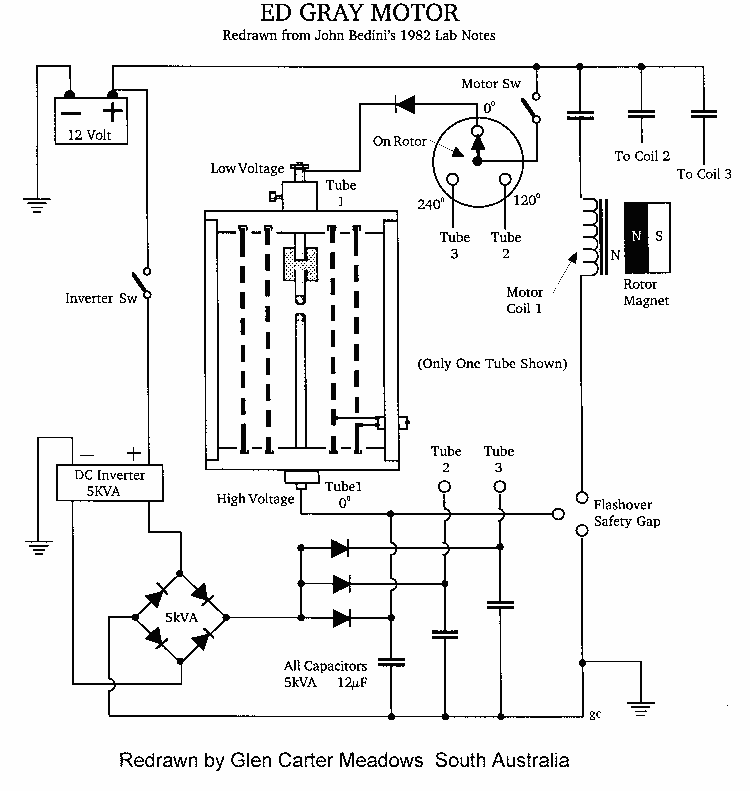
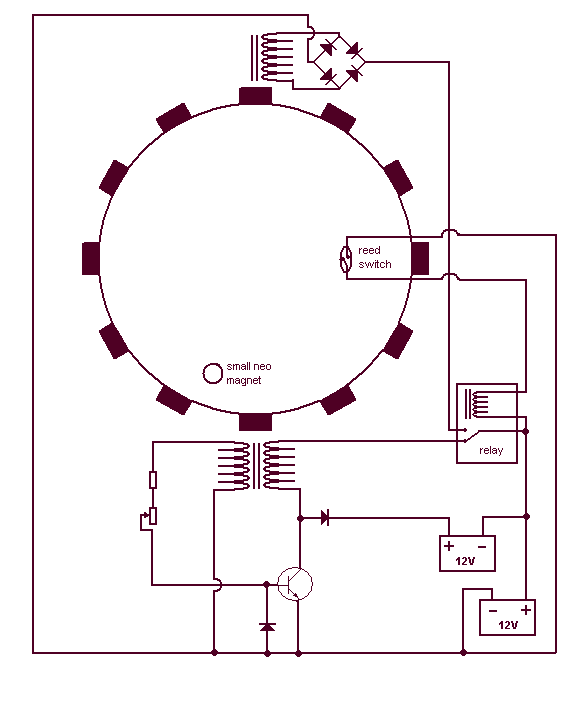
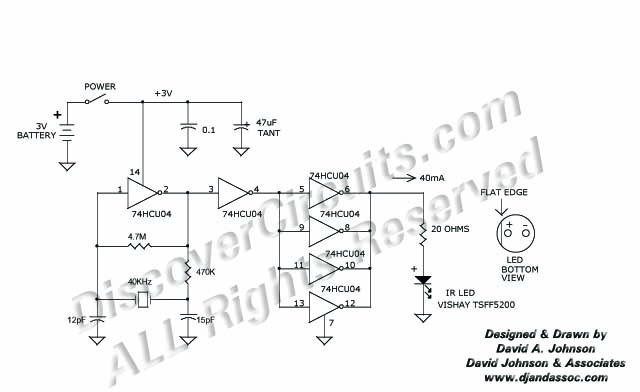
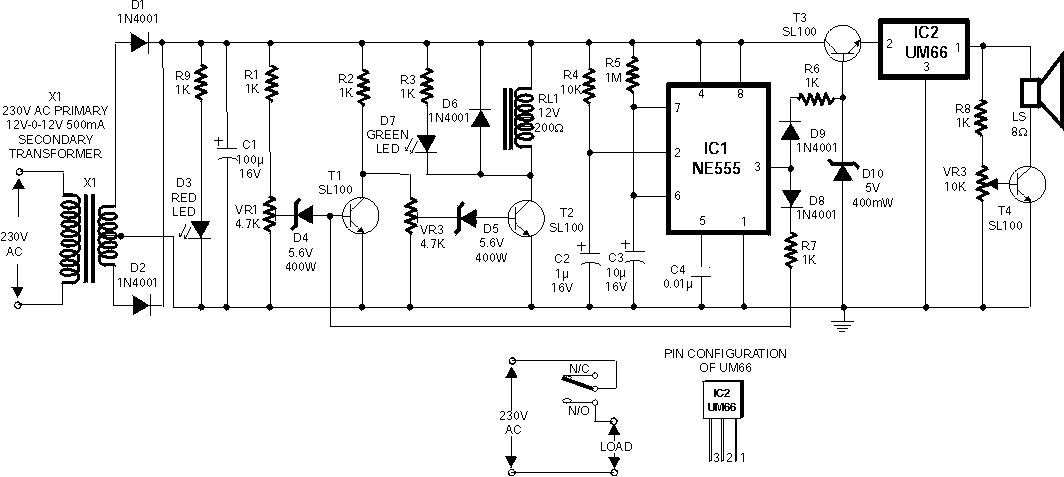
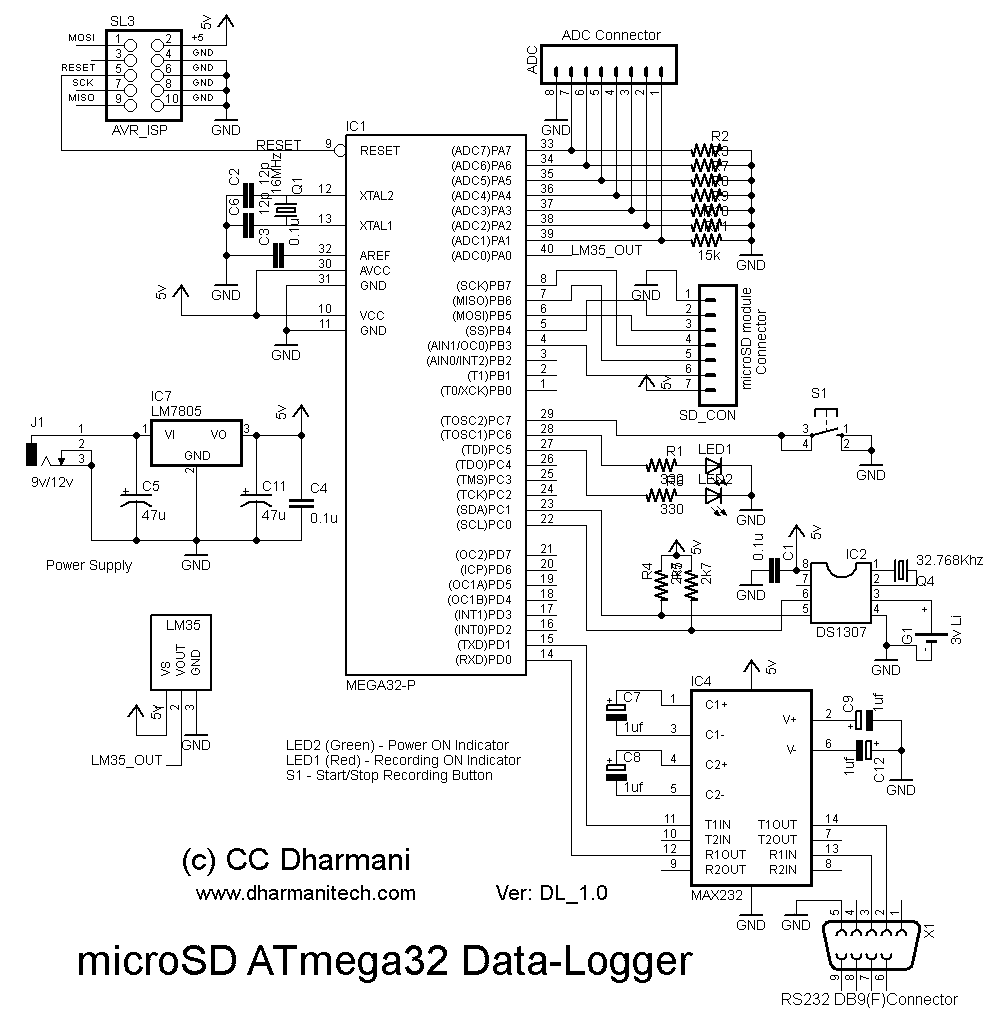
Programmable pulse generator
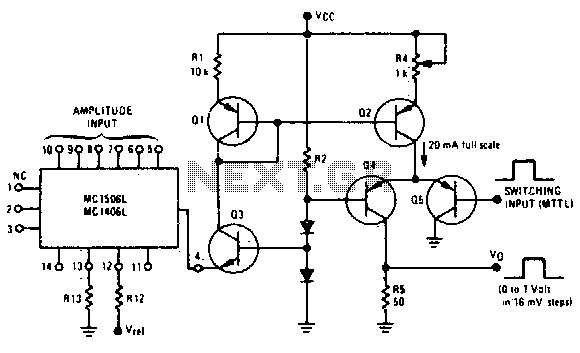
Fast rise and fall times necessitate the utilization of high-speed switching transistors for the differential pair, Q4 and Q5. Linear ramps and sine waves can be produced using the suitable reference input.
The circuit employs high-speed switching transistors, specifically Q4 and Q5, to achieve rapid rise and fall times essential for applications requiring precise signal integrity. These transistors are configured in a differential pair arrangement, which enhances performance by minimizing noise and improving linearity in signal processing. The choice of transistors is critical; they must have low capacitance and high current gain to facilitate fast switching and maintain signal fidelity.
The circuit also incorporates a reference input that is capable of generating linear ramps and sine waves. This input can be utilized to modulate the output signals, providing versatility in waveform generation. The reference input's characteristics, including its amplitude and frequency, directly influence the output waveform's shape and behavior. By carefully selecting the reference input parameters, the circuit can be tailored for specific applications, such as analog signal processing, waveform generation, or communication systems.
In summary, the combination of high-speed switching transistors in a differential configuration and a versatile reference input allows for the generation of high-quality linear ramps and sine waves, making this circuit suitable for a variety of high-performance electronic applications.Fast rise and fall times require the use of high speed switching transistors for the differential pair, Q4 and Q5 Linear ramps and sine waves may be generated by the appropriate reference input.
The circuit employs high-speed switching transistors, specifically Q4 and Q5, to achieve rapid rise and fall times essential for applications requiring precise signal integrity. These transistors are configured in a differential pair arrangement, which enhances performance by minimizing noise and improving linearity in signal processing. The choice of transistors is critical; they must have low capacitance and high current gain to facilitate fast switching and maintain signal fidelity.
The circuit also incorporates a reference input that is capable of generating linear ramps and sine waves. This input can be utilized to modulate the output signals, providing versatility in waveform generation. The reference input's characteristics, including its amplitude and frequency, directly influence the output waveform's shape and behavior. By carefully selecting the reference input parameters, the circuit can be tailored for specific applications, such as analog signal processing, waveform generation, or communication systems.
In summary, the combination of high-speed switching transistors in a differential configuration and a versatile reference input allows for the generation of high-quality linear ramps and sine waves, making this circuit suitable for a variety of high-performance electronic applications.Fast rise and fall times require the use of high speed switching transistors for the differential pair, Q4 and Q5 Linear ramps and sine waves may be generated by the appropriate reference input.