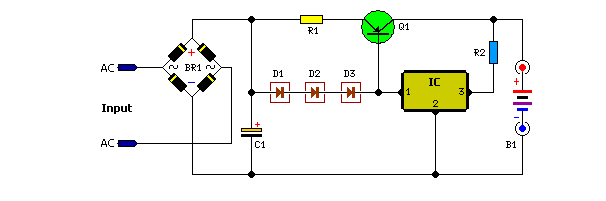
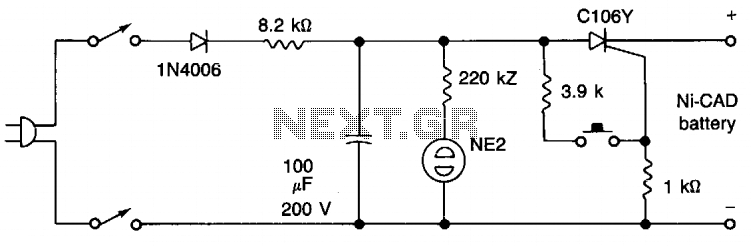
charger for nicd batteries
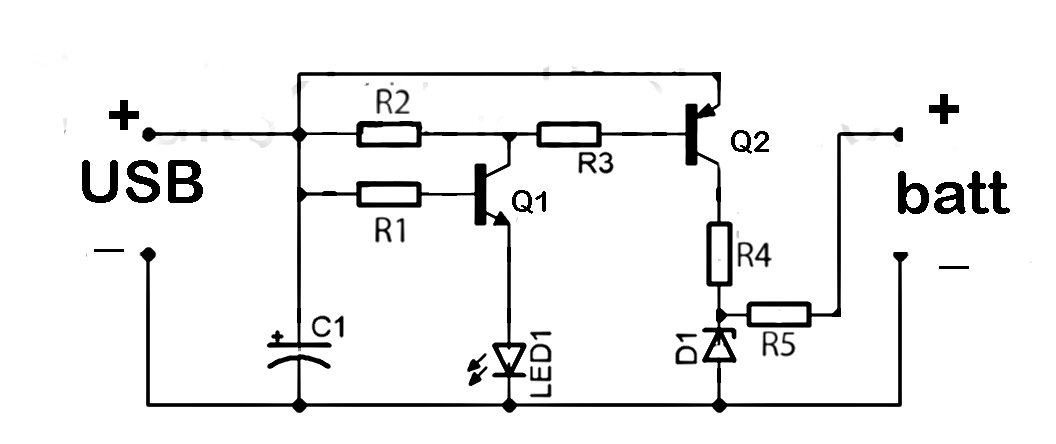
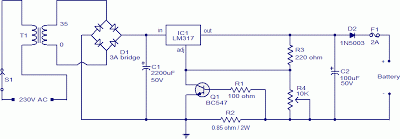
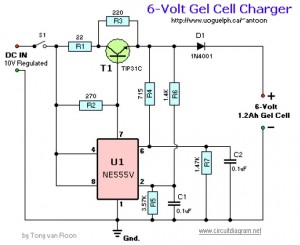
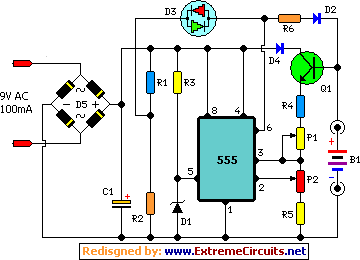
Charger for NiCd batteries power supply. This is a car NiCd battery charger circuit that can charge any Ni-Cd battery between 4.8 and 4.4 volts from a classic 12 volts car battery. The charging current is constant and can be selected from the values of 50 to 120 mA using the selector S. This feature is very useful for model-making enthusiasts, video operators, and those who use small appliances for transmission and reception, as well as anyone who uses Ni-Cd batteries and needs to recharge when a voltage network is not available.
The described circuit functions as a dedicated charger for nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, specifically designed to operate from a standard 12-volt automotive battery. The circuit is capable of charging NiCd batteries with voltage ratings between 4.4 volts and 4.8 volts, making it versatile for various applications where NiCd batteries are employed.
The charging mechanism is characterized by a constant current output, which is essential for maintaining battery health and longevity. The current can be adjusted between 50 mA and 120 mA through the use of a selector switch labeled 'S'. This adjustability allows users to tailor the charging rate according to the specific requirements of their batteries and applications. For instance, a lower charging current may be preferable for smaller batteries or for applications requiring a gentler charge, while a higher current can expedite the charging process for larger capacity batteries.
The circuit is particularly beneficial for model-making enthusiasts and video operators who often rely on portable battery-operated devices. It provides a reliable solution for recharging NiCd batteries when access to conventional voltage networks is limited or unavailable, such as in remote locations or during outdoor activities.
In summary, this car NiCd battery charger circuit represents a practical and efficient solution for users who require a dependable method to recharge their NiCd batteries, ensuring that their devices remain operational even in the absence of standard power sources.Charger for NiCd Batteries power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. This is a car nicd battery charger circuitthat can chargeanyNi-Cdbatterybetween 4. 8 and4. 4 voltsfromaclassic12Voltscar battery. Thecharging currentis constantitcan beselected fr om the values of 50 to120mAbythe selectorS. This feature is veryuseful formodel makingenthusiasts, forvideooperators, to those who usesmall appliancestransmissionandreceptionto all thosethat useNi-Cdbatteriesand needto rechargeorvoltagenetworkis not available. . 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a dedicated charger for nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, specifically designed to operate from a standard 12-volt automotive battery. The circuit is capable of charging NiCd batteries with voltage ratings between 4.4 volts and 4.8 volts, making it versatile for various applications where NiCd batteries are employed.
The charging mechanism is characterized by a constant current output, which is essential for maintaining battery health and longevity. The current can be adjusted between 50 mA and 120 mA through the use of a selector switch labeled 'S'. This adjustability allows users to tailor the charging rate according to the specific requirements of their batteries and applications. For instance, a lower charging current may be preferable for smaller batteries or for applications requiring a gentler charge, while a higher current can expedite the charging process for larger capacity batteries.
The circuit is particularly beneficial for model-making enthusiasts and video operators who often rely on portable battery-operated devices. It provides a reliable solution for recharging NiCd batteries when access to conventional voltage networks is limited or unavailable, such as in remote locations or during outdoor activities.
In summary, this car NiCd battery charger circuit represents a practical and efficient solution for users who require a dependable method to recharge their NiCd batteries, ensuring that their devices remain operational even in the absence of standard power sources.Charger for NiCd Batteries power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. This is a car nicd battery charger circuitthat can chargeanyNi-Cdbatterybetween 4. 8 and4. 4 voltsfromaclassic12Voltscar battery. Thecharging currentis constantitcan beselected fr om the values of 50 to120mAbythe selectorS. This feature is veryuseful formodel makingenthusiasts, forvideooperators, to those who usesmall appliancestransmissionandreceptionto all thosethat useNi-Cdbatteriesand needto rechargeorvoltagenetworkis not available. . 🔗 External reference