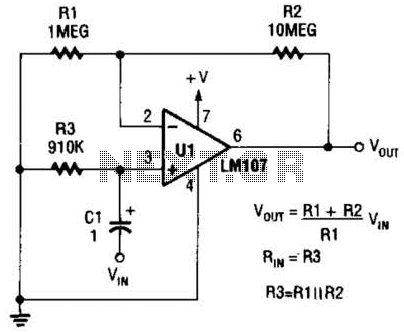
power amplifier speaker protection
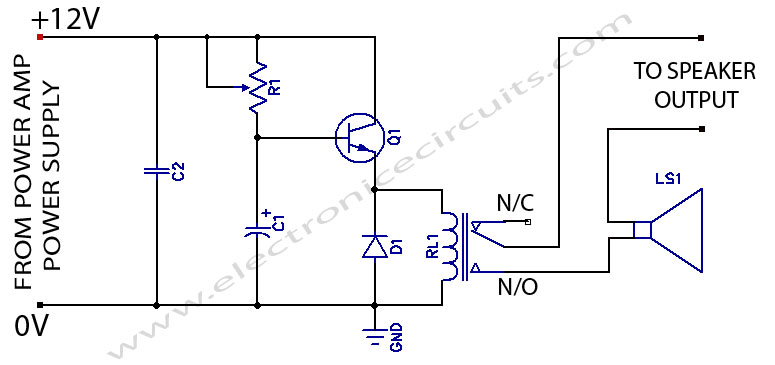
When powering on a power amplifier, a loud thump sound occurs due to a sudden heavy discharge current through the speaker. This current has the potential to damage the speaker, particularly in the case of a direct-coupled amplifier.
The phenomenon described is commonly referred to as "turn-on thump," which is a transient noise generated during the power-up sequence of audio amplifiers. This noise is primarily caused by the rapid charging of coupling capacitors or the sudden application of power to the amplifier's output stage, leading to an immediate surge of current that can drive the speaker cone to its limits.
In direct-coupled amplifiers, where there are no capacitive coupling elements between the output stage and the speaker, the risk of speaker damage is heightened. The absence of capacitors means that any DC offset present at the output can directly affect the speaker, potentially leading to overheating or physical damage if the output stage is not properly controlled during power-up.
To mitigate this issue, several design strategies can be employed. Implementing a soft-start circuit can help in gradually ramping up the power supply to the amplifier, thus reducing the initial surge current. Additionally, incorporating a relay-based speaker protection circuit can disconnect the speaker during the initial power-up phase and reconnect it only after the amplifier has stabilized. This not only protects the speaker from damaging transients but also enhances overall system reliability.
Furthermore, using a delay circuit that monitors the amplifier's output can ensure that the speaker is only connected once the output is stable and free from DC offsets. This can be achieved through a combination of time-delay relays and sensing circuits that detect the presence of DC voltage at the output.
In conclusion, careful consideration of the power-up sequence and the implementation of protective measures can significantly reduce the risk of speaker damage due to turn-on thump in power amplifier designs.While switching a power amplifier on, a loud thump sound is heard to sudden heavy discharge current through the speaker at the time of power on. This current may damage the speaker, especially in case of direct coupled amplifier. 🔗 External reference
The phenomenon described is commonly referred to as "turn-on thump," which is a transient noise generated during the power-up sequence of audio amplifiers. This noise is primarily caused by the rapid charging of coupling capacitors or the sudden application of power to the amplifier's output stage, leading to an immediate surge of current that can drive the speaker cone to its limits.
In direct-coupled amplifiers, where there are no capacitive coupling elements between the output stage and the speaker, the risk of speaker damage is heightened. The absence of capacitors means that any DC offset present at the output can directly affect the speaker, potentially leading to overheating or physical damage if the output stage is not properly controlled during power-up.
To mitigate this issue, several design strategies can be employed. Implementing a soft-start circuit can help in gradually ramping up the power supply to the amplifier, thus reducing the initial surge current. Additionally, incorporating a relay-based speaker protection circuit can disconnect the speaker during the initial power-up phase and reconnect it only after the amplifier has stabilized. This not only protects the speaker from damaging transients but also enhances overall system reliability.
Furthermore, using a delay circuit that monitors the amplifier's output can ensure that the speaker is only connected once the output is stable and free from DC offsets. This can be achieved through a combination of time-delay relays and sensing circuits that detect the presence of DC voltage at the output.
In conclusion, careful consideration of the power-up sequence and the implementation of protective measures can significantly reduce the risk of speaker damage due to turn-on thump in power amplifier designs.While switching a power amplifier on, a loud thump sound is heard to sudden heavy discharge current through the speaker at the time of power on. This current may damage the speaker, especially in case of direct coupled amplifier. 🔗 External reference