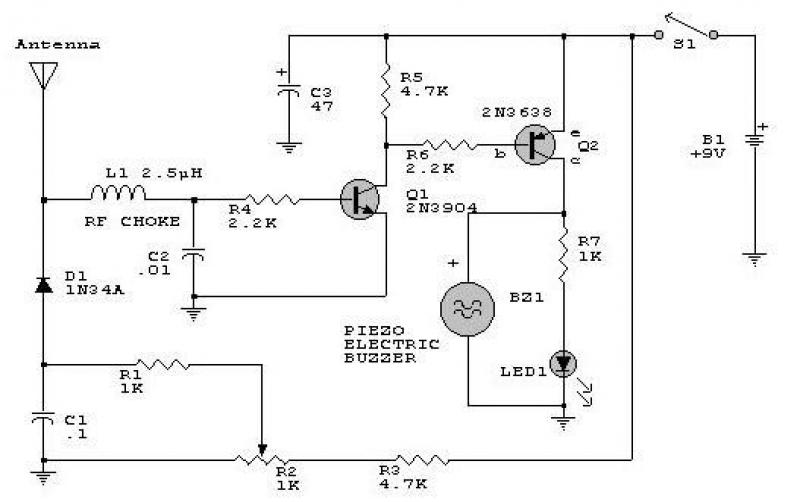
Phase sequence detector
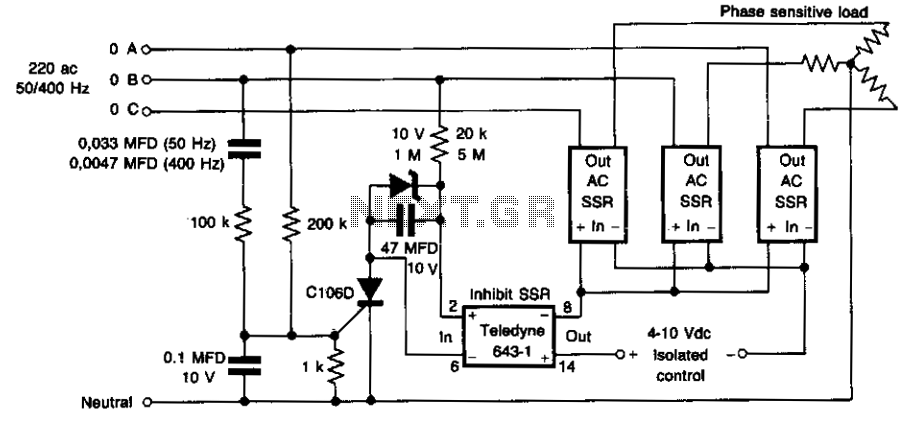
This circuit prevents damage to the load due to incorrect phasing. The three power solid-state relays (SSRs) are only permitted to turn on for a phase sequence where phase A leads phase B. If phase A lags phase B, the input currents will cancel, causing the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and the inhibit SSR to remain off until the sequence is reversed. The inhibit SSR is included to maintain isolation at the input.
The circuit utilizes three power solid-state relays (SSRs) to control the load based on the phase relationship between phase A and phase B. The primary function of this circuit is to prevent potential damage to the load that could occur due to incorrect phasing, which is a critical concern in three-phase systems.
In normal operation, when phase A leads phase B, the SSRs are activated, allowing current to flow to the load. This leads to the desired operation of the connected equipment. However, if the phase sequence is incorrect, specifically if phase A lags phase B, a cancellation effect occurs in the input currents. This cancellation prevents the necessary triggering of the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and the inhibit SSR, which effectively isolates the load from the power source, thereby protecting it from damage.
The inclusion of the inhibit SSR is essential for maintaining electrical isolation at the input. This SSR serves as a safety mechanism, ensuring that under conditions of incorrect phasing, the circuit remains inactive, preventing any unintended operation of the load. The design of this circuit emphasizes reliability and safety, making it suitable for applications where phase integrity is critical.
Overall, the circuit provides a robust solution for managing phase relationships in three-phase systems, ensuring that loads are only energized under correct phasing conditions, thus enhancing the longevity and reliability of the connected equipment.This circuit prevents damage to the load due to incorrect phasing. The three power SSR's are only permitted to turn-on for a phase sequence of phase A leading phase B. If phase A lags phase the input currents will cancel, causing the SCR and the inhibit SSR to remain off until the sequence is reversed. The inhibit SSR is included to maintain isolation at the input. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes three power solid-state relays (SSRs) to control the load based on the phase relationship between phase A and phase B. The primary function of this circuit is to prevent potential damage to the load that could occur due to incorrect phasing, which is a critical concern in three-phase systems.
In normal operation, when phase A leads phase B, the SSRs are activated, allowing current to flow to the load. This leads to the desired operation of the connected equipment. However, if the phase sequence is incorrect, specifically if phase A lags phase B, a cancellation effect occurs in the input currents. This cancellation prevents the necessary triggering of the silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and the inhibit SSR, which effectively isolates the load from the power source, thereby protecting it from damage.
The inclusion of the inhibit SSR is essential for maintaining electrical isolation at the input. This SSR serves as a safety mechanism, ensuring that under conditions of incorrect phasing, the circuit remains inactive, preventing any unintended operation of the load. The design of this circuit emphasizes reliability and safety, making it suitable for applications where phase integrity is critical.
Overall, the circuit provides a robust solution for managing phase relationships in three-phase systems, ensuring that loads are only energized under correct phasing conditions, thus enhancing the longevity and reliability of the connected equipment.This circuit prevents damage to the load due to incorrect phasing. The three power SSR's are only permitted to turn-on for a phase sequence of phase A leading phase B. If phase A lags phase the input currents will cancel, causing the SCR and the inhibit SSR to remain off until the sequence is reversed. The inhibit SSR is included to maintain isolation at the input. 🔗 External reference