OpAmp based Voltage Translator Ciruit for ADC of Micro-controller
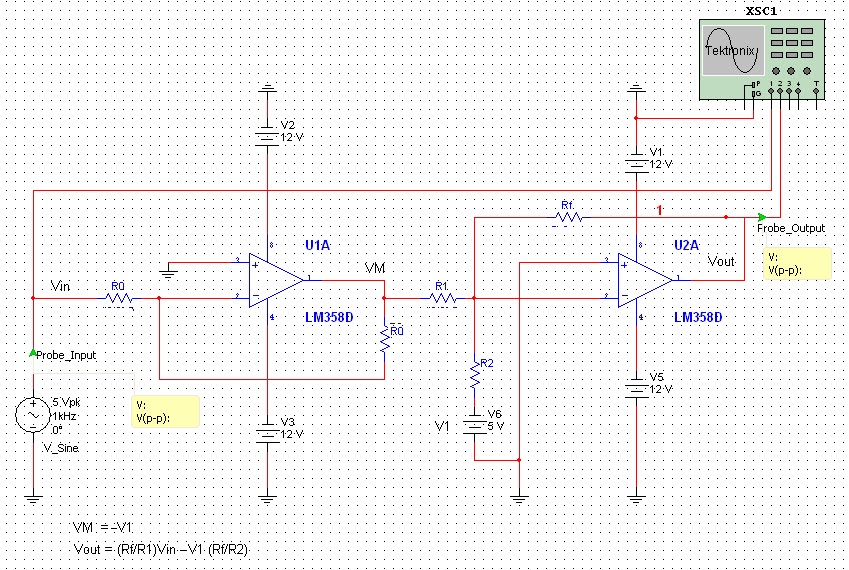
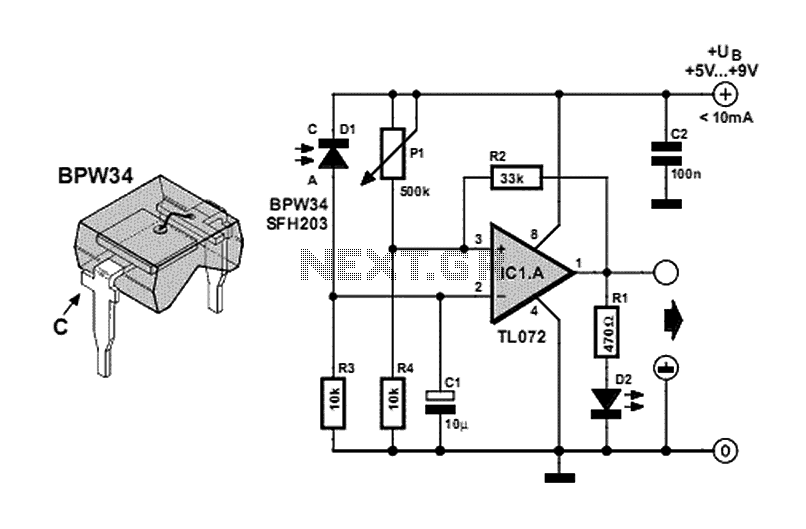
All naturally occurring phenomena such as sound, temperature, and pressure are analog in nature. To enable a microcontroller to read analog signals for the analog-to-digital conversion process using a built-in analog-to-digital converter (ADC), it is essential to condition the analog signal generated by a transducer. This involves analog signal conditioning and processing through analog circuits. A microcontroller can only interpret such a signal if it has been conditioned and scaled to a range that the microcontroller can read for analog-to-digital conversion. This is particularly necessary for microcontrollers like AVR, PIC, and Freescale, which feature built-in ADCs and typically operate with a 5V power supply. The circuit depicted in Figure 1 is designed to scale down the voltages generated by the transducer to the 0-5V range. This circuit can convert voltages from other ranges (such as -5V to +5V or -10V to +10V) to the 0-5V range, allowing a microcontroller powered by a 5V supply to read this signal through its ADC input without the risk of damage. A sinusoidal input voltage with a frequency of 1kHz and a peak-to-peak voltage of -5V to +5V is applied to the input of this circuit, which translates to a sinusoidal output voltage with a peak-to-peak amplitude varying from 0 to 5 volts.
The circuit for analog signal conditioning typically consists of several key components: operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and capacitors. The op-amps are configured to perform tasks such as level shifting, amplification, and filtering. A common configuration for this purpose is the inverting or non-inverting amplifier setup, which allows for the adjustment of gain to ensure that the output voltage fits within the desired range.
To achieve the necessary level shifting for a signal that ranges from -5V to +5V, a biasing method is often employed. This involves adding a reference voltage (usually 2.5V) to the input signal, effectively shifting the entire waveform upward. This can be accomplished using a voltage divider network composed of resistors that provides the required reference voltage.
Filtering is also an important aspect of analog signal conditioning. Capacitors can be used in conjunction with resistors to create low-pass or high-pass filters, depending on the application. For instance, a low-pass filter can help remove high-frequency noise from the signal, ensuring that only the desired frequency components reach the ADC.
The final output signal, which now varies from 0V to 5V, can be directly interfaced with the microcontroller's ADC input. It is crucial to ensure that the output impedance of the conditioning circuit is compatible with the input impedance of the ADC to prevent signal distortion. Additionally, proper power supply decoupling techniques should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the circuit.
In summary, the described circuit effectively conditions and scales analog signals from transducers, allowing microcontrollers with built-in ADCs to accurately read and process these signals while maintaining operational integrity and preventing damage.All the naturally occurring phenomena like sound, temperature and pressure etc, are analog in nature. Therefore to make an micro-controller read analog signal for analog-to-digital conversion process, through built-in analog-to-digital converter (ADC), it is necessary to subject the analog signal, generated by a transducer, to some analog signal con
ditioning and analog signal processing using analog circuits. The micro-controller can read such a signal, generated by a transducer, only if it has been conditioned and scaled down to a range which micro-controller can read for analog-to-digital conversion. This is necessary in particular for micro-controllers like AVR, PIC and Free-scale which have built-in ADCs.
These micro-controllers usually operate with 5Volts power supply. The circuits shown in the Figure1 below is appropriate for scaling down the transducer generated voltages to 0-5 Volts range. This circuit can translate the voltage falling in some other voltage range ( like -5 to +5 Volts or -10 to +10 Volts etc.
) to 0-5Volt range so that a micro- controller, being operated from 5Volt power supply, may read this signal, through its ADC input, without getting damaged. A sinusoidal input voltage of frequency 1KHz and -5V-to-+5V peak-to-peak voltage has been applied to the input of this circuit, which is translated to a sinusoidal output voltage with peak-to-peak amplitude varying from 0-5 Volts.
🔗 External reference
The circuit for analog signal conditioning typically consists of several key components: operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and capacitors. The op-amps are configured to perform tasks such as level shifting, amplification, and filtering. A common configuration for this purpose is the inverting or non-inverting amplifier setup, which allows for the adjustment of gain to ensure that the output voltage fits within the desired range.
To achieve the necessary level shifting for a signal that ranges from -5V to +5V, a biasing method is often employed. This involves adding a reference voltage (usually 2.5V) to the input signal, effectively shifting the entire waveform upward. This can be accomplished using a voltage divider network composed of resistors that provides the required reference voltage.
Filtering is also an important aspect of analog signal conditioning. Capacitors can be used in conjunction with resistors to create low-pass or high-pass filters, depending on the application. For instance, a low-pass filter can help remove high-frequency noise from the signal, ensuring that only the desired frequency components reach the ADC.
The final output signal, which now varies from 0V to 5V, can be directly interfaced with the microcontroller's ADC input. It is crucial to ensure that the output impedance of the conditioning circuit is compatible with the input impedance of the ADC to prevent signal distortion. Additionally, proper power supply decoupling techniques should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation of the circuit.
In summary, the described circuit effectively conditions and scales analog signals from transducers, allowing microcontrollers with built-in ADCs to accurately read and process these signals while maintaining operational integrity and preventing damage.All the naturally occurring phenomena like sound, temperature and pressure etc, are analog in nature. Therefore to make an micro-controller read analog signal for analog-to-digital conversion process, through built-in analog-to-digital converter (ADC), it is necessary to subject the analog signal, generated by a transducer, to some analog signal con
ditioning and analog signal processing using analog circuits. The micro-controller can read such a signal, generated by a transducer, only if it has been conditioned and scaled down to a range which micro-controller can read for analog-to-digital conversion. This is necessary in particular for micro-controllers like AVR, PIC and Free-scale which have built-in ADCs.
These micro-controllers usually operate with 5Volts power supply. The circuits shown in the Figure1 below is appropriate for scaling down the transducer generated voltages to 0-5 Volts range. This circuit can translate the voltage falling in some other voltage range ( like -5 to +5 Volts or -10 to +10 Volts etc.
) to 0-5Volt range so that a micro- controller, being operated from 5Volt power supply, may read this signal, through its ADC input, without getting damaged. A sinusoidal input voltage of frequency 1KHz and -5V-to-+5V peak-to-peak voltage has been applied to the input of this circuit, which is translated to a sinusoidal output voltage with peak-to-peak amplitude varying from 0-5 Volts.
🔗 External reference