arduino, output pins for the motors, and a power supply input. The heat sink attached to the L298N chip is crucial for dissipating heat generated during operation, especially when driving high-current motors. The inclusion of diodes in the circuit is essential for protecting the driver chip from voltage spikes caused by back EMF when the motors are switched off. This back EMF can create damaging voltage levels that could potentially harm the driver circuitry.
The presence of LEDs on the output side serves a dual purpose; they not only indicate motor activity but also provide visual feedback regarding the direction of current flow, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of the system. The +5 volt regulator (MC78M05) ensures that the L298N chip receives a stable voltage supply, which is critical for reliable operation.
Overall, this motor driver setup allows for effective control of DC motors through an Arduino platform, providing a practical solution for projects that require motorized movement.Arduino can drive many kinds of motors. But the low-power signals from Arduino need to control high-power circuits to run the actual motors. Here we will give examples of ways that Arduino can control different types of motors of different sizes. A Motor Driver will usually be a circuit board with several electronics components on it, including a
high-power motor driver chip or some power transistors. (Examples Here:) Boards like this cost about $10 to $15 these days. Here`s an example of an Arduino "Shield" that plugs on top of an Arduino. This uses a motor driver chip L298N which we will detail more about later. Details of operation of the L298N Arduino Motor Driver Shield are HERE: This includes a heat sink for the L298N chip, allowing higher currents. It is also less expensive than a shield version. Often it can be mounted near the motors 2 DC Motors may be connected to the outputs on the right. Arduino controls the inputs so that the motor terminals are connected to Ground or Vcc (Motor Power Supply).
So voltage can be applied in either direction through the motors, or both terminals can be connected to Ground to stop. Note the measures taken here to control "Back EMF" and "power supply noise" as mentioned in the tutorial (DC Motors).
There are 8 diodes that are connected from the motor outputs to ground and the motor power supply. These are to limit or "snub" the back EMF voltages that otherwise would damage the chip. The diodes on the right side are LEDs that light up when the motors are powered and indicate what direction the current is flowing. There is also a +5 volt regulator chip (MC78M05) which supplies +5 volts to the L298N chip. 🔗 External reference
The Arduino motor control system utilizes the L298N motor driver chip, which is designed to control the direction and speed of DC motors. The chip operates by receiving control signals from the Arduino, which dictate whether the motors should rotate forward, backward, or stop. The L298N can control two motors simultaneously, making it suitable for various applications including robotics and automation.
The circuit board layout typically includes input pins connected to the Arduino, output pins for the motors, and a power supply input. The heat sink attached to the L298N chip is crucial for dissipating heat generated during operation, especially when driving high-current motors. The inclusion of diodes in the circuit is essential for protecting the driver chip from voltage spikes caused by back EMF when the motors are switched off. This back EMF can create damaging voltage levels that could potentially harm the driver circuitry.
The presence of LEDs on the output side serves a dual purpose; they not only indicate motor activity but also provide visual feedback regarding the direction of current flow, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of the system. The +5 volt regulator (MC78M05) ensures that the L298N chip receives a stable voltage supply, which is critical for reliable operation.
Overall, this motor driver setup allows for effective control of DC motors through an Arduino platform, providing a practical solution for projects that require motorized movement.Arduino can drive many kinds of motors. But the low-power signals from Arduino need to control high-power circuits to run the actual motors. Here we will give examples of ways that Arduino can control different types of motors of different sizes. A Motor Driver will usually be a circuit board with several electronics components on it, including a
high-power motor driver chip or some power transistors. (Examples Here:) Boards like this cost about $10 to $15 these days. Here`s an example of an Arduino "Shield" that plugs on top of an Arduino. This uses a motor driver chip L298N which we will detail more about later. Details of operation of the L298N Arduino Motor Driver Shield are HERE: This includes a heat sink for the L298N chip, allowing higher currents. It is also less expensive than a shield version. Often it can be mounted near the motors 2 DC Motors may be connected to the outputs on the right. Arduino controls the inputs so that the motor terminals are connected to Ground or Vcc (Motor Power Supply).
So voltage can be applied in either direction through the motors, or both terminals can be connected to Ground to stop. Note the measures taken here to control "Back EMF" and "power supply noise" as mentioned in the tutorial (DC Motors).
There are 8 diodes that are connected from the motor outputs to ground and the motor power supply. These are to limit or "snub" the back EMF voltages that otherwise would damage the chip. The diodes on the right side are LEDs that light up when the motors are powered and indicate what direction the current is flowing. There is also a +5 volt regulator chip (MC78M05) which supplies +5 volts to the L298N chip. 🔗 External reference