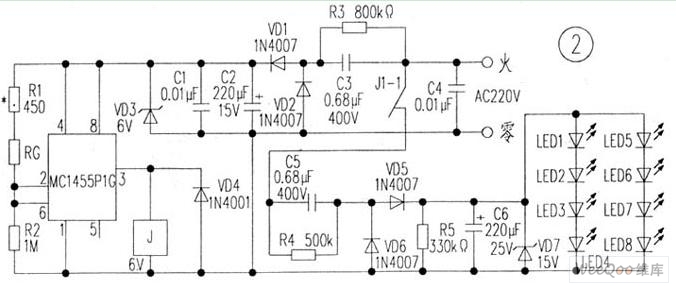
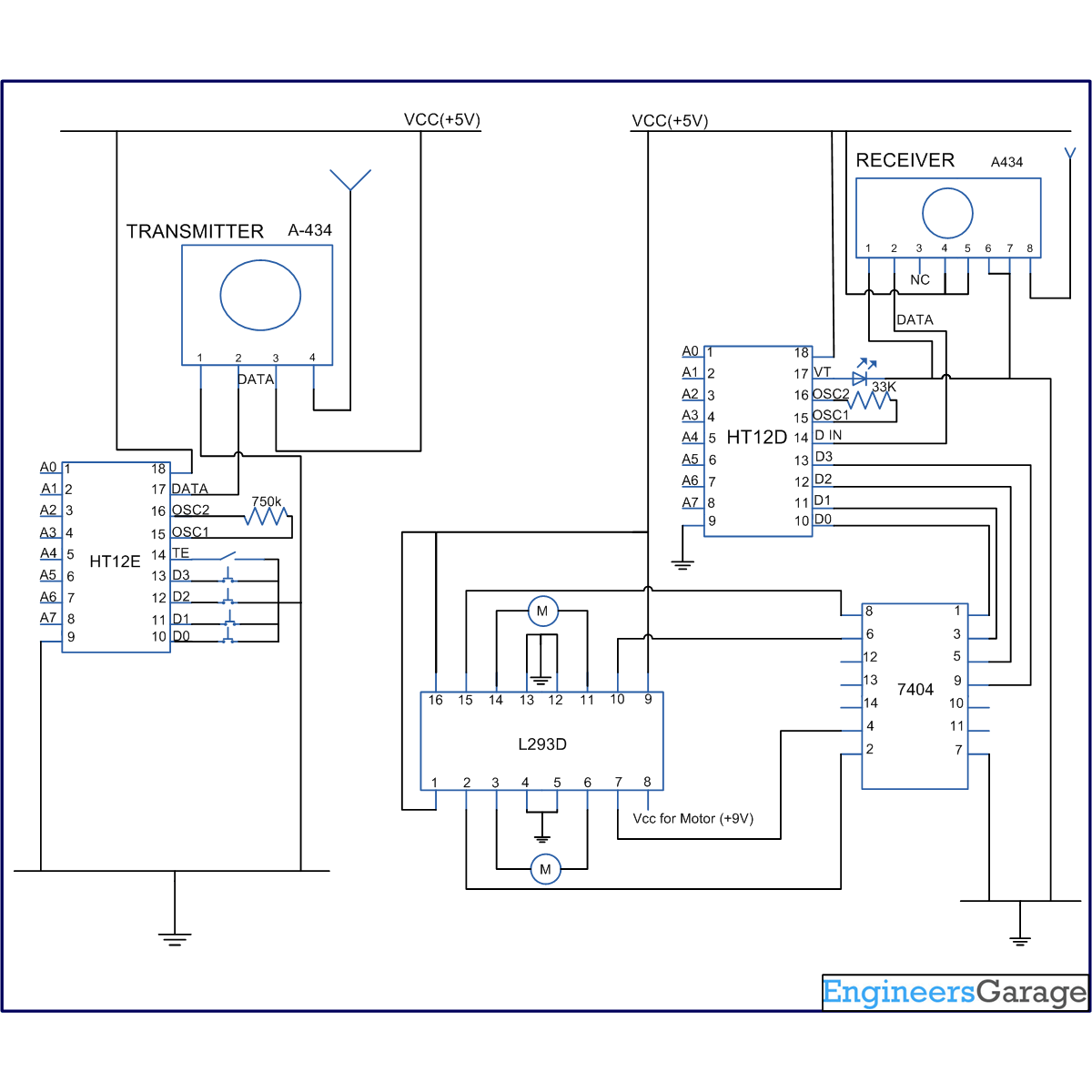
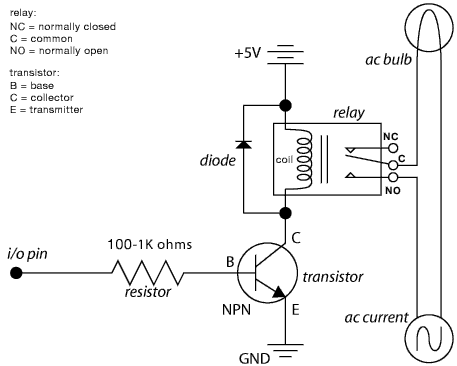
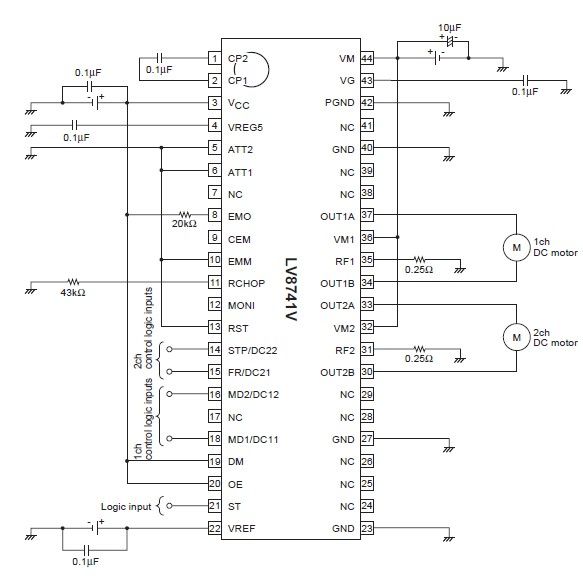
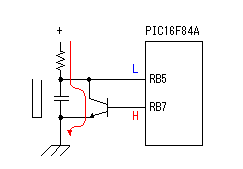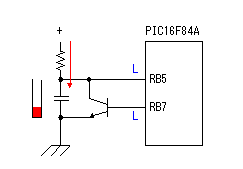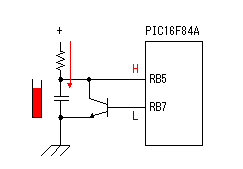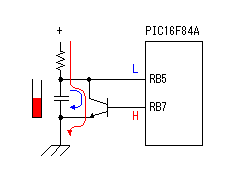
3 Phase AC Motor Speed Control
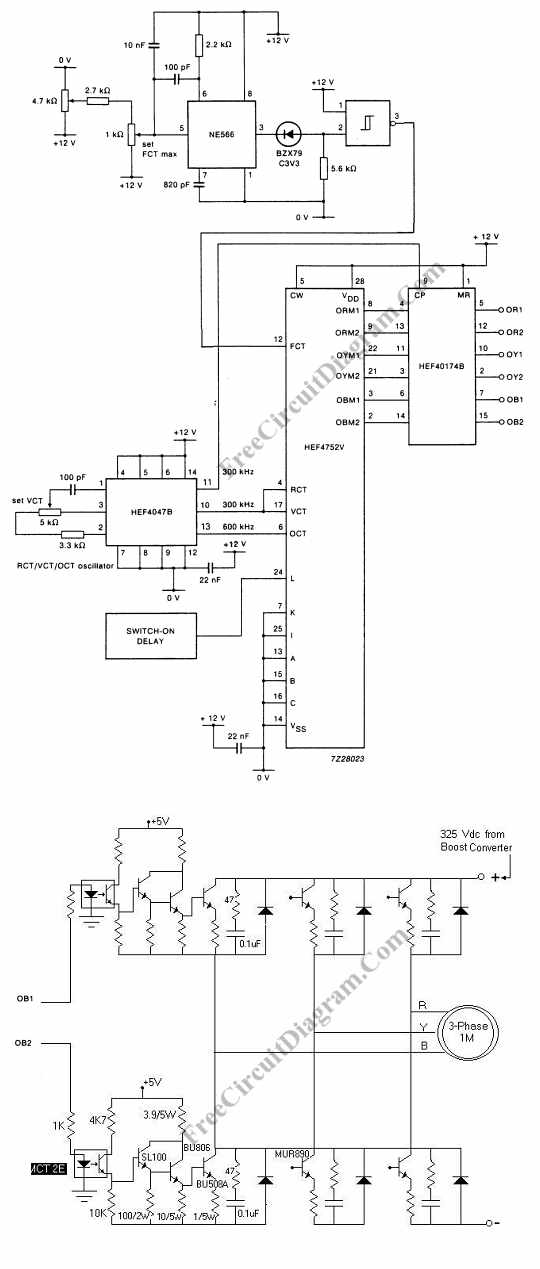
Controlling the speed of a three-phase AC motor is achieved by regulating the frequency of the power supply, as the motor operates in synchronization with the line.
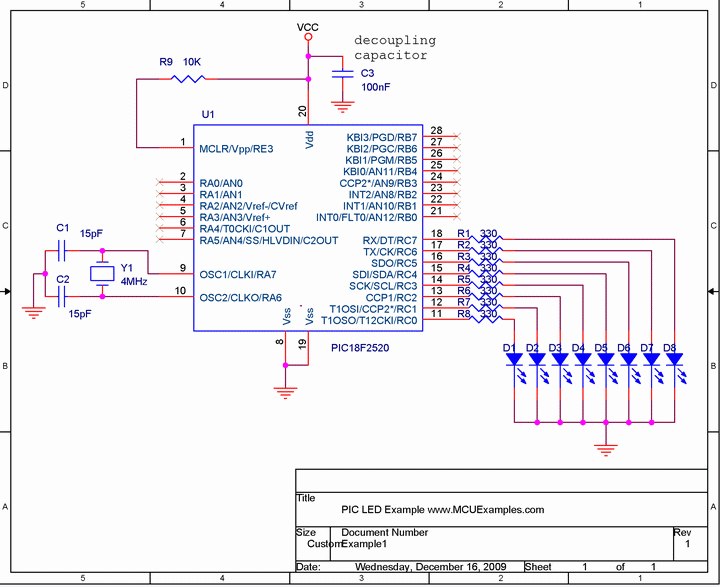
To control the speed of a three-phase AC motor, it is essential to utilize a variable frequency drive (VFD). The VFD adjusts the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for precise control over its speed and torque characteristics. In a typical setup, the VFD receives input from a control system, which can include sensors and user interfaces for setting desired operational parameters.
The VFD comprises several key components: a rectifier, a DC bus, and an inverter. The rectifier converts the incoming AC voltage from the power line into DC voltage. This DC voltage is then smoothed and stored in the DC bus. The inverter takes this DC voltage and converts it back into AC voltage at the desired frequency and amplitude, which is then supplied to the motor.
To achieve effective speed control, the VFD employs pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques. By varying the width of the pulses in the output waveform, the effective voltage and frequency delivered to the motor can be adjusted. This method not only allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration but also enhances energy efficiency by reducing power consumption during low-load conditions.
Additionally, feedback mechanisms, such as encoders or tachometers, can be integrated into the system to provide real-time data on motor speed and position. This feedback can be utilized by the VFD to make dynamic adjustments, ensuring optimal performance and stability of the motor under varying load conditions.
Overall, the implementation of a variable frequency drive for controlling a three-phase AC motor facilitates enhanced operational flexibility, energy savings, and improved performance in various industrial applications.Controlling the speed of three phase ac motor is done by controlling the frequency of the power line supply,? since the motor is synchronized with the line. 🔗 External reference
To control the speed of a three-phase AC motor, it is essential to utilize a variable frequency drive (VFD). The VFD adjusts the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for precise control over its speed and torque characteristics. In a typical setup, the VFD receives input from a control system, which can include sensors and user interfaces for setting desired operational parameters.
The VFD comprises several key components: a rectifier, a DC bus, and an inverter. The rectifier converts the incoming AC voltage from the power line into DC voltage. This DC voltage is then smoothed and stored in the DC bus. The inverter takes this DC voltage and converts it back into AC voltage at the desired frequency and amplitude, which is then supplied to the motor.
To achieve effective speed control, the VFD employs pulse-width modulation (PWM) techniques. By varying the width of the pulses in the output waveform, the effective voltage and frequency delivered to the motor can be adjusted. This method not only allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration but also enhances energy efficiency by reducing power consumption during low-load conditions.
Additionally, feedback mechanisms, such as encoders or tachometers, can be integrated into the system to provide real-time data on motor speed and position. This feedback can be utilized by the VFD to make dynamic adjustments, ensuring optimal performance and stability of the motor under varying load conditions.
Overall, the implementation of a variable frequency drive for controlling a three-phase AC motor facilitates enhanced operational flexibility, energy savings, and improved performance in various industrial applications.Controlling the speed of three phase ac motor is done by controlling the frequency of the power line supply,? since the motor is synchronized with the line. 🔗 External reference