power Problem with high voltage in a project
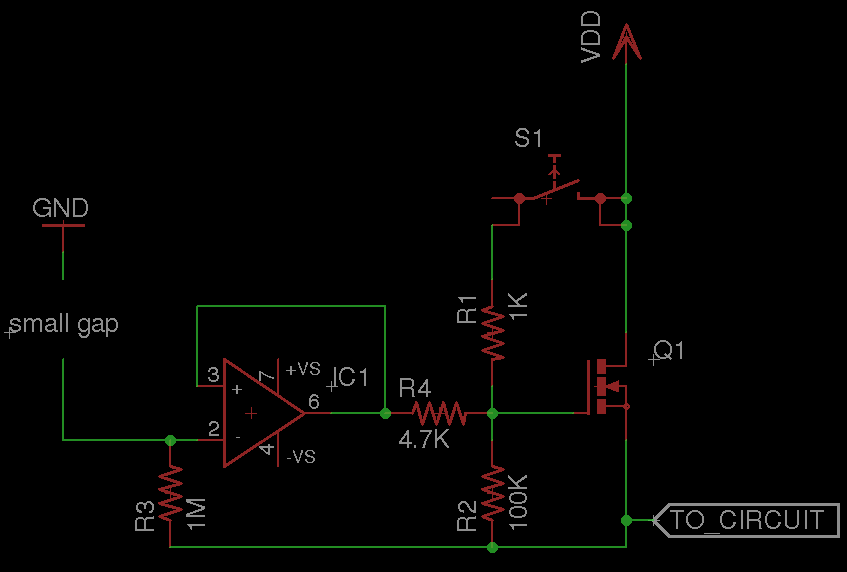
A circuit that requires protection from high voltage. Is there a component other than a fuse that does not need to be replaced every time? Something like a switch that activates only when high voltage is supplied, diverts the flow, grounds it, and then closes. There is a triac connected to a submersible motor via a microcontroller IC mounted on a printed circuit board assembly. The issue is that there are occasional short circuits due to water, which have already damaged the circuit twice. Is an optocoupler or solid-state relay advisable for isolation? Additional information is needed regarding the voltage and duration. A schematic would greatly help in understanding the requirements. There is a significant difference between protecting against static discharge and a direct lightning strike, requiring different solutions. It is also unclear whether the protection is needed against high currents caused by shorts within the submerged equipment or against high voltages from a short circuit between a higher-voltage input power wire and internal nodes. For high currents, polyfuses (resettable fuses) may be suitable, while for high voltages, zener diodes and transorbs could be considered. The proposed circuit includes an input power MOSFET that controls the power flow to the circuit. A button press raises the gate voltage, allowing power to flow. The circuit assumes a shared ground and includes a physical gap; if water connects ground and the wire from the op-amp, the op-amp outputs low, resulting in power loss. This circuit is a starting point and should serve as a general guide.
To protect the circuit from high voltage and high current conditions, several approaches can be considered. The use of a triac in conjunction with a microcontroller can facilitate control over the submersible motor while providing a means of protection against over-voltage situations. A voltage sensing circuit can be designed to monitor the input voltage and trigger a protective response when high voltage is detected. This can be achieved using a voltage divider and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) within the microcontroller to continuously monitor the voltage levels.
When high voltage is detected, the microcontroller can activate a solid-state relay or an optocoupler to disconnect the power supply to the triac and motor, effectively isolating the sensitive components from the high voltage. The solid-state relay offers fast switching capabilities and can handle high currents, making it suitable for this application. Additionally, the use of a zener diode across the input can provide clamping protection against voltage spikes, while transorbs can be used for transient voltage suppression.
For short-circuit protection, incorporating a polyfuse in series with the motor circuit can provide a resettable solution. Polyfuses automatically reset after the fault condition is removed, eliminating the need for manual replacement. This is particularly advantageous in environments prone to water ingress, as it reduces maintenance requirements.
To enhance the reliability of the circuit, a physical barrier should be implemented to prevent water from bridging connections on the PCB. Conformal coating can also be applied to protect the circuit from moisture and corrosion. Additionally, the circuit layout should consider proper spacing and insulation between high-voltage and low-voltage components to minimize the risk of accidental shorts.
In summary, a combination of solid-state relays, polyfuses, zener diodes, and transorbs, along with careful circuit design and environmental protection measures, can create a robust system capable of withstanding high voltage and current conditions in a submersible application.A circuit that should be protected from high voltage. Is there any component other than a fuse that I don`t have to change every time Something like a switch that activates only when high voltage is supplied, diverts the flow and grounds it, and then closes. Sorry, I can`t scan the schematic right now but I can give you information. I have a triac connected to a submersible motor via a MCU IC mounted on PCBA. The problem is sometimes there is a short circuit due to water. I want to know how to protect the circuit in this case as I already have fried it twice. Is an optocoupler or solid state relay advisable for isolation We`re going to need a LOT more information. What voltage What duration A schematic would go a very long way to showing us what you want. There is a huge difference between a static discharge and a direct lightning strike, and different solutions.
user3624 Dec 19 `12 at 5:21 Still not very clear. Are you trying to protect from high currents (caused by shorts within your submerged equipment) or from high voltages (maybe caused by a short circuit between a higher-voltage input power wire and internal nodes) The Photon Dec 19 `12 at 5:34 In case you`re protecting from high currents, do you know about polyfuses (resettable fuses) In case of protecting from high voltages, do you know about zener diodes and transorbs The Photon Dec 19 `12 at 5:36 So essentially, the idea is that there is an input power mosfet which controls the flow of power to your circuit. You push a button, which causes the gate voltage to rise, and power flows to your circuit. "VDD" in this diagram is the battery positive rail. Ground is assumed to be available and shared all over this circuit. The "small gap" is a physical one. If water connects ground and the wire coming off of that op-amp, then the op-amp will output low, and you`ll suddenly lose power.
Now this circuit needs a lot of things, it`s only meant to be the beginnings of a circuit that you could use. But it should push you in the right general direction. The robotics team I was on built an underwater vehicle and I can tell you for a fact that the idea behind this circuit is tried and true.
the schematic I have for that part of the craft though was a bit more complex because it was dealing with a lot of other parts, so you get the simplified but incomplete version for now! 🔗 External reference
To protect the circuit from high voltage and high current conditions, several approaches can be considered. The use of a triac in conjunction with a microcontroller can facilitate control over the submersible motor while providing a means of protection against over-voltage situations. A voltage sensing circuit can be designed to monitor the input voltage and trigger a protective response when high voltage is detected. This can be achieved using a voltage divider and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) within the microcontroller to continuously monitor the voltage levels.
When high voltage is detected, the microcontroller can activate a solid-state relay or an optocoupler to disconnect the power supply to the triac and motor, effectively isolating the sensitive components from the high voltage. The solid-state relay offers fast switching capabilities and can handle high currents, making it suitable for this application. Additionally, the use of a zener diode across the input can provide clamping protection against voltage spikes, while transorbs can be used for transient voltage suppression.
For short-circuit protection, incorporating a polyfuse in series with the motor circuit can provide a resettable solution. Polyfuses automatically reset after the fault condition is removed, eliminating the need for manual replacement. This is particularly advantageous in environments prone to water ingress, as it reduces maintenance requirements.
To enhance the reliability of the circuit, a physical barrier should be implemented to prevent water from bridging connections on the PCB. Conformal coating can also be applied to protect the circuit from moisture and corrosion. Additionally, the circuit layout should consider proper spacing and insulation between high-voltage and low-voltage components to minimize the risk of accidental shorts.
In summary, a combination of solid-state relays, polyfuses, zener diodes, and transorbs, along with careful circuit design and environmental protection measures, can create a robust system capable of withstanding high voltage and current conditions in a submersible application.A circuit that should be protected from high voltage. Is there any component other than a fuse that I don`t have to change every time Something like a switch that activates only when high voltage is supplied, diverts the flow and grounds it, and then closes. Sorry, I can`t scan the schematic right now but I can give you information. I have a triac connected to a submersible motor via a MCU IC mounted on PCBA. The problem is sometimes there is a short circuit due to water. I want to know how to protect the circuit in this case as I already have fried it twice. Is an optocoupler or solid state relay advisable for isolation We`re going to need a LOT more information. What voltage What duration A schematic would go a very long way to showing us what you want. There is a huge difference between a static discharge and a direct lightning strike, and different solutions.
user3624 Dec 19 `12 at 5:21 Still not very clear. Are you trying to protect from high currents (caused by shorts within your submerged equipment) or from high voltages (maybe caused by a short circuit between a higher-voltage input power wire and internal nodes) The Photon Dec 19 `12 at 5:34 In case you`re protecting from high currents, do you know about polyfuses (resettable fuses) In case of protecting from high voltages, do you know about zener diodes and transorbs The Photon Dec 19 `12 at 5:36 So essentially, the idea is that there is an input power mosfet which controls the flow of power to your circuit. You push a button, which causes the gate voltage to rise, and power flows to your circuit. "VDD" in this diagram is the battery positive rail. Ground is assumed to be available and shared all over this circuit. The "small gap" is a physical one. If water connects ground and the wire coming off of that op-amp, then the op-amp will output low, and you`ll suddenly lose power.
Now this circuit needs a lot of things, it`s only meant to be the beginnings of a circuit that you could use. But it should push you in the right general direction. The robotics team I was on built an underwater vehicle and I can tell you for a fact that the idea behind this circuit is tried and true.
the schematic I have for that part of the craft though was a bit more complex because it was dealing with a lot of other parts, so you get the simplified but incomplete version for now! 🔗 External reference