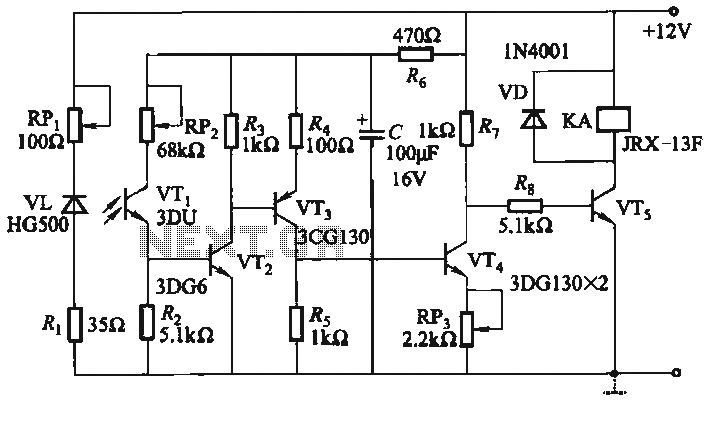
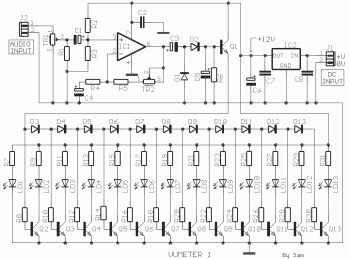
Photomultiplier Circuit Circuit
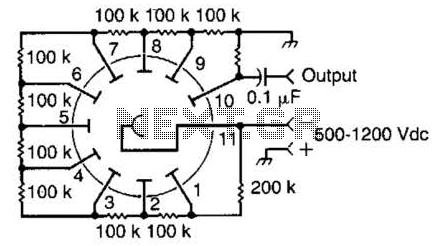
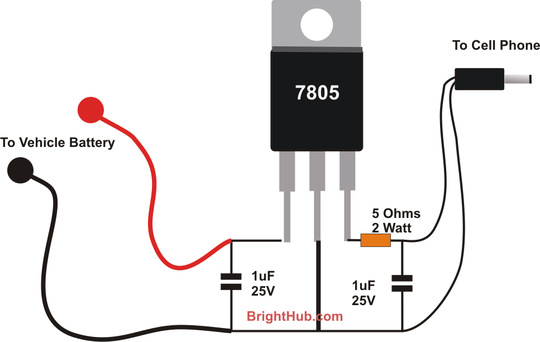
This circuit is representative of the typical application of a photomultiplier tube. The circuit depicted is AC coupled; however, if DC coupling is required, the capacitor can be removed, and an appropriate interfacing method should be employed. A common example of such a tube is the widely accessible 931/931A model.
The described circuit utilizes a photomultiplier tube (PMT), which is a highly sensitive device capable of detecting low levels of light. The PMT amplifies the signal produced by incident photons through a process of photoelectric effect and secondary emission, making it suitable for applications in fields such as scientific research, medical imaging, and radiation detection.
In the AC coupled configuration, the coupling capacitor serves to block any DC component of the signal, allowing only the AC variations (representing the light signal) to pass through. This arrangement is beneficial in applications where the DC offset might interfere with the measurement or processing of the signal. If the application requires DC coupling, the capacitor can be omitted, allowing both AC and DC components of the signal to be transmitted. This may be important in scenarios where the baseline light level needs to be monitored.
The 931/931A photomultiplier tube is a popular choice due to its availability and performance characteristics. It typically features a high gain and a fast response time, making it suitable for detecting fast light pulses. The specifications of the tube, including its dark current, quantum efficiency, and maximum count rate, should be considered when designing the circuit to ensure optimal performance for the intended application.
In designing the circuit, attention should also be paid to the power supply requirements of the PMT, as it often operates at high voltages. Proper decoupling and filtering techniques should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation. Additionally, the output stage of the circuit may include amplification and filtering components to further process the signal before it is sent to subsequent stages, such as data acquisition systems or analog-to-digital converters.
Overall, the design of the circuit incorporating a photomultiplier tube like the 931/931A requires careful consideration of coupling methods, signal processing, and power supply requirements to achieve the desired performance in light detection applications. This circuit is typical of the way that a photomultiplier tube is used. The circuit shown is ac coupled, but if dc coupling is needed, the capacitor can be omitted and a suitable interfacing method used. A typical tube is the widely available 931/931A. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a photomultiplier tube (PMT), which is a highly sensitive device capable of detecting low levels of light. The PMT amplifies the signal produced by incident photons through a process of photoelectric effect and secondary emission, making it suitable for applications in fields such as scientific research, medical imaging, and radiation detection.
In the AC coupled configuration, the coupling capacitor serves to block any DC component of the signal, allowing only the AC variations (representing the light signal) to pass through. This arrangement is beneficial in applications where the DC offset might interfere with the measurement or processing of the signal. If the application requires DC coupling, the capacitor can be omitted, allowing both AC and DC components of the signal to be transmitted. This may be important in scenarios where the baseline light level needs to be monitored.
The 931/931A photomultiplier tube is a popular choice due to its availability and performance characteristics. It typically features a high gain and a fast response time, making it suitable for detecting fast light pulses. The specifications of the tube, including its dark current, quantum efficiency, and maximum count rate, should be considered when designing the circuit to ensure optimal performance for the intended application.
In designing the circuit, attention should also be paid to the power supply requirements of the PMT, as it often operates at high voltages. Proper decoupling and filtering techniques should be implemented to minimize noise and ensure stable operation. Additionally, the output stage of the circuit may include amplification and filtering components to further process the signal before it is sent to subsequent stages, such as data acquisition systems or analog-to-digital converters.
Overall, the design of the circuit incorporating a photomultiplier tube like the 931/931A requires careful consideration of coupling methods, signal processing, and power supply requirements to achieve the desired performance in light detection applications. This circuit is typical of the way that a photomultiplier tube is used. The circuit shown is ac coupled, but if dc coupling is needed, the capacitor can be omitted and a suitable interfacing method used. A typical tube is the widely available 931/931A. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713