PC Heat Monitor
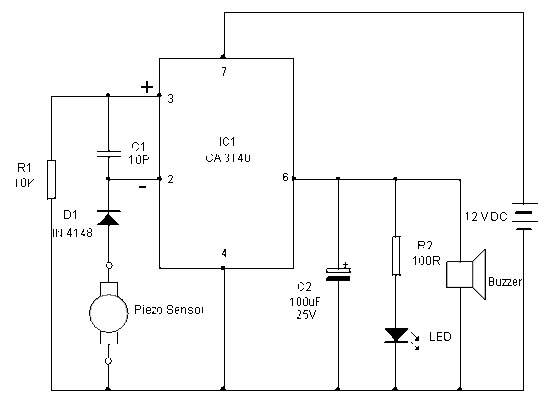
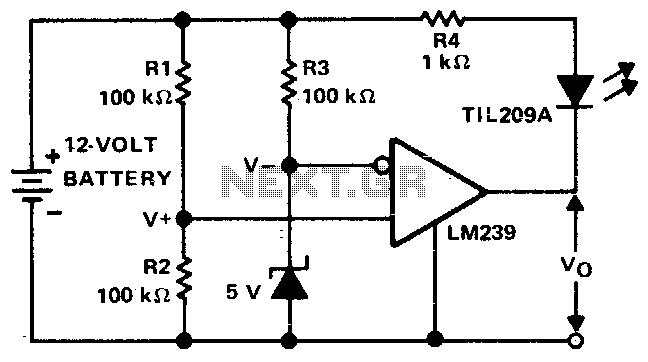
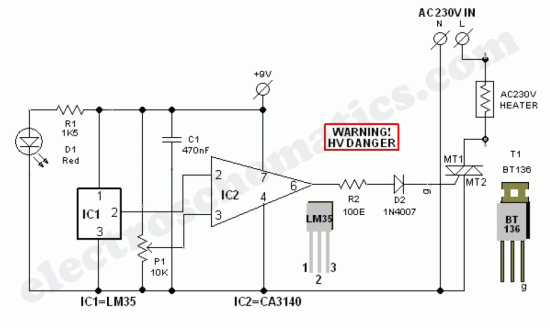
The PC processor generates very high temperatures during its operation, which are dissipated by the large heat sink placed above the processor.
The thermal management of a PC processor is critical to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The processor, when operating under load, can generate significant heat due to the high frequency and voltage at which it operates. To manage this heat, a large heat sink is employed, typically made of aluminum or copper, which has a high thermal conductivity.
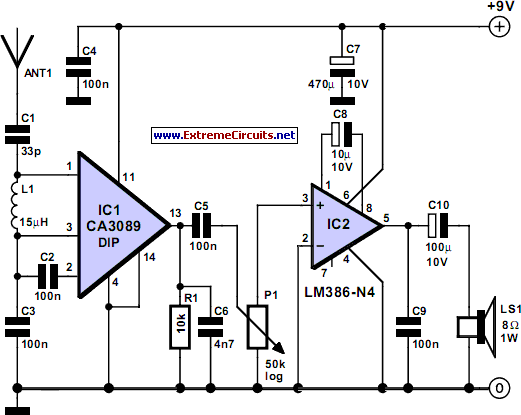
The heat sink is designed with fins or extended surfaces to increase the surface area available for heat dissipation into the surrounding air. This passive cooling solution relies on natural convection, where warmer air rises and is replaced by cooler air. In systems where the processor operates at higher temperatures, additional cooling methods such as active cooling with fans or liquid cooling systems may be integrated to enhance heat removal.
The heat sink is usually mounted directly onto the processor using a thermal interface material (TIM), which improves thermal conductivity between the processor and the heat sink. Proper application of TIM is essential, as it fills microscopic gaps and imperfections on the surfaces to facilitate efficient heat transfer.
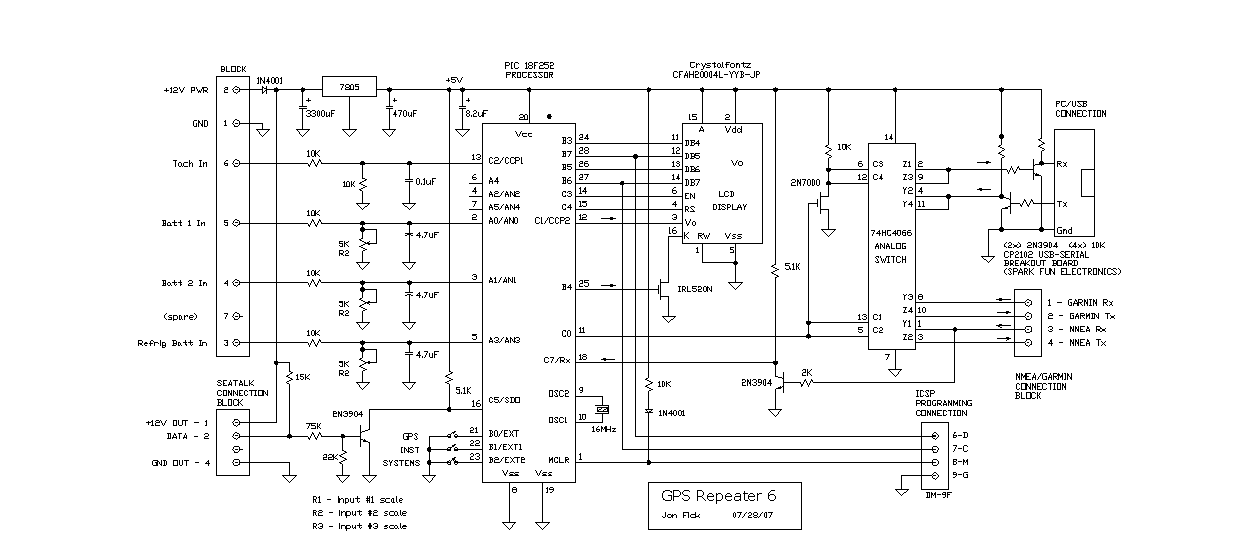
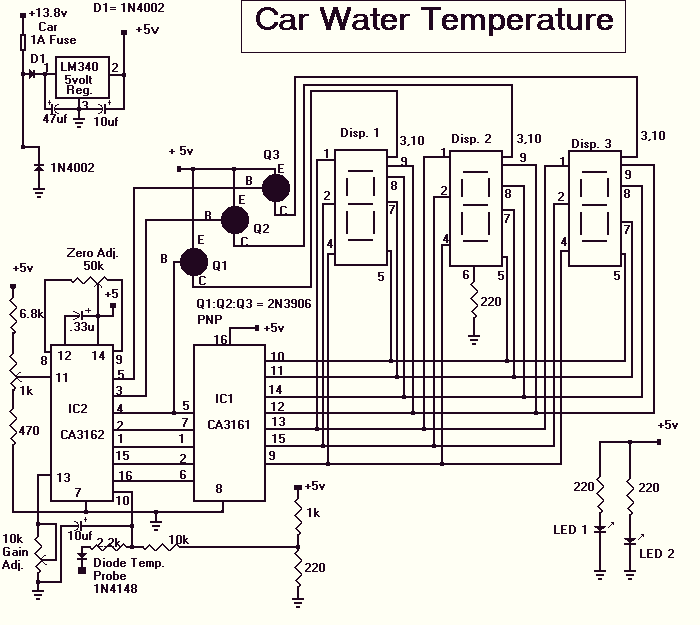
In high-performance computing environments, monitoring the temperature of the processor is crucial. Temperature sensors can be integrated into the processor or placed near the heat sink to provide real-time feedback to the system. This data can be utilized by the system's firmware to adjust fan speeds or throttle the processor's performance to prevent overheating.
Overall, the design and implementation of effective heat dissipation strategies are vital for maintaining the reliability and efficiency of PC processors under varying operational conditions.The PC processor generates very high temperature during its operation which is dissipated by the large heat sink placed above the processor. If the heat s.. 🔗 External reference
The thermal management of a PC processor is critical to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The processor, when operating under load, can generate significant heat due to the high frequency and voltage at which it operates. To manage this heat, a large heat sink is employed, typically made of aluminum or copper, which has a high thermal conductivity.
The heat sink is designed with fins or extended surfaces to increase the surface area available for heat dissipation into the surrounding air. This passive cooling solution relies on natural convection, where warmer air rises and is replaced by cooler air. In systems where the processor operates at higher temperatures, additional cooling methods such as active cooling with fans or liquid cooling systems may be integrated to enhance heat removal.
The heat sink is usually mounted directly onto the processor using a thermal interface material (TIM), which improves thermal conductivity between the processor and the heat sink. Proper application of TIM is essential, as it fills microscopic gaps and imperfections on the surfaces to facilitate efficient heat transfer.
In high-performance computing environments, monitoring the temperature of the processor is crucial. Temperature sensors can be integrated into the processor or placed near the heat sink to provide real-time feedback to the system. This data can be utilized by the system's firmware to adjust fan speeds or throttle the processor's performance to prevent overheating.
Overall, the design and implementation of effective heat dissipation strategies are vital for maintaining the reliability and efficiency of PC processors under varying operational conditions.The PC processor generates very high temperature during its operation which is dissipated by the large heat sink placed above the processor. If the heat s.. 🔗 External reference