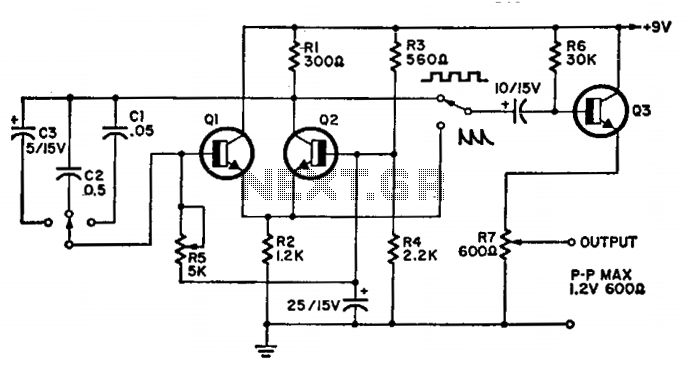
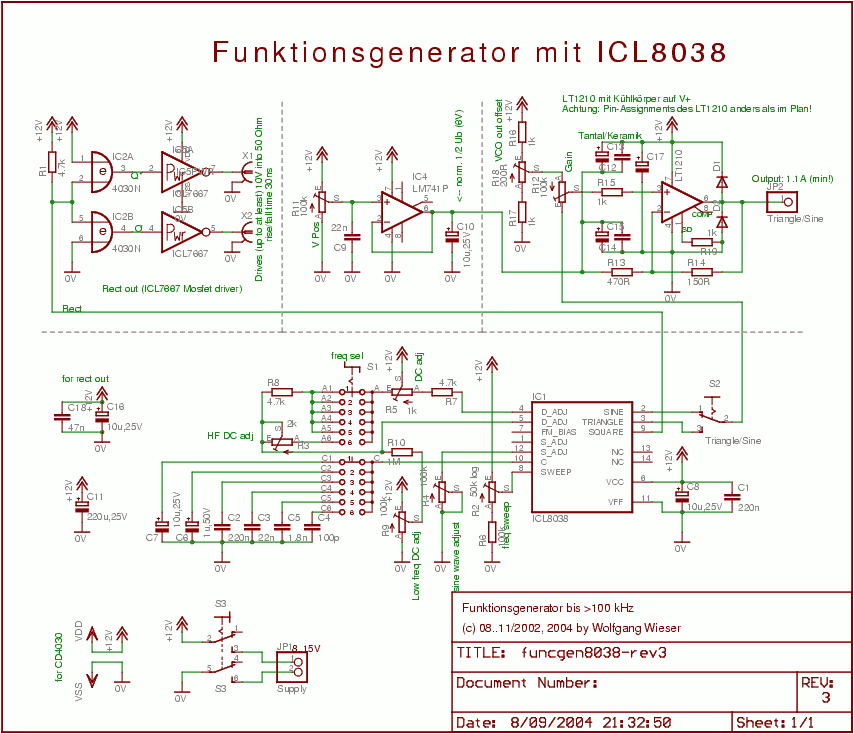
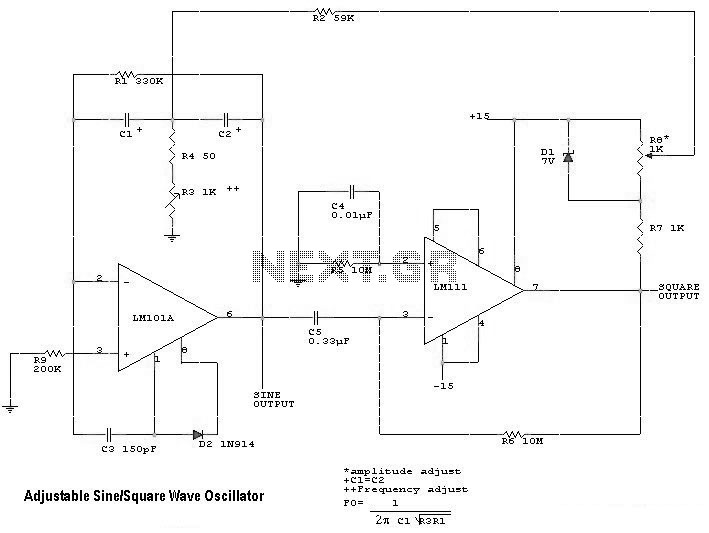
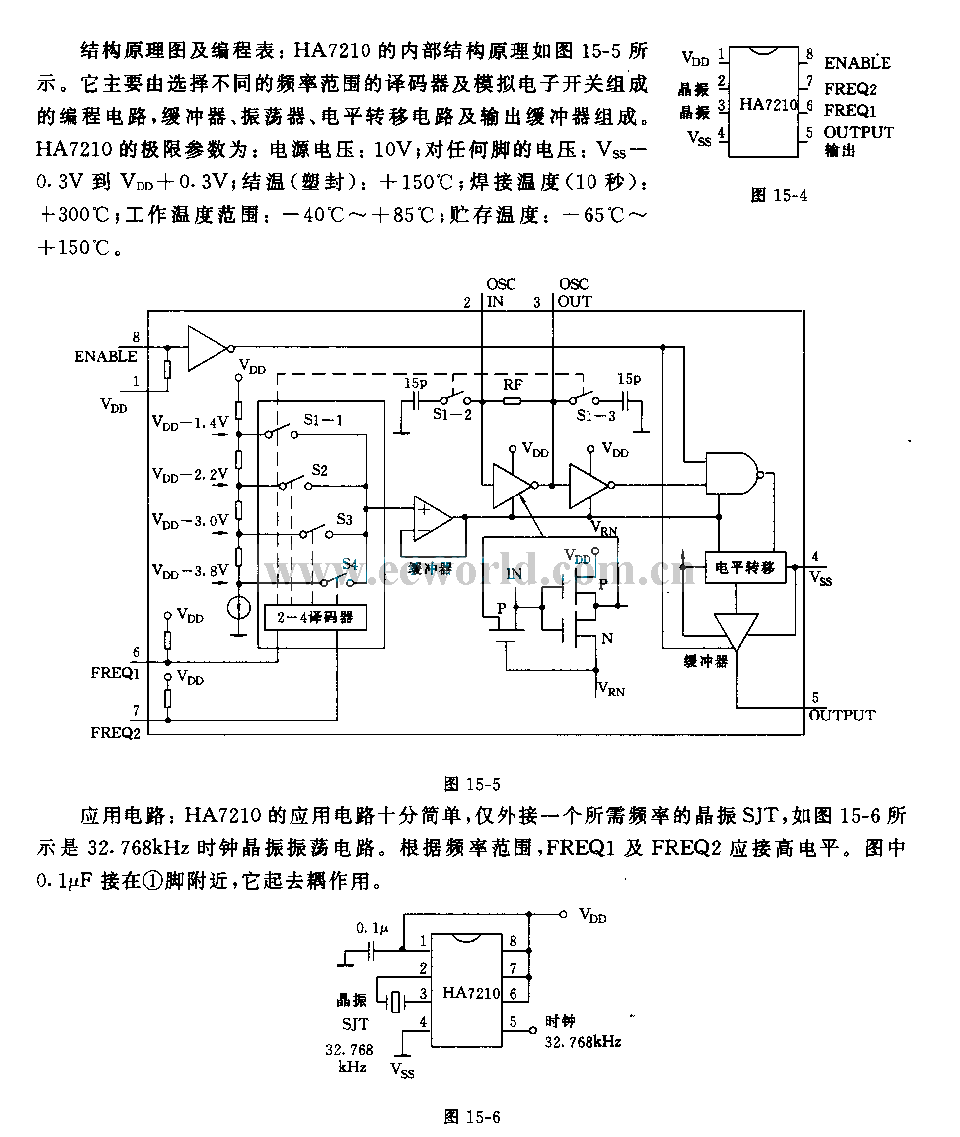
Pierce-gate oscillator crystal load calculation
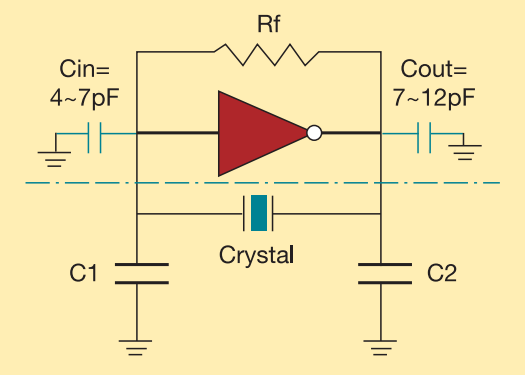
The crystal used in the topology of Figure 1 can be either a fundamental AT-CUT or BT-CUT. A BT-CUT crystal has poor frequency stability over temperature compared to an AT-CUT. This topology uses a parallel crystal and not a series crystal.
The circuit topology described involves the use of a parallel crystal oscillator configuration, which is essential for generating stable frequency signals in various electronic applications. The choice between an AT-CUT and BT-CUT crystal is critical, as it directly influences the oscillator's performance characteristics, particularly in terms of frequency stability over temperature variations.
AT-CUT crystals are known for their superior temperature stability, making them suitable for precision applications where frequency accuracy is paramount. These crystals utilize a specific cut of quartz that minimizes the effects of temperature changes on the oscillation frequency, resulting in a more reliable performance in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
In contrast, BT-CUT crystals exhibit poorer frequency stability, which may limit their effectiveness in applications requiring high precision. However, they may still be suitable for less critical applications where cost considerations are more significant than frequency accuracy.
The parallel crystal configuration allows the crystal to be connected in parallel with the load capacitance, which can enhance the oscillator's performance by providing a lower equivalent series resistance (ESR). This configuration also enables the circuit to benefit from the inherent characteristics of the crystal, such as its resonant frequency and quality factor (Q), which are crucial for determining the oscillator's output signal integrity.
In summary, the choice of crystal type and oscillator configuration plays a significant role in the design of frequency generation circuits. The described topology effectively utilizes the advantages of a parallel crystal arrangement to achieve desired performance metrics while considering the thermal stability characteristics of the selected crystal type.The crystal used in the topology of Figure 1 can be either a fundamental AT-CUT or BT-CUT. A BT-CUT crystal has poor frequency stability over temperature compared to an AT-CUT. This topology uses a parallel crystal and not a series crystal. 🔗 External reference
The circuit topology described involves the use of a parallel crystal oscillator configuration, which is essential for generating stable frequency signals in various electronic applications. The choice between an AT-CUT and BT-CUT crystal is critical, as it directly influences the oscillator's performance characteristics, particularly in terms of frequency stability over temperature variations.
AT-CUT crystals are known for their superior temperature stability, making them suitable for precision applications where frequency accuracy is paramount. These crystals utilize a specific cut of quartz that minimizes the effects of temperature changes on the oscillation frequency, resulting in a more reliable performance in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
In contrast, BT-CUT crystals exhibit poorer frequency stability, which may limit their effectiveness in applications requiring high precision. However, they may still be suitable for less critical applications where cost considerations are more significant than frequency accuracy.
The parallel crystal configuration allows the crystal to be connected in parallel with the load capacitance, which can enhance the oscillator's performance by providing a lower equivalent series resistance (ESR). This configuration also enables the circuit to benefit from the inherent characteristics of the crystal, such as its resonant frequency and quality factor (Q), which are crucial for determining the oscillator's output signal integrity.
In summary, the choice of crystal type and oscillator configuration plays a significant role in the design of frequency generation circuits. The described topology effectively utilizes the advantages of a parallel crystal arrangement to achieve desired performance metrics while considering the thermal stability characteristics of the selected crystal type.The crystal used in the topology of Figure 1 can be either a fundamental AT-CUT or BT-CUT. A BT-CUT crystal has poor frequency stability over temperature compared to an AT-CUT. This topology uses a parallel crystal and not a series crystal. 🔗 External reference