Quiz Circuit PCB
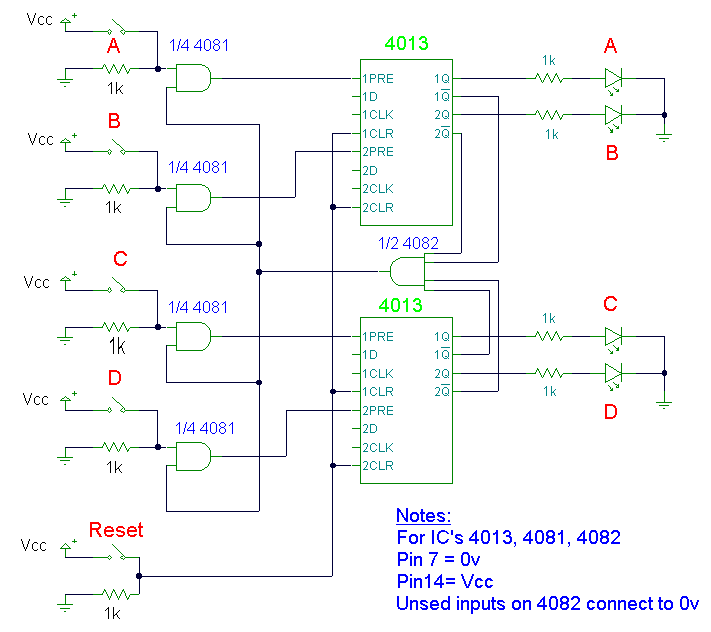
There have been several requests for a quiz circuit, leading to the development of a design featuring four inputs that can be easily modified. This circuit employs four integrated circuits (ICs) and includes four input circuits with independent outputs, along with a single master reset switch. The outputs are represented by LEDs, though they can be adapted to drive lamps or buzzers. Only one output LED can be illuminated at any given time. The first participant to press their designated input switch—A, B, C, or D—will activate the corresponding output LED, while disabling the other inputs. The circuit utilizes CMOS ICs, with part numbers indicated in the schematic. It can be powered by a supply voltage ranging from 3 to 15 volts, or it can be constructed using equivalent TTL ICs operating at 5 volts. The primary component of this circuit is a bistable latch, specifically based on the dual 4013 D-type flip-flop. Engaging the reset switch will clear all flip-flops and extinguish any lit LEDs. In this state, all Q outputs will be low (logic 0), and all NOT Q outputs will be high (logic 1). The four NOT Q outputs are connected to a four-input AND gate (4082), whose output will also be high. This output is then connected to one input of each two-input AND gate (4081). The switch inputs A, B, C, and D are non-latching push-button switches. The first switch pressed will cause the corresponding AND gate (4081) to output high, triggering the preset input of the 4013 D-type flip-flop, which will latch and illuminate the appropriate LED. The triggered flip-flop will set its NOT Q output to low, changing the output of the 4082 to low and preventing any further triggering of the other flip-flops. Switch contact debouncing is unnecessary, as the first press will latch one of the bistables. Pressing the reset switch will return the circuit to its initial state. It is advisable to use heavy-duty push-button switches, as they are likely to experience significant stress during operation.
The quiz circuit design is structured to facilitate a simple yet effective interactive experience. The four input switches, labeled A, B, C, and D, are strategically placed to ensure easy access for participants. Each switch is connected to a corresponding two-input AND gate (4081), which serves to process the input signals. The output of each AND gate is linked to the preset input of the dual 4013 D-type flip-flop, which is the core of the circuit's memory function.
The bistable latch configuration of the 4013 allows the circuit to maintain a stable state once an input is activated. When a participant presses one of the input switches, the corresponding AND gate receives a high signal, triggering the preset of the flip-flop. This action sets the Q output high, illuminating the associated LED, while simultaneously pulling the NOT Q output low. The change in the NOT Q output state results in the AND gate (4082) output going low, effectively disabling all other inputs and preventing any other LEDs from lighting until the reset switch is activated.
The reset switch is critical for returning the circuit to its initial state. When engaged, it clears the flip-flops, turning off all LEDs and resetting the outputs to their default logic levels. This functionality ensures that the quiz can be restarted easily after each round.
The design accommodates a wide range of supply voltages, making it versatile for various applications. The use of CMOS technology allows for low power consumption, which is advantageous in battery-operated scenarios. Alternatively, the circuit can be implemented using TTL logic, providing flexibility in component selection based on availability and desired performance characteristics.
In summary, this quiz circuit offers a robust and interactive solution for multiple participants. Its reliance on standard ICs and simple logic design makes it an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike. The incorporation of heavy-duty push-button switches enhances reliability during use, ensuring that the circuit performs optimally under stress.I`ve had a few requests for a quiz circuit, so here is a 4 input design which can easily be modified. Maybe, I should write the application notes in the style of a game show host. This design uses four IC`s and has four input circuits and four independent outputs and a single master reset switch.
The outputs here are LED`s but may be modified to d rive lamps or buzzers. Only one output LED can be lit at any time. The first person to press their input switch, A, B, C, D will light the corresponding output LED, disabling the other inputs. The circuit uses all CMOS IC`s part numbers shown on the diagram. The supply voltage may be anything between 3 and 15 volts. Alternatively, it may be built using equivalent TTL IC`s and powered on 5 volts. The main component in this circuit is a bistable latch, here it is based on the dual 4013 D-type flip flop.
Pressing the reset switch will clear all flip flops and extinguish any lit LED`s. Under this condition the Q outputs will all be low (logic 0) and NOT Q outputs will be high (logic 1). All four NOT Q outputs are fed to a 4 input AND gate, the 4082 whose output will also be high. The output of the 4082 is wired to one input of each 2 input AND gate (4081). Switch inputs A, B, C, D are all non latching push button switches, the first person to press their switch will cause the corresponding AND gate (4081) to go high and trigger the preset input of the 4013 D-type flip flop.
This will latch and light the appropriate LED. Also the triggered flip flop will have its NOT Q output, set at low, this changes the 4082 output to low and prevents any further triggering of the other flip flops. Switch contact de-bouncing is not required as the first press will latch one of the bistables. Pressing the reset switch, restores the circuit to its former state. I would recommend using heavy duty push button switches, as in use they are likely to be under some stress.
🔗 External reference
The quiz circuit design is structured to facilitate a simple yet effective interactive experience. The four input switches, labeled A, B, C, and D, are strategically placed to ensure easy access for participants. Each switch is connected to a corresponding two-input AND gate (4081), which serves to process the input signals. The output of each AND gate is linked to the preset input of the dual 4013 D-type flip-flop, which is the core of the circuit's memory function.
The bistable latch configuration of the 4013 allows the circuit to maintain a stable state once an input is activated. When a participant presses one of the input switches, the corresponding AND gate receives a high signal, triggering the preset of the flip-flop. This action sets the Q output high, illuminating the associated LED, while simultaneously pulling the NOT Q output low. The change in the NOT Q output state results in the AND gate (4082) output going low, effectively disabling all other inputs and preventing any other LEDs from lighting until the reset switch is activated.
The reset switch is critical for returning the circuit to its initial state. When engaged, it clears the flip-flops, turning off all LEDs and resetting the outputs to their default logic levels. This functionality ensures that the quiz can be restarted easily after each round.
The design accommodates a wide range of supply voltages, making it versatile for various applications. The use of CMOS technology allows for low power consumption, which is advantageous in battery-operated scenarios. Alternatively, the circuit can be implemented using TTL logic, providing flexibility in component selection based on availability and desired performance characteristics.
In summary, this quiz circuit offers a robust and interactive solution for multiple participants. Its reliance on standard ICs and simple logic design makes it an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike. The incorporation of heavy-duty push-button switches enhances reliability during use, ensuring that the circuit performs optimally under stress.I`ve had a few requests for a quiz circuit, so here is a 4 input design which can easily be modified. Maybe, I should write the application notes in the style of a game show host. This design uses four IC`s and has four input circuits and four independent outputs and a single master reset switch.
The outputs here are LED`s but may be modified to d rive lamps or buzzers. Only one output LED can be lit at any time. The first person to press their input switch, A, B, C, D will light the corresponding output LED, disabling the other inputs. The circuit uses all CMOS IC`s part numbers shown on the diagram. The supply voltage may be anything between 3 and 15 volts. Alternatively, it may be built using equivalent TTL IC`s and powered on 5 volts. The main component in this circuit is a bistable latch, here it is based on the dual 4013 D-type flip flop.
Pressing the reset switch will clear all flip flops and extinguish any lit LED`s. Under this condition the Q outputs will all be low (logic 0) and NOT Q outputs will be high (logic 1). All four NOT Q outputs are fed to a 4 input AND gate, the 4082 whose output will also be high. The output of the 4082 is wired to one input of each 2 input AND gate (4081). Switch inputs A, B, C, D are all non latching push button switches, the first person to press their switch will cause the corresponding AND gate (4081) to go high and trigger the preset input of the 4013 D-type flip flop.
This will latch and light the appropriate LED. Also the triggered flip flop will have its NOT Q output, set at low, this changes the 4082 output to low and prevents any further triggering of the other flip flops. Switch contact de-bouncing is not required as the first press will latch one of the bistables. Pressing the reset switch, restores the circuit to its former state. I would recommend using heavy duty push button switches, as in use they are likely to be under some stress.
🔗 External reference