Precision Light-Activated Alarm Circuit
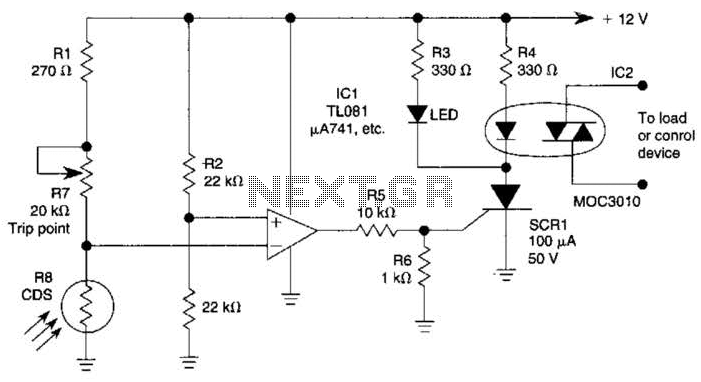
The light-sensitive CDS cell R8 is configured in a bridge circuit with IC1 functioning as a comparator. When light strikes the CDS cell R8, the output of IC1 goes high, triggering SCR1. This action illuminates LED1 and activates opto isolator IC2, which subsequently switches the load.
The circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (CDS cell R8) that changes its resistance based on the intensity of light it receives. In this configuration, R8 is part of a bridge circuit, which typically consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape. The bridge circuit is balanced under normal lighting conditions, and when light intensity changes, it causes an imbalance, resulting in a voltage difference that is detected by the comparator IC1.
IC1 compares the voltage across the bridge circuit to a reference voltage. When the light intensity exceeds a certain threshold, the voltage at one of the bridge's nodes rises above the reference level, causing the output of IC1 to transition to a high state. This output signal is then used to trigger SCR1 (Silicon Controlled Rectifier), which is a type of thyristor that can control high power loads.
Upon triggering, SCR1 allows current to flow through its anode to cathode, effectively activating the connected load. In this circuit, the load activation is indicated by the illumination of LED1, which serves as a visual indicator of the system's operation. Additionally, the activation of SCR1 also energizes opto isolator IC2. The opto isolator is crucial for providing electrical isolation between the control circuit and the load circuit, ensuring that the low voltage control side does not interfere with the high voltage load side. This design enhances safety and protects sensitive components from potential damage due to high voltage spikes.
Overall, this circuit effectively demonstrates a light-sensing mechanism that can control electrical loads based on ambient light levels, utilizing a combination of analog components and semiconductor devices for efficient operation. The light-sensitive CDS cell R8 configured in a bridge circuit with IC1 as a comparator causes ICl`s output to go high when light strikes the CDS cell R8, triggering SCR1. This lights LED1 and turns on opto isolator IC2, which switches the load. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a light-dependent resistor (CDS cell R8) that changes its resistance based on the intensity of light it receives. In this configuration, R8 is part of a bridge circuit, which typically consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape. The bridge circuit is balanced under normal lighting conditions, and when light intensity changes, it causes an imbalance, resulting in a voltage difference that is detected by the comparator IC1.
IC1 compares the voltage across the bridge circuit to a reference voltage. When the light intensity exceeds a certain threshold, the voltage at one of the bridge's nodes rises above the reference level, causing the output of IC1 to transition to a high state. This output signal is then used to trigger SCR1 (Silicon Controlled Rectifier), which is a type of thyristor that can control high power loads.
Upon triggering, SCR1 allows current to flow through its anode to cathode, effectively activating the connected load. In this circuit, the load activation is indicated by the illumination of LED1, which serves as a visual indicator of the system's operation. Additionally, the activation of SCR1 also energizes opto isolator IC2. The opto isolator is crucial for providing electrical isolation between the control circuit and the load circuit, ensuring that the low voltage control side does not interfere with the high voltage load side. This design enhances safety and protects sensitive components from potential damage due to high voltage spikes.
Overall, this circuit effectively demonstrates a light-sensing mechanism that can control electrical loads based on ambient light levels, utilizing a combination of analog components and semiconductor devices for efficient operation. The light-sensitive CDS cell R8 configured in a bridge circuit with IC1 as a comparator causes ICl`s output to go high when light strikes the CDS cell R8, triggering SCR1. This lights LED1 and turns on opto isolator IC2, which switches the load. 🔗 External reference