power supply design
The more one understands about any subject, the more interesting it becomes. As this article is read, it will be found that the subject of...
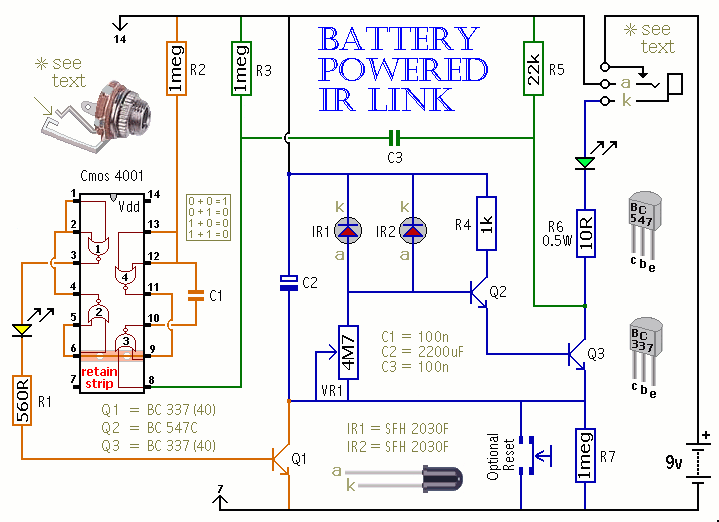
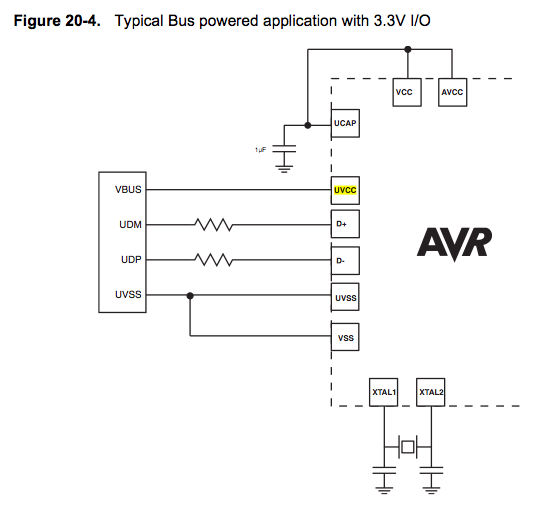
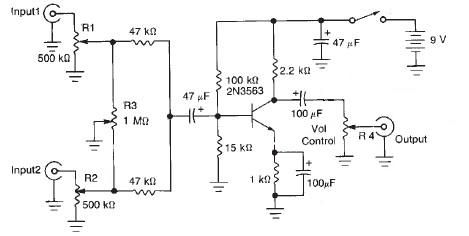
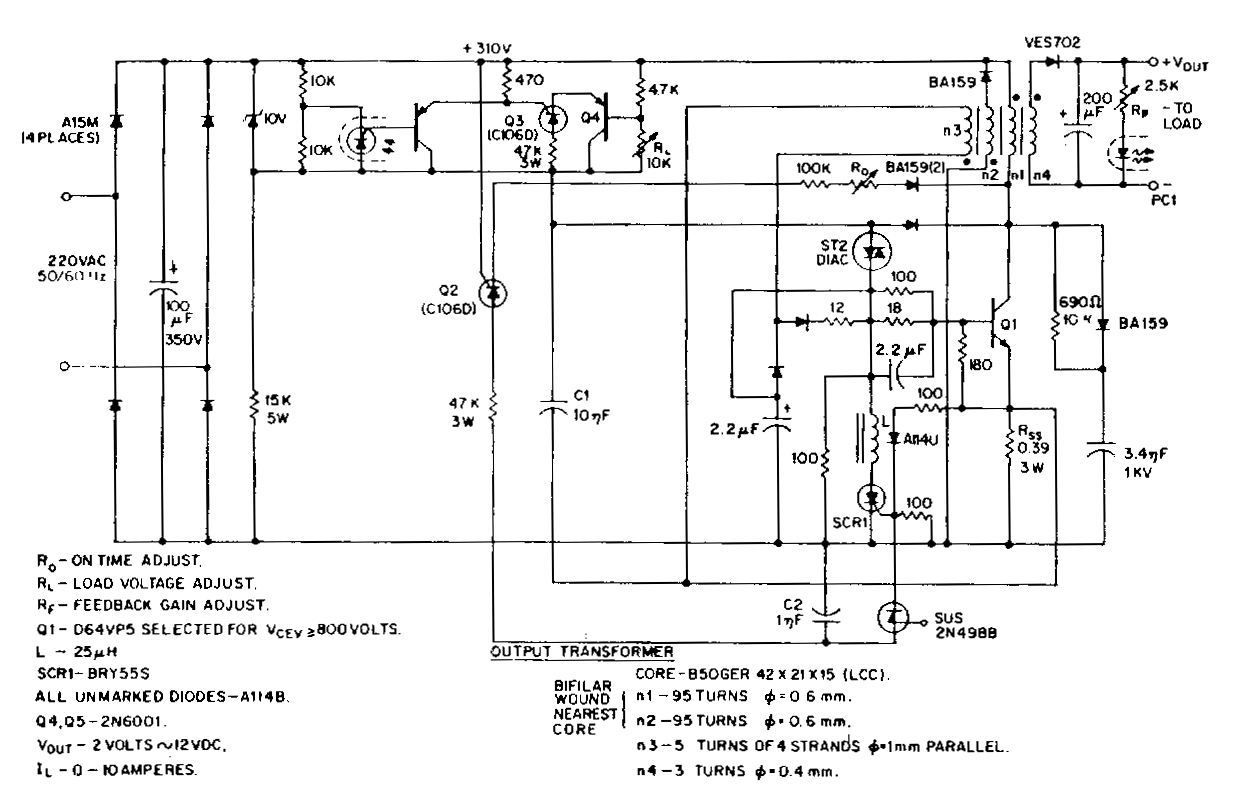
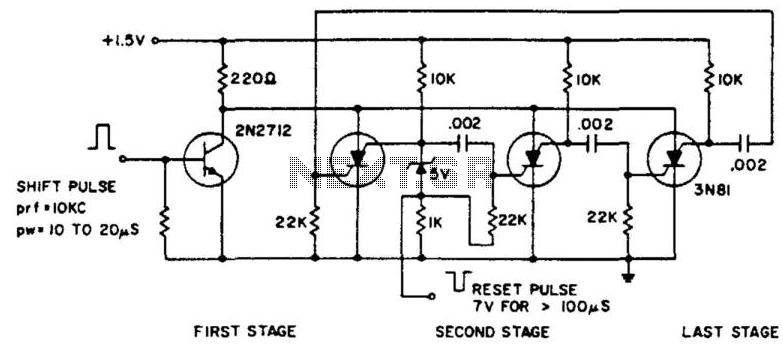
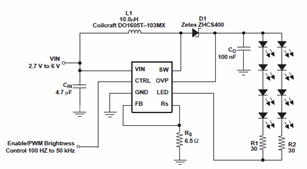
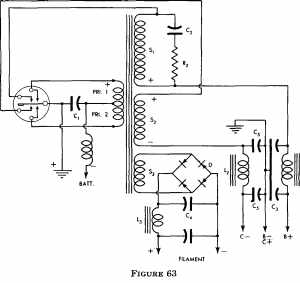
A comprehensive electronic schematic typically involves various components, each serving a specific function in the overall circuit design. In a basic schematic, elements such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and transistors are represented by standardized symbols. Each component is connected by lines, which represent the electrical connections between them.
Resistors are used to limit current flow and divide voltages, while capacitors store and release electrical energy, often used for filtering applications. Inductors, on the other hand, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through them. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only, providing rectification in power supply circuits. Transistors function as switches or amplifiers, controlling the flow of current in a circuit.
Power sources, such as batteries or power supplies, are typically indicated in a schematic, providing the necessary voltage and current for the circuit to operate. Ground connections are also crucial, serving as a reference point for voltage levels in the circuit.
In addition to these components, a well-designed schematic may include labels for each part, values for components (like resistance in ohms or capacitance in farads), and notes on the operation of the circuit. This information aids in understanding the functionality and interconnections of the circuit, facilitating troubleshooting, and further development.
Overall, a detailed electronic schematic serves as a vital tool for engineers, allowing for the effective design, analysis, and implementation of electronic systems.Hello world!, The more you understand about any subject, the more interesting it becomes. As you read this article you`ll find that the subject of.. 🔗 External reference
A comprehensive electronic schematic typically involves various components, each serving a specific function in the overall circuit design. In a basic schematic, elements such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and transistors are represented by standardized symbols. Each component is connected by lines, which represent the electrical connections between them.
Resistors are used to limit current flow and divide voltages, while capacitors store and release electrical energy, often used for filtering applications. Inductors, on the other hand, store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through them. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only, providing rectification in power supply circuits. Transistors function as switches or amplifiers, controlling the flow of current in a circuit.
Power sources, such as batteries or power supplies, are typically indicated in a schematic, providing the necessary voltage and current for the circuit to operate. Ground connections are also crucial, serving as a reference point for voltage levels in the circuit.
In addition to these components, a well-designed schematic may include labels for each part, values for components (like resistance in ohms or capacitance in farads), and notes on the operation of the circuit. This information aids in understanding the functionality and interconnections of the circuit, facilitating troubleshooting, and further development.
Overall, a detailed electronic schematic serves as a vital tool for engineers, allowing for the effective design, analysis, and implementation of electronic systems.Hello world!, The more you understand about any subject, the more interesting it becomes. As you read this article you`ll find that the subject of.. 🔗 External reference