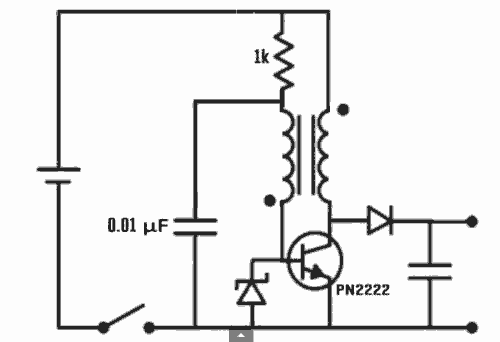
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Battery Charger
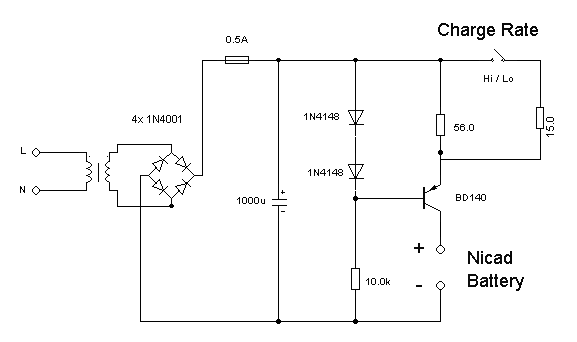
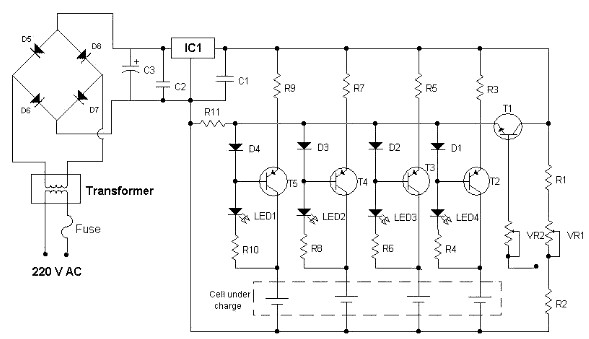
The circuit diagram illustrates a conventional charger powered by an AC input source, designed for charging batteries. This type of rechargeable battery is...
The circuit consists of several key components that facilitate the conversion of AC voltage from the mains supply into a suitable DC voltage required for charging batteries. The primary element is the transformer, which steps down the high AC voltage to a lower level. Following the transformer, a rectifier circuit, typically composed of diodes, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC.
To smooth out the pulsating DC, a filter capacitor is employed, which reduces voltage ripple, providing a more stable DC output. The output of the rectifier and filter circuit is then regulated to ensure that the voltage remains constant despite variations in the input voltage or load conditions. This is often achieved using a voltage regulator IC, which can maintain the output voltage within specified limits.
Additionally, the circuit may include protection features such as a fuse or circuit breaker to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions. A charging control circuit may also be implemented to monitor the battery voltage and current, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently and safely, preventing overcharging.
Overall, this charger circuit is designed to provide a reliable and efficient method for charging rechargeable batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the battery cells.The circuit diagram shows a regular charger being powered by an AC input source, intended for charging batteries. This type of rechargeable batteries are.. 🔗 External reference
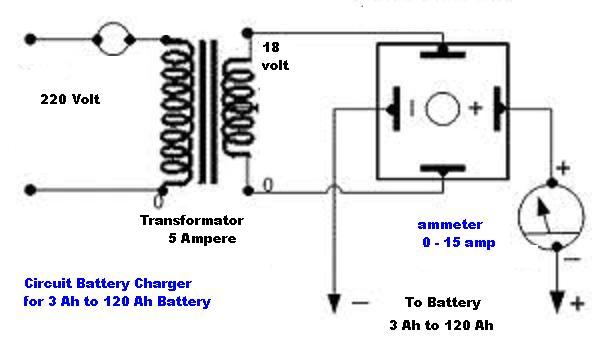
The circuit consists of several key components that facilitate the conversion of AC voltage from the mains supply into a suitable DC voltage required for charging batteries. The primary element is the transformer, which steps down the high AC voltage to a lower level. Following the transformer, a rectifier circuit, typically composed of diodes, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC.
To smooth out the pulsating DC, a filter capacitor is employed, which reduces voltage ripple, providing a more stable DC output. The output of the rectifier and filter circuit is then regulated to ensure that the voltage remains constant despite variations in the input voltage or load conditions. This is often achieved using a voltage regulator IC, which can maintain the output voltage within specified limits.
Additionally, the circuit may include protection features such as a fuse or circuit breaker to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions. A charging control circuit may also be implemented to monitor the battery voltage and current, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently and safely, preventing overcharging.
Overall, this charger circuit is designed to provide a reliable and efficient method for charging rechargeable batteries, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the battery cells.The circuit diagram shows a regular charger being powered by an AC input source, intended for charging batteries. This type of rechargeable batteries are.. 🔗 External reference