Nicad Battery Charger
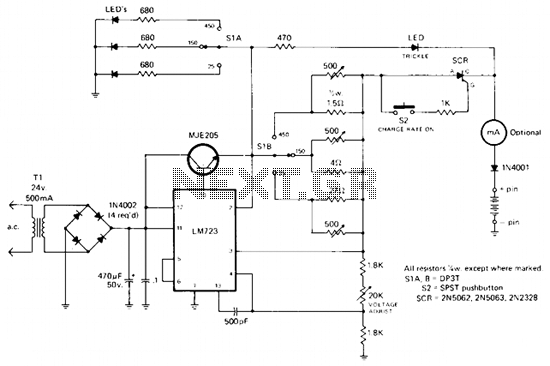
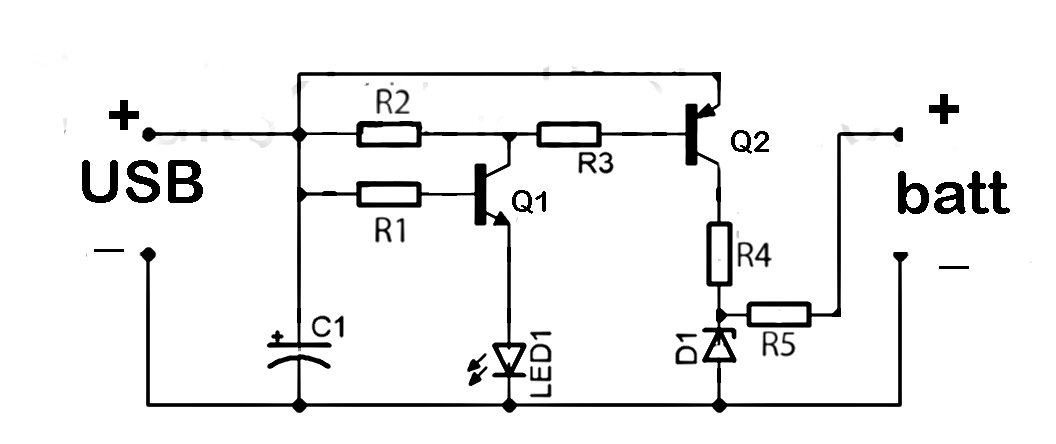
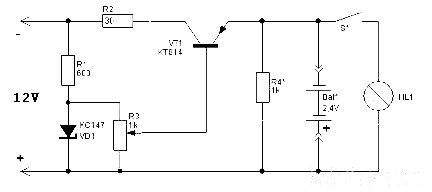
This simple charger utilizes a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across a pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor. The base-emitter voltage of the transistor and the forward voltage drop across the diodes are relatively stable. The charging current is approximately 15mA or 45mA when the switch is closed. This configuration is suitable for most 1.5V and 9V rechargeable batteries. The transformer should have a secondary rating of 12V AC at 0.5A, with the primary rated for 220/240 volts for Europe or 120 volts AC for North America. WARNING: Caution is advised with this circuit. A voltmeter should be used to verify correct polarity, as nickel-cadmium batteries can explode if short-circuited or connected with the wrong polarity.
The charger circuit described operates by employing a BD140 transistor configured as a constant current source, which is essential for safely charging rechargeable batteries. The use of two 1N4148 diodes in series creates a stable voltage drop that is necessary for biasing the transistor's base. This arrangement ensures that the transistor operates within its linear region, allowing it to maintain a steady output current, which is critical in battery charging applications.
When the switch is closed, the circuit can deliver two different charging currents: 15mA for lower capacity batteries and 45mA for higher capacity batteries. This feature provides flexibility in charging various types of batteries, making the charger versatile for both 1.5V and 9V applications. The choice of a transformer with a 12V AC secondary rating at 0.5A is appropriate, as it provides sufficient power for the charging process while maintaining safety and efficiency.
The primary side of the transformer must be selected based on the regional voltage supply, either 220/240 volts for European systems or 120 volts AC for North American systems. This ensures that the transformer operates correctly within its specified voltage range, preventing overheating or failure.
Safety precautions are paramount when working with this circuit. The use of a voltmeter to check polarity before connecting the battery is crucial, as incorrect connections can lead to catastrophic failures, such as battery explosions. Nickel-cadmium batteries, in particular, are sensitive to improper handling, and caution should always be exercised during operation. By following these guidelines and understanding the circuit's functionality, users can effectively and safely charge their rechargeable batteries.This simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor. The base - emitter voltage of the transistor and the forward voltage drop across the diodes are relatively stable. The charging current is approximately 15mA or 45mA with the switch closed. This suits most 1. 5V and 9V rechargeable batteries. The transformer should have a secondary rating of 12V ac at 0. 5amp, the primary should be 220/240volts for Europe or 120volts ac for North America. WARNING: Take care with this circuit. Use a voltmeter to observe correct polarity. Nicads can explode if short circuited or connected with the wrong polarity. 🔗 External reference
The charger circuit described operates by employing a BD140 transistor configured as a constant current source, which is essential for safely charging rechargeable batteries. The use of two 1N4148 diodes in series creates a stable voltage drop that is necessary for biasing the transistor's base. This arrangement ensures that the transistor operates within its linear region, allowing it to maintain a steady output current, which is critical in battery charging applications.
When the switch is closed, the circuit can deliver two different charging currents: 15mA for lower capacity batteries and 45mA for higher capacity batteries. This feature provides flexibility in charging various types of batteries, making the charger versatile for both 1.5V and 9V applications. The choice of a transformer with a 12V AC secondary rating at 0.5A is appropriate, as it provides sufficient power for the charging process while maintaining safety and efficiency.
The primary side of the transformer must be selected based on the regional voltage supply, either 220/240 volts for European systems or 120 volts AC for North American systems. This ensures that the transformer operates correctly within its specified voltage range, preventing overheating or failure.
Safety precautions are paramount when working with this circuit. The use of a voltmeter to check polarity before connecting the battery is crucial, as incorrect connections can lead to catastrophic failures, such as battery explosions. Nickel-cadmium batteries, in particular, are sensitive to improper handling, and caution should always be exercised during operation. By following these guidelines and understanding the circuit's functionality, users can effectively and safely charge their rechargeable batteries.This simple charger uses a single transistor as a constant current source. The voltage across the pair of 1N4148 diodes biases the base of the BD140 medium power transistor. The base - emitter voltage of the transistor and the forward voltage drop across the diodes are relatively stable. The charging current is approximately 15mA or 45mA with the switch closed. This suits most 1. 5V and 9V rechargeable batteries. The transformer should have a secondary rating of 12V ac at 0. 5amp, the primary should be 220/240volts for Europe or 120volts ac for North America. WARNING: Take care with this circuit. Use a voltmeter to observe correct polarity. Nicads can explode if short circuited or connected with the wrong polarity. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713