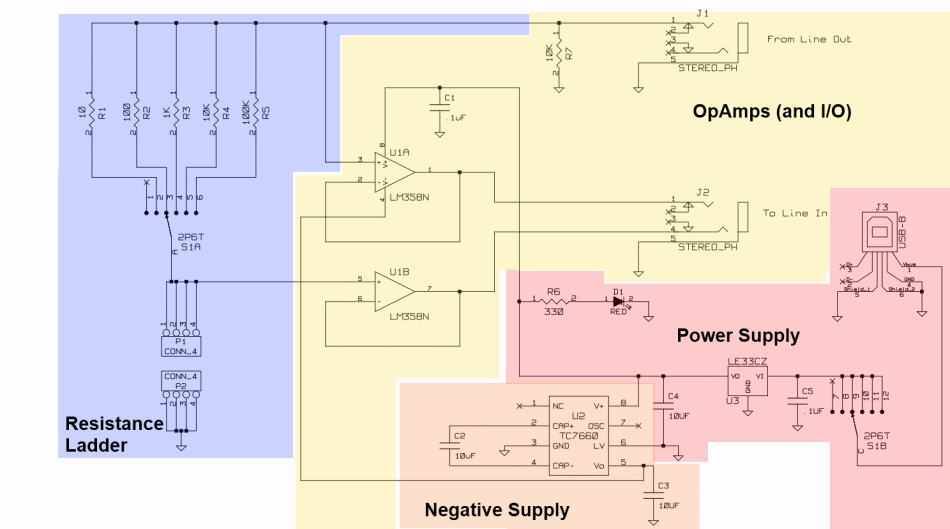
ATmega32u2 USB powered how to ground
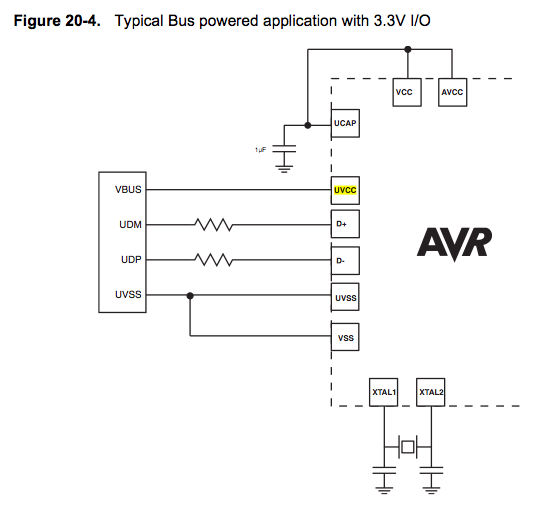
Since the microcontroller unit (MCU) is powered through USB, the common zero voltage should align with the supply voltage and thus be connected to the 0V (UVSS) line.
In electronic circuit design, it is essential to ensure that the ground reference points are consistent throughout the system. When powering a microcontroller unit (MCU) via a USB connection, the common ground (zero voltage reference) must be connected to the supply voltage ground. This is critical to prevent potential ground loops and ensure proper operation of the MCU.
The USB interface typically provides a power supply of 5V, which is the standard voltage level for many microcontrollers. The 0V line, also referred to as the UVSS line, serves as the reference point for all voltage levels in the circuit. Properly connecting the UVSS line to the common ground of the USB power supply ensures that the MCU can accurately interpret signal levels and operate reliably.
In practical implementation, the circuit should include bypass capacitors near the MCU power pins to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply. Additionally, careful routing of ground traces is necessary to minimize inductance and maintain a low-resistance path to ground. This layout consideration is vital for high-speed digital circuits, where signal integrity can be adversely affected by poor grounding practices.
Furthermore, it is advisable to include protection components such as diodes to safeguard the MCU from potential overvoltage conditions that may arise from the USB connection. This protection will enhance the robustness of the circuit, ensuring that the MCU remains functional even under unexpected electrical conditions.
Overall, maintaining a consistent ground reference by connecting the common zero voltage to the UVSS line is a fundamental practice in electronic circuit design, particularly when integrating USB-powered microcontrollers.Because you are powering the MCU via USB, this common zero voltage should be the same as the supply and therefore connected to the 0V (UVSS) line. 🔗 External reference
In electronic circuit design, it is essential to ensure that the ground reference points are consistent throughout the system. When powering a microcontroller unit (MCU) via a USB connection, the common ground (zero voltage reference) must be connected to the supply voltage ground. This is critical to prevent potential ground loops and ensure proper operation of the MCU.
The USB interface typically provides a power supply of 5V, which is the standard voltage level for many microcontrollers. The 0V line, also referred to as the UVSS line, serves as the reference point for all voltage levels in the circuit. Properly connecting the UVSS line to the common ground of the USB power supply ensures that the MCU can accurately interpret signal levels and operate reliably.
In practical implementation, the circuit should include bypass capacitors near the MCU power pins to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply. Additionally, careful routing of ground traces is necessary to minimize inductance and maintain a low-resistance path to ground. This layout consideration is vital for high-speed digital circuits, where signal integrity can be adversely affected by poor grounding practices.
Furthermore, it is advisable to include protection components such as diodes to safeguard the MCU from potential overvoltage conditions that may arise from the USB connection. This protection will enhance the robustness of the circuit, ensuring that the MCU remains functional even under unexpected electrical conditions.
Overall, maintaining a consistent ground reference by connecting the common zero voltage to the UVSS line is a fundamental practice in electronic circuit design, particularly when integrating USB-powered microcontrollers.Because you are powering the MCU via USB, this common zero voltage should be the same as the supply and therefore connected to the 0V (UVSS) line. 🔗 External reference