Phono Preamplifier

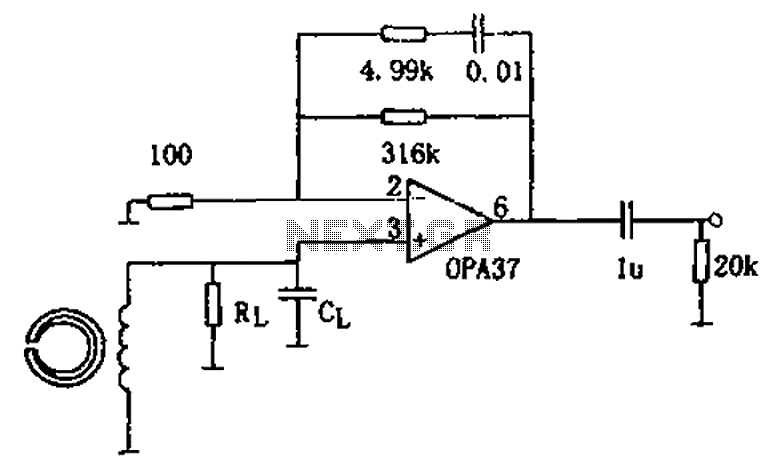
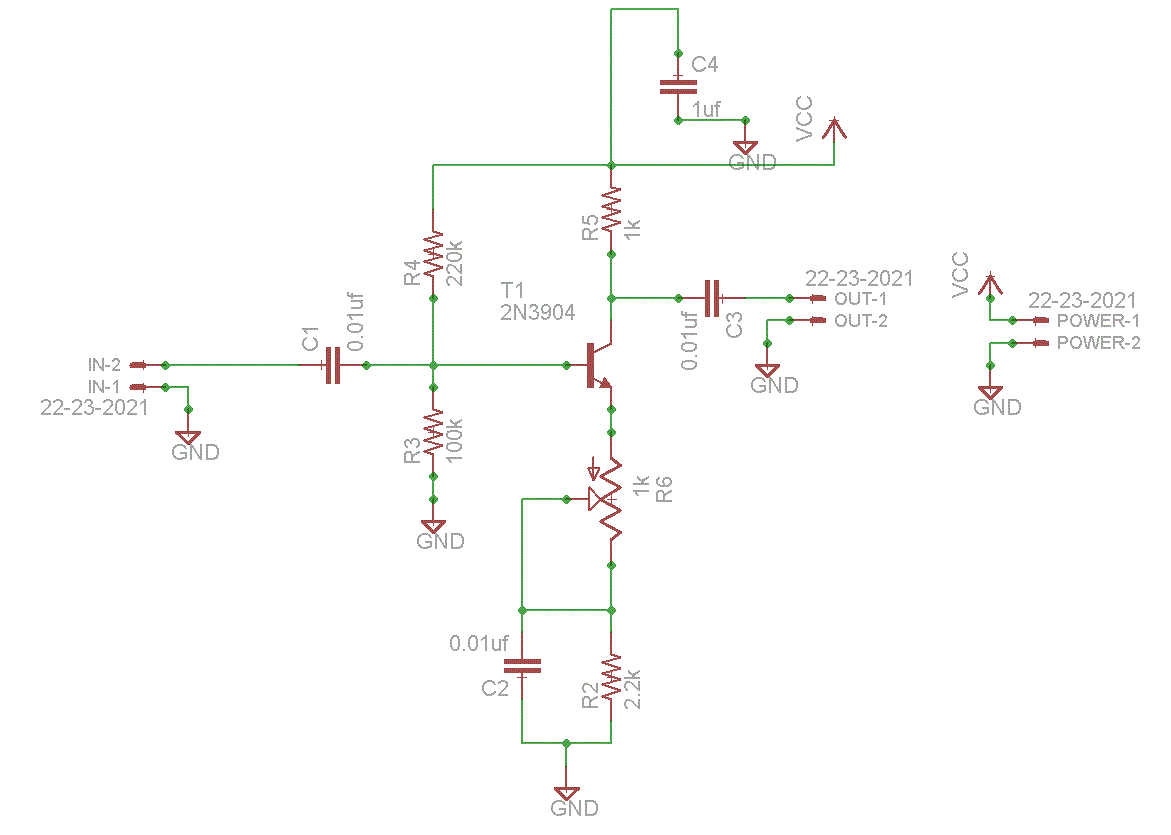
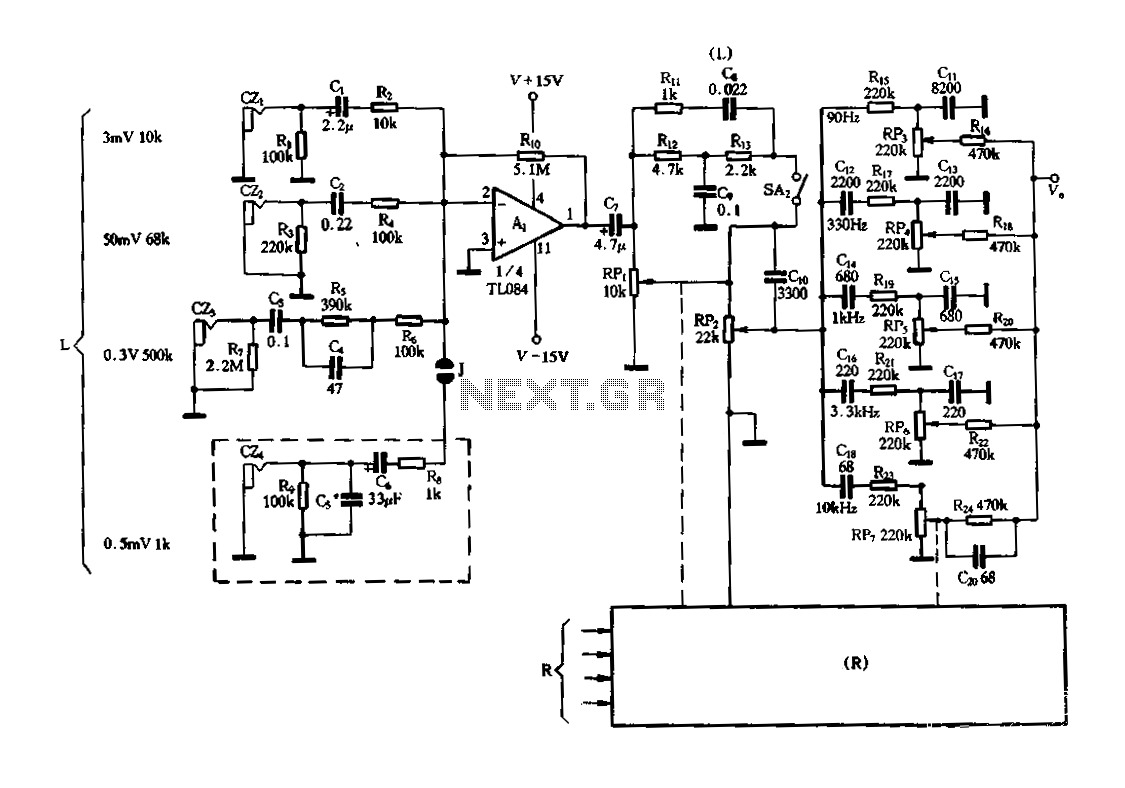
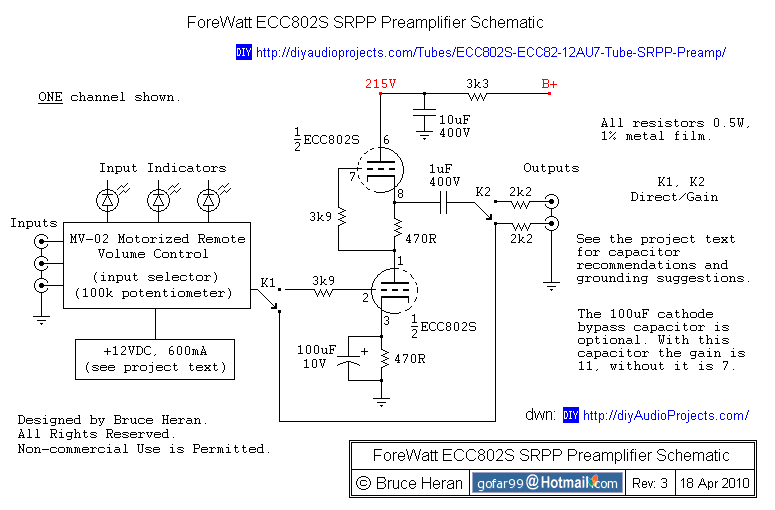
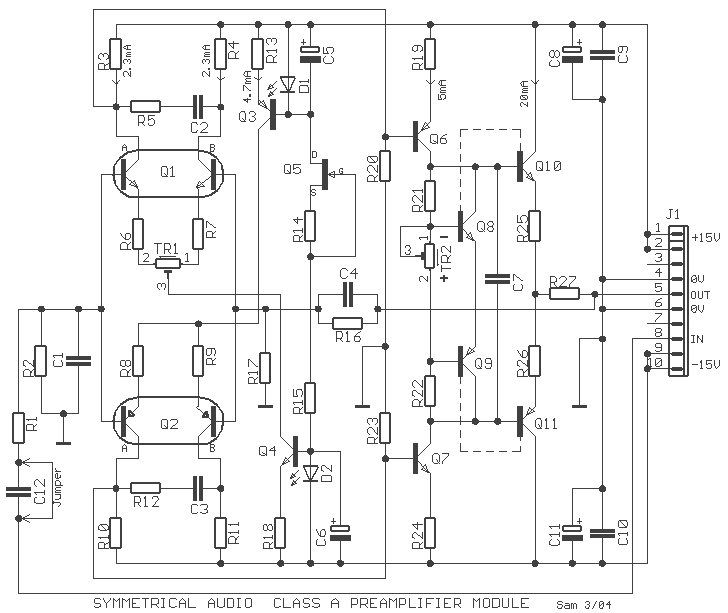
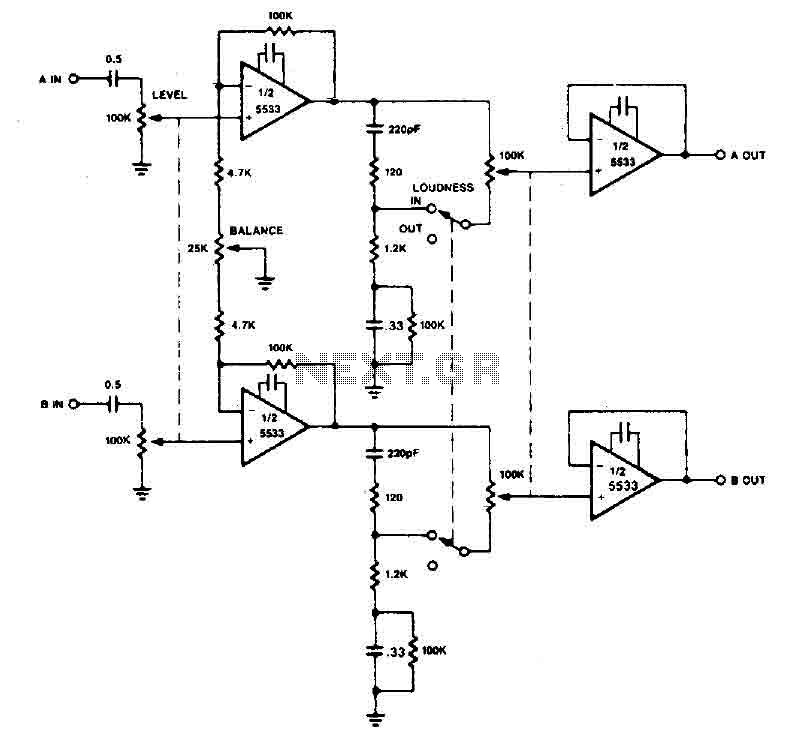
The original description discusses the increasing rarity of vinyl recordings in the wake of the introduction of CDs. However, it notes the continued utility of a phono preamplifier for the purpose of listening to older vinyl records from a well-maintained collection. The description goes on to detail a simple yet effective circuit designed for inexpensive moving-magnet cartridges. This circuit can be used in conjunction with both audio power amplifiers displayed in preceding pages. The circuit is characterized by low noise, an accurate RIAA frequency response curve, minimal distortion, and a strong performance in handling high frequency transients. This is largely due to the passive equalization in the 1 to 20KHz range. The description concludes by noting that the transistors and associated components provide a ± 18V supply to the op-amp, which enhances headroom and maximum output voltage.
Expanding on this, the circuit's efficiency is largely due to its simple design, which includes a phono preamplifier that is adept at handling the demands of older vinyl records. The moving-magnet cartridges, which are a popular choice due to their affordability, contribute to the overall effectiveness of the circuit. This is particularly true when the circuit is used in conjunction with audio power amplifiers, as the description suggests.
The low noise characteristic of the circuit ensures a clean, clear audio output, free from unwanted interference. This is complemented by the accurate RIAA frequency response curve which ensures a faithful reproduction of the audio signal across the full range of audible frequencies. Moreover, the minimal distortion characteristic of the circuit ensures that the audio output remains true to the original recording, without any unwanted alterations or colorations.
The circuit's strong performance in handling high frequency transients, due to the passive equalization in the 1 to 20KHz range, is a key factor in its ability to deliver a high-quality audio output. This ensures that the audio signal remains stable and consistent, even when dealing with complex or demanding audio material.
The final element of the circuit, the transistors and associated components, provide a ± 18V supply to the op-amp. This not only improves the headroom, allowing for greater dynamic range in the audio signal, but also enhances the maximum output voltage, ensuring that the circuit can deliver a powerful audio output when required.In recent years, following CD`s introduction, vinyl recordings are almost disappeared. Nevertheless, a phone preamplifier is still useful for listening old vinyl discs from a well preserved collection. This simple but efficient circuit devised for cheap moving-magnet cartridges, can be used in connection with both audio power amplifiers shown in preceding pages, featuring low noise, good RIAA frequency response curve, low distortion and good high frequency transients behavior due to passive equalization in the 1 to 20KHz range.
Transistors and associated components provide ± 18V supply to the op-amp, improving headroom and maximum output voltage. 🔗 External reference
Expanding on this, the circuit's efficiency is largely due to its simple design, which includes a phono preamplifier that is adept at handling the demands of older vinyl records. The moving-magnet cartridges, which are a popular choice due to their affordability, contribute to the overall effectiveness of the circuit. This is particularly true when the circuit is used in conjunction with audio power amplifiers, as the description suggests.
The low noise characteristic of the circuit ensures a clean, clear audio output, free from unwanted interference. This is complemented by the accurate RIAA frequency response curve which ensures a faithful reproduction of the audio signal across the full range of audible frequencies. Moreover, the minimal distortion characteristic of the circuit ensures that the audio output remains true to the original recording, without any unwanted alterations or colorations.
The circuit's strong performance in handling high frequency transients, due to the passive equalization in the 1 to 20KHz range, is a key factor in its ability to deliver a high-quality audio output. This ensures that the audio signal remains stable and consistent, even when dealing with complex or demanding audio material.
The final element of the circuit, the transistors and associated components, provide a ± 18V supply to the op-amp. This not only improves the headroom, allowing for greater dynamic range in the audio signal, but also enhances the maximum output voltage, ensuring that the circuit can deliver a powerful audio output when required.In recent years, following CD`s introduction, vinyl recordings are almost disappeared. Nevertheless, a phone preamplifier is still useful for listening old vinyl discs from a well preserved collection. This simple but efficient circuit devised for cheap moving-magnet cartridges, can be used in connection with both audio power amplifiers shown in preceding pages, featuring low noise, good RIAA frequency response curve, low distortion and good high frequency transients behavior due to passive equalization in the 1 to 20KHz range.
Transistors and associated components provide ± 18V supply to the op-amp, improving headroom and maximum output voltage. 🔗 External reference