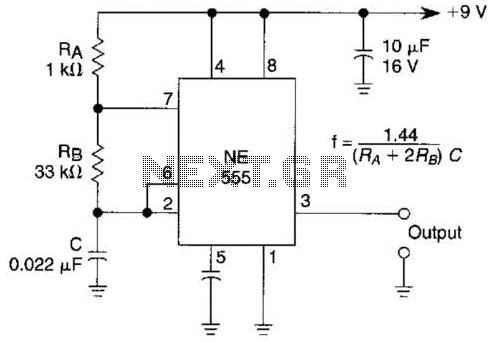
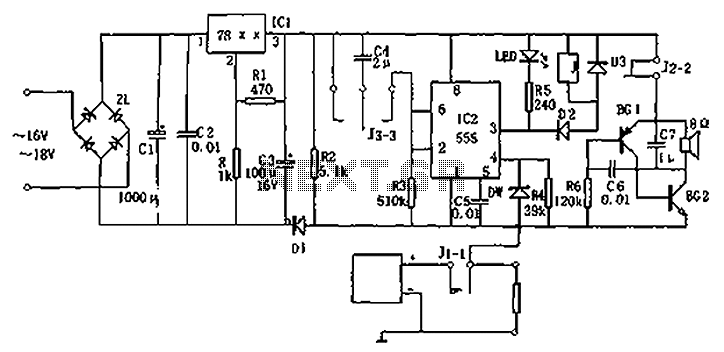
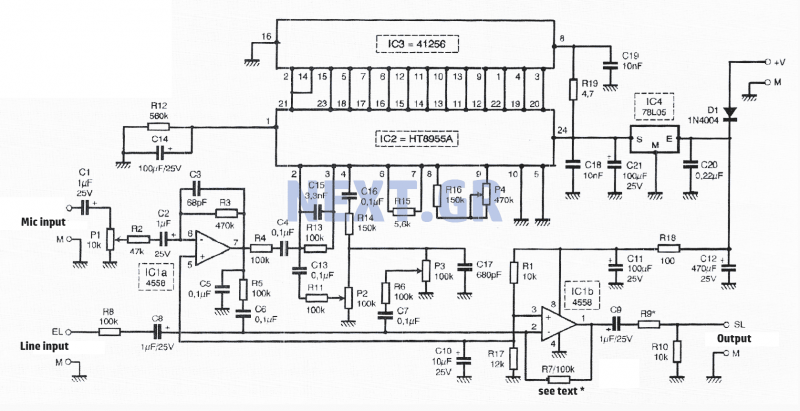
Motor time division control circuit composed of transistor and NE555
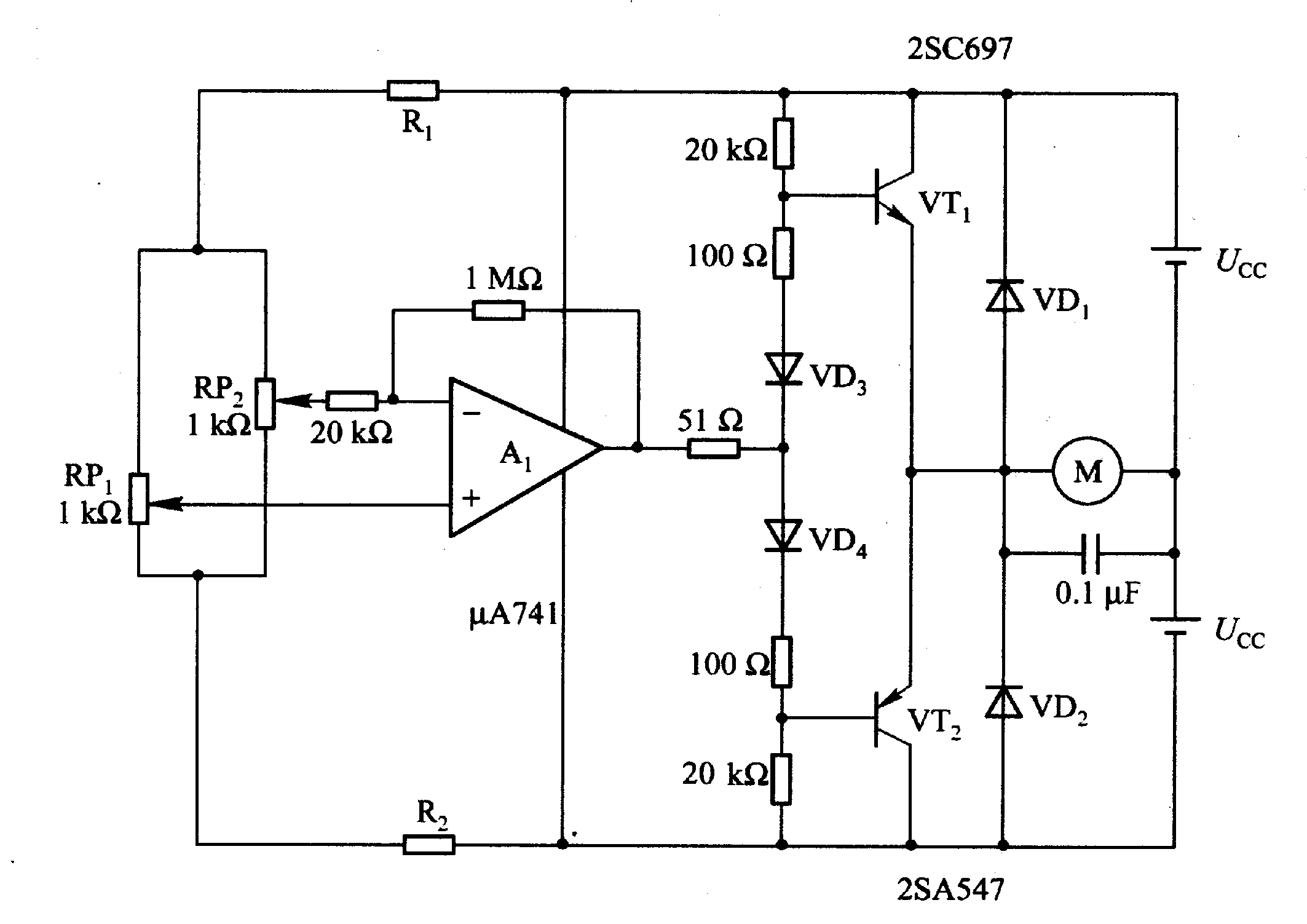
Figure 2-32 (a) illustrates the time control diagram for a motor operated by switch S1. When S1 is set to position 1, the power driver circuit supplies current to the motor, enabling it to run. When S1 is switched to position 2, the drive current is interrupted, and the electric motor functions as a generator, with the back electromotive force managed by the sampling circuit.
The circuit depicted in Figure 2-32 (a) represents a control system for an electric motor that can alternate between running and generating modes. The operation is initiated by the user through switch S1, which has two positions: position 1 for motor operation and position 2 for generator operation.
In position 1, the power driver circuit is engaged, allowing current to flow to the motor. This current is responsible for the motor's operation, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to perform work. The driver circuit typically consists of a transistor or a relay that acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current based on the switch's position.
When S1 is switched to position 2, the power to the motor is cut off, halting its operation. In this mode, the motor begins to act as a generator due to its inertia. The mechanical energy stored in the motor is converted back into electrical energy, generating a back electromotive force (EMF). This generated voltage can be utilized in various applications, such as charging batteries or supplying power to other circuits.
The sampling circuit plays a crucial role in this configuration. It monitors the back EMF produced by the motor during the generator mode. This feedback is essential for ensuring that the system operates efficiently and safely, as it can prevent over-voltage conditions that may damage the components. The sampling circuit typically includes resistors, capacitors, and possibly an operational amplifier to condition the signal for further processing.
Overall, this schematic showcases a versatile motor control system that can efficiently switch between driving and generating modes, utilizing a simple switch to manage the operational state of the motor while incorporating safety features through the sampling circuit. The design is applicable in various fields, including renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and automated machinery.Figure 2-32 (a) shows the time control diagram, and the motor is operated by the switch S1. When Sl is turned to 1, the power driver circuit provides current to the motor for running; When S1 is turned to 2, the drive current is cut off, and the electric motor is used as a generator to hold out the back electromotive force by the sampling circuit. S1is turne.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit depicted in Figure 2-32 (a) represents a control system for an electric motor that can alternate between running and generating modes. The operation is initiated by the user through switch S1, which has two positions: position 1 for motor operation and position 2 for generator operation.
In position 1, the power driver circuit is engaged, allowing current to flow to the motor. This current is responsible for the motor's operation, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to perform work. The driver circuit typically consists of a transistor or a relay that acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current based on the switch's position.
When S1 is switched to position 2, the power to the motor is cut off, halting its operation. In this mode, the motor begins to act as a generator due to its inertia. The mechanical energy stored in the motor is converted back into electrical energy, generating a back electromotive force (EMF). This generated voltage can be utilized in various applications, such as charging batteries or supplying power to other circuits.
The sampling circuit plays a crucial role in this configuration. It monitors the back EMF produced by the motor during the generator mode. This feedback is essential for ensuring that the system operates efficiently and safely, as it can prevent over-voltage conditions that may damage the components. The sampling circuit typically includes resistors, capacitors, and possibly an operational amplifier to condition the signal for further processing.
Overall, this schematic showcases a versatile motor control system that can efficiently switch between driving and generating modes, utilizing a simple switch to manage the operational state of the motor while incorporating safety features through the sampling circuit. The design is applicable in various fields, including renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and automated machinery.Figure 2-32 (a) shows the time control diagram, and the motor is operated by the switch S1. When Sl is turned to 1, the power driver circuit provides current to the motor for running; When S1 is turned to 2, the drive current is cut off, and the electric motor is used as a generator to hold out the back electromotive force by the sampling circuit. S1is turne.. 🔗 External reference