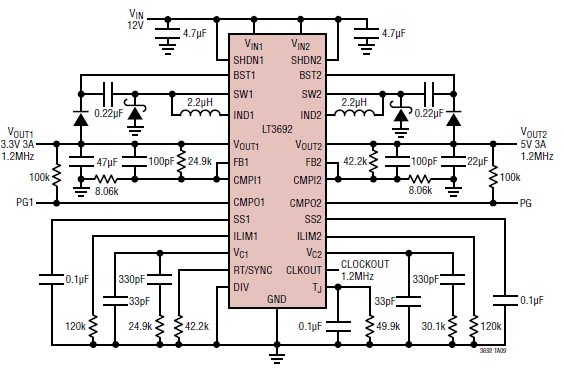
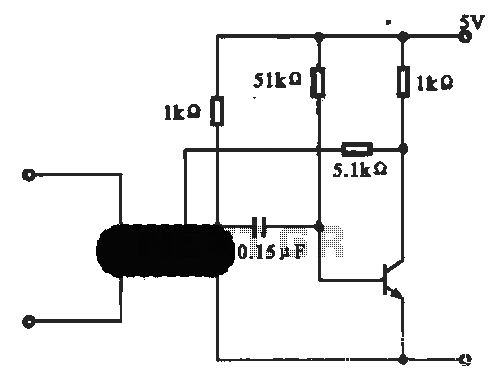
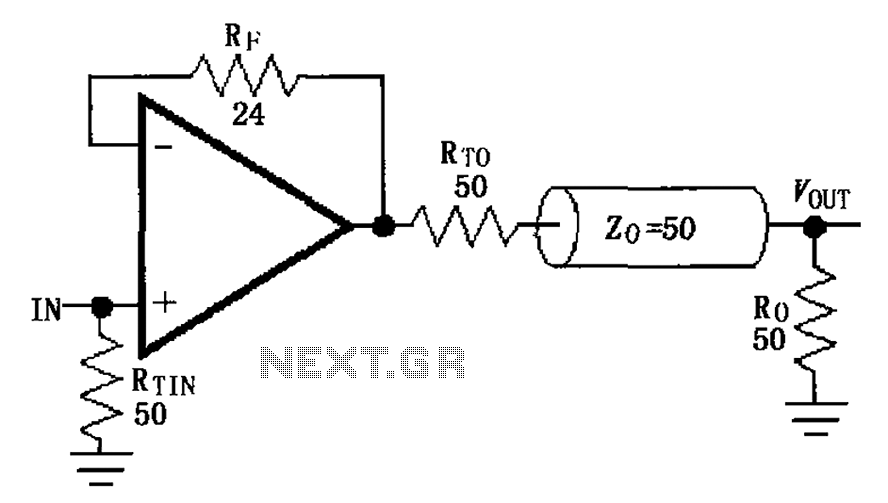
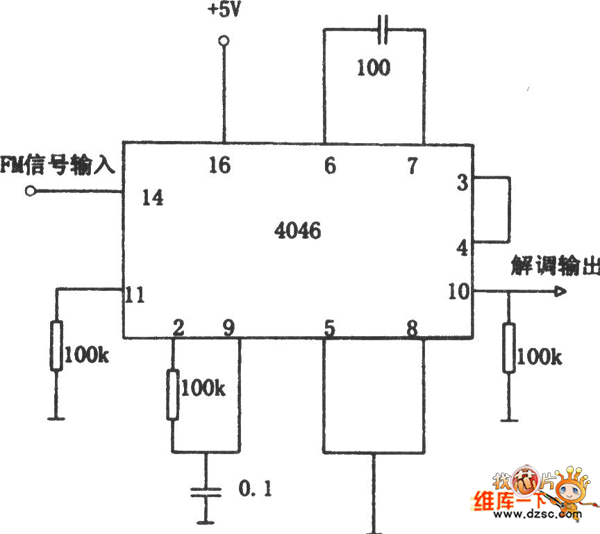
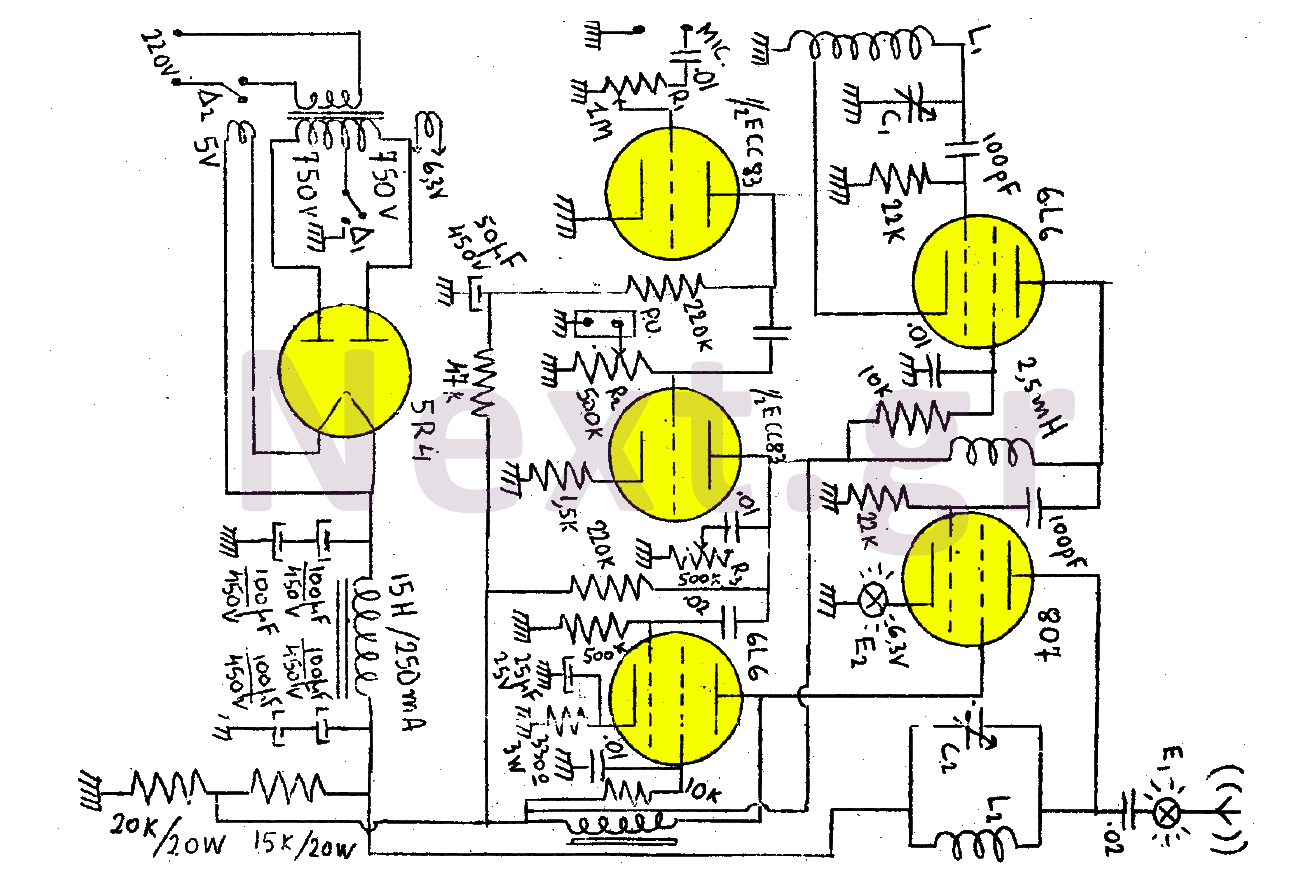
Polarity Gain Adjustment Circuit
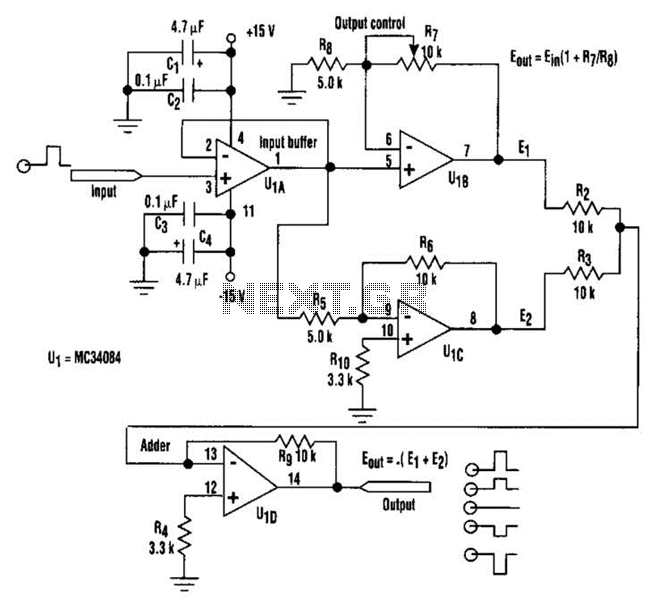
By adjusting one potentiometer, the output of this circuit can be varied from a positive version of the input signal, smoothly transitioning through zero output, and then to a negative version of the input. For instance, if the input signal is a positive pulse with a peak of +2 V, the output pulse amplitude can be smoothly adjusted from +2 V through ground (no output) to -2 V peak. In this configuration, assuming a +2 V peak input signal, the A section of the quad operational amplifier (op amp) acts as an input buffer, while op amp 0 provides a fixed negative output of -4 V peak. Another op amp provides a positive output that varies from +2 V to +6 V peak. The D section combines the outputs from the C and D sections. Consequently, by varying the output, the circuit output transitions smoothly from -2 V to +2 V peak. This circuit can also function as a phase switcher, such as the 07180. For example, with a ground-centered sine wave input of 4 V peak-to-peak, the output can vary from 4 V peak-to-peak in phase with the input, smoothly transitioning through 0 V, to 4 V peak-to-peak that is 180 degrees out of phase with the input.
The described circuit utilizes a quad operational amplifier configuration, which allows for versatile signal manipulation. The input buffer provided by the A section ensures that the input signal is isolated from the subsequent processing stages, preventing loading effects that could distort the signal. The fixed negative output of -4 V from op amp 0 serves as a reference point for the output variations, while the adjustable output from the other op amp allows for fine-tuning of the signal range.
The ability to vary the output from +2 V to +6 V peak enables a wide range of applications, particularly in audio and signal processing where phase and amplitude control are crucial. The D section's function of summing the outputs from the C and D sections facilitates the smooth transition of the output voltage, making it suitable for applications requiring precise control over the output signal's amplitude and phase.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in audio systems to create effects such as amplitude modulation or dynamic range compression, where the output signal needs to be carefully adjusted in relation to the input. Additionally, the capability to switch the phase of the output signal makes this circuit useful in applications such as phase-sensitive detection, where the relationship between input and output phases is critical for signal integrity and processing accuracy. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a flexible and effective approach to signal modulation using operational amplifiers. By adjusting one potentiometer, this circuit`s output can be varied from a positive-going version of the input signal, smoothly through zero output, then to a negative-going version of the input (see the figure). If the input signal is a positive pulse of, for example, +2-V peak/the output pulse amplitude can be smoothly varied from +2-V through ground (no output) to a -2-V peak.
Taking a closer look at the setup, assume that the signal has a +2-V peak input. The A section of the quad op amp is an input buffer, op amp 0 provides a fixed negative-going output of -4-V peak, and op amp supplies a positive-going output that varies from +2-V to +6-V peak. The D section adds the and C outputs. Thus, by varying the output, the circuit output varies smoothly from -2-V to +2-V peak. The circuit can, of course, also be used as a 07180 phase switcher. For instance, with a ground-centered sine-wave input of 4V p-p, the output varies from 4-V p-p in phase with the input, smoothly through 0 V, to 4V p-p 180 out of phase with the input. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a quad operational amplifier configuration, which allows for versatile signal manipulation. The input buffer provided by the A section ensures that the input signal is isolated from the subsequent processing stages, preventing loading effects that could distort the signal. The fixed negative output of -4 V from op amp 0 serves as a reference point for the output variations, while the adjustable output from the other op amp allows for fine-tuning of the signal range.
The ability to vary the output from +2 V to +6 V peak enables a wide range of applications, particularly in audio and signal processing where phase and amplitude control are crucial. The D section's function of summing the outputs from the C and D sections facilitates the smooth transition of the output voltage, making it suitable for applications requiring precise control over the output signal's amplitude and phase.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in audio systems to create effects such as amplitude modulation or dynamic range compression, where the output signal needs to be carefully adjusted in relation to the input. Additionally, the capability to switch the phase of the output signal makes this circuit useful in applications such as phase-sensitive detection, where the relationship between input and output phases is critical for signal integrity and processing accuracy. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a flexible and effective approach to signal modulation using operational amplifiers. By adjusting one potentiometer, this circuit`s output can be varied from a positive-going version of the input signal, smoothly through zero output, then to a negative-going version of the input (see the figure). If the input signal is a positive pulse of, for example, +2-V peak/the output pulse amplitude can be smoothly varied from +2-V through ground (no output) to a -2-V peak.
Taking a closer look at the setup, assume that the signal has a +2-V peak input. The A section of the quad op amp is an input buffer, op amp 0 provides a fixed negative-going output of -4-V peak, and op amp supplies a positive-going output that varies from +2-V to +6-V peak. The D section adds the and C outputs. Thus, by varying the output, the circuit output varies smoothly from -2-V to +2-V peak. The circuit can, of course, also be used as a 07180 phase switcher. For instance, with a ground-centered sine-wave input of 4V p-p, the output varies from 4-V p-p in phase with the input, smoothly through 0 V, to 4V p-p 180 out of phase with the input. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713