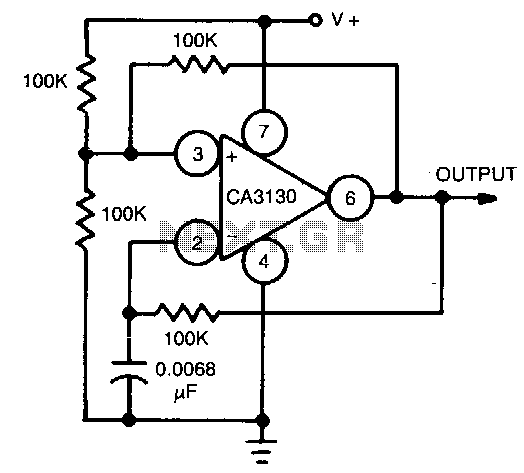
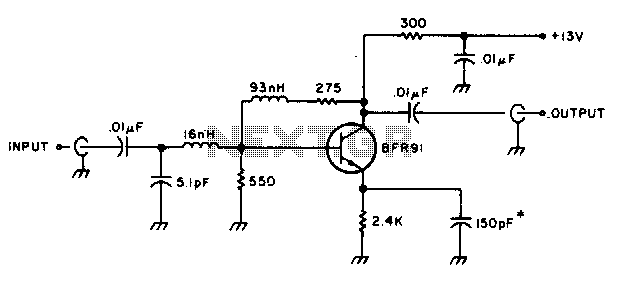
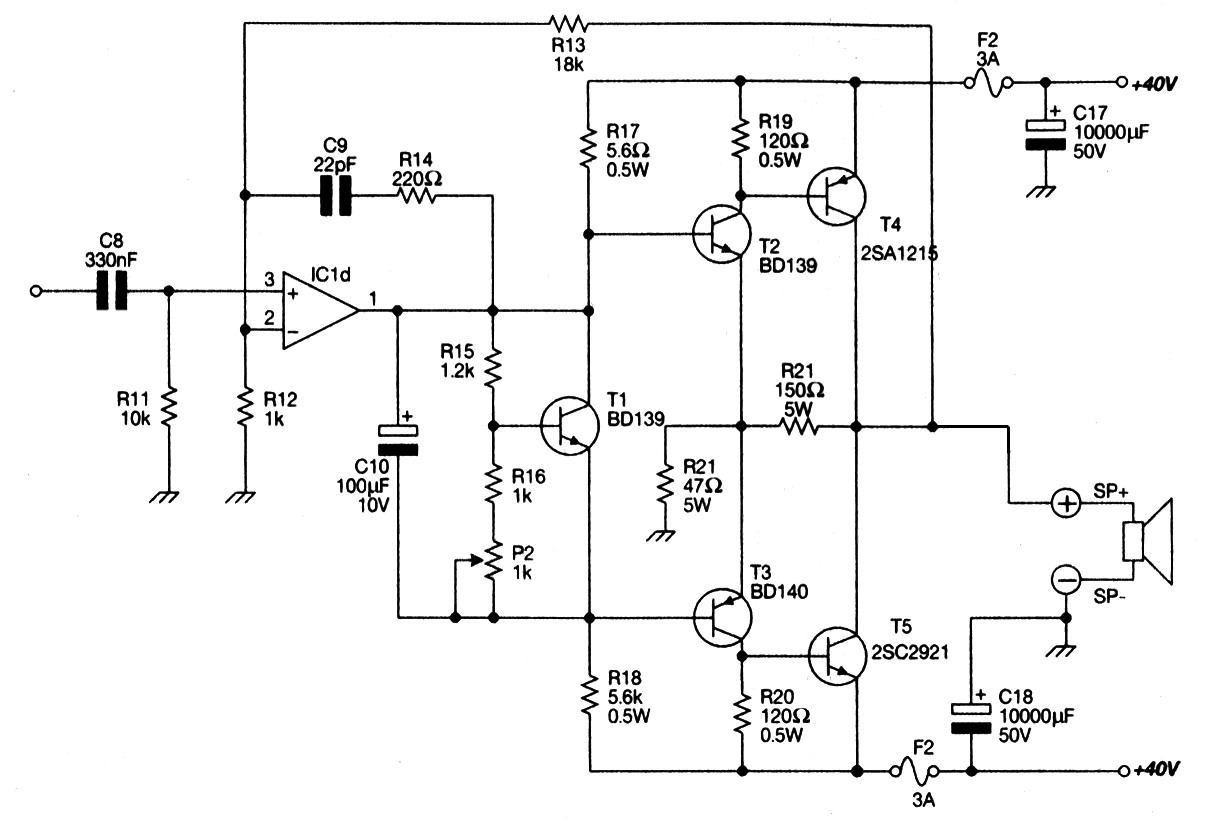
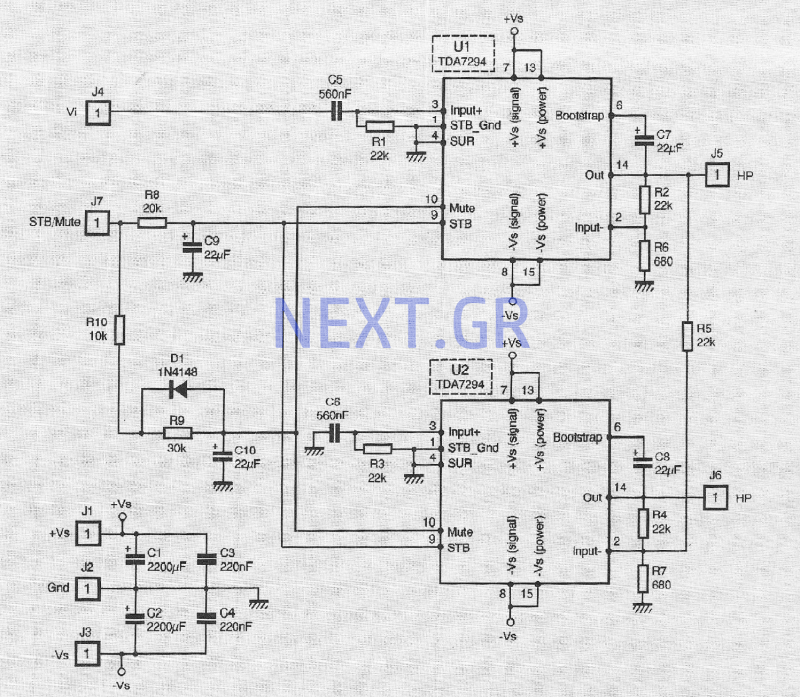
Op-Amp Application: Level Shifting Amplifier
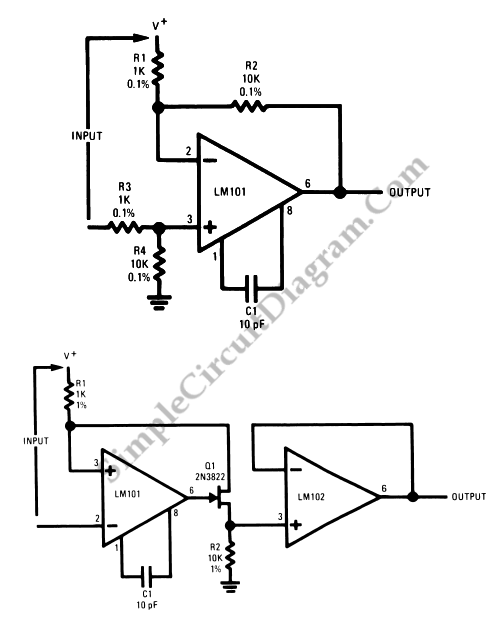
In linear equipment design, it is sometimes necessary to take a voltage that is referenced to a certain DC level and generate an amplified output that is also referenced.
In linear circuit design, the process of amplifying a voltage that is referenced to a specific DC level is crucial for various applications, such as signal conditioning, audio amplification, and sensor interfacing. This involves using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a non-inverting or inverting amplifier configuration, depending on the desired gain and output characteristics.
The op-amp receives an input voltage (V_in) that is offset by a DC bias voltage (V_ref). The output voltage (V_out) is then expressed as a function of the input voltage and the gain determined by external resistors. In a non-inverting configuration, the gain (A) can be calculated using the formula A = 1 + (R_f/R_in), where R_f is the feedback resistor and R_in is the input resistor. The output voltage can be represented as V_out = V_ref + (V_in * A).
It is essential to ensure that the op-amp operates within its specified voltage range to avoid saturation and distortion of the amplified signal. Additionally, considerations such as bandwidth, slew rate, and power supply requirements must be taken into account when designing the circuit.
The output can then be used in various applications, including driving loads, interfacing with analog-to-digital converters, or further processing in subsequent stages of a more complex electronic system. Proper filtering and decoupling techniques should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the amplifier circuit.Sometimes, in linear equipment design, it`s necessary to take a voltage which is referred to some dc level and generate an amplified output which is referred.. 🔗 External reference
In linear circuit design, the process of amplifying a voltage that is referenced to a specific DC level is crucial for various applications, such as signal conditioning, audio amplification, and sensor interfacing. This involves using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a non-inverting or inverting amplifier configuration, depending on the desired gain and output characteristics.
The op-amp receives an input voltage (V_in) that is offset by a DC bias voltage (V_ref). The output voltage (V_out) is then expressed as a function of the input voltage and the gain determined by external resistors. In a non-inverting configuration, the gain (A) can be calculated using the formula A = 1 + (R_f/R_in), where R_f is the feedback resistor and R_in is the input resistor. The output voltage can be represented as V_out = V_ref + (V_in * A).
It is essential to ensure that the op-amp operates within its specified voltage range to avoid saturation and distortion of the amplified signal. Additionally, considerations such as bandwidth, slew rate, and power supply requirements must be taken into account when designing the circuit.
The output can then be used in various applications, including driving loads, interfacing with analog-to-digital converters, or further processing in subsequent stages of a more complex electronic system. Proper filtering and decoupling techniques should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the amplifier circuit.Sometimes, in linear equipment design, it`s necessary to take a voltage which is referred to some dc level and generate an amplified output which is referred.. 🔗 External reference