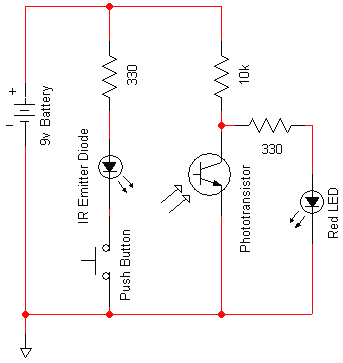
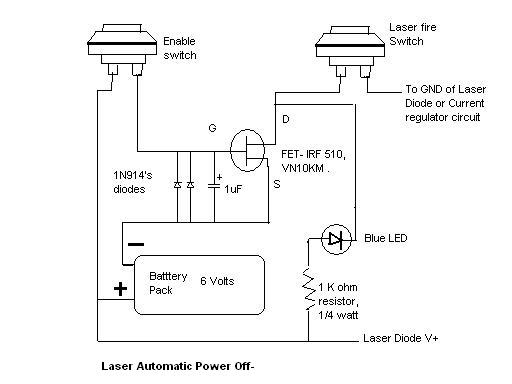
The Infrared Demodulation Circuit Using Low-Noise Amplifier
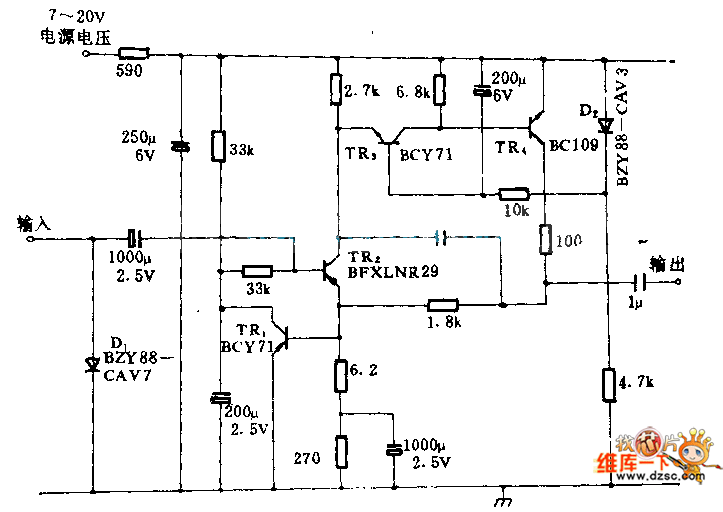
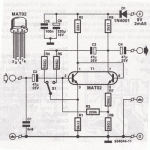
This circuit employs an HgCdTe demodulation device that can be cooled to 77K using liquid nitrogen. It utilizes a constant current bias for the demodulation device, which is connected to the input port. The voltage amplification factor is 200, and the bandwidth exceeds 1 MHz. The noise factor is 1.5 dB when using the typical demodulation device. This circuit incorporates two...
This circuit is designed to operate with an HgCdTe (mercury cadmium telluride) demodulation device, which is a critical component in infrared detection applications. The ability to cool the device to 77K enhances its sensitivity and performance, making it suitable for low-temperature applications such as infrared spectroscopy and thermal imaging.
The constant current biasing method ensures stable operation of the demodulation device, which is essential for maintaining linearity and minimizing distortion during signal processing. The input port is configured to facilitate optimal signal capture, ensuring that the incoming signals are efficiently directed to the demodulation device.
With a voltage amplification factor of 200, this circuit is capable of significantly boosting weak signals, making it effective for detecting low-level infrared signals. The bandwidth of over 1 MHz allows the circuit to handle a wide range of frequencies, which is crucial for applications requiring rapid signal processing.
The circuit's noise factor of 1.5 dB indicates a low level of noise introduction into the system, which is vital for maintaining signal integrity, especially in sensitive applications. The design considerations and components used in this circuit contribute to its overall performance, making it suitable for advanced detection and measurement tasks in various fields, including medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and military applications.
Overall, this circuit represents a sophisticated approach to infrared signal demodulation, leveraging the unique properties of the HgCdTe material and optimized design parameters to achieve high performance in demanding environments.This circuit uses the HgCdTe demodulation device which can be cooled to 77K in liquid nitrogen. It uses a constant current bias for the demodulation device which is connected to the input port. The voltage`s amplification factor is 200 and the bandwidth is above 1MHz. The noise factor is 1.5dB when use the typical demodulation device. This circuit uses two.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to operate with an HgCdTe (mercury cadmium telluride) demodulation device, which is a critical component in infrared detection applications. The ability to cool the device to 77K enhances its sensitivity and performance, making it suitable for low-temperature applications such as infrared spectroscopy and thermal imaging.
The constant current biasing method ensures stable operation of the demodulation device, which is essential for maintaining linearity and minimizing distortion during signal processing. The input port is configured to facilitate optimal signal capture, ensuring that the incoming signals are efficiently directed to the demodulation device.
With a voltage amplification factor of 200, this circuit is capable of significantly boosting weak signals, making it effective for detecting low-level infrared signals. The bandwidth of over 1 MHz allows the circuit to handle a wide range of frequencies, which is crucial for applications requiring rapid signal processing.
The circuit's noise factor of 1.5 dB indicates a low level of noise introduction into the system, which is vital for maintaining signal integrity, especially in sensitive applications. The design considerations and components used in this circuit contribute to its overall performance, making it suitable for advanced detection and measurement tasks in various fields, including medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and military applications.
Overall, this circuit represents a sophisticated approach to infrared signal demodulation, leveraging the unique properties of the HgCdTe material and optimized design parameters to achieve high performance in demanding environments.This circuit uses the HgCdTe demodulation device which can be cooled to 77K in liquid nitrogen. It uses a constant current bias for the demodulation device which is connected to the input port. The voltage`s amplification factor is 200 and the bandwidth is above 1MHz. The noise factor is 1.5dB when use the typical demodulation device. This circuit uses two.. 🔗 External reference