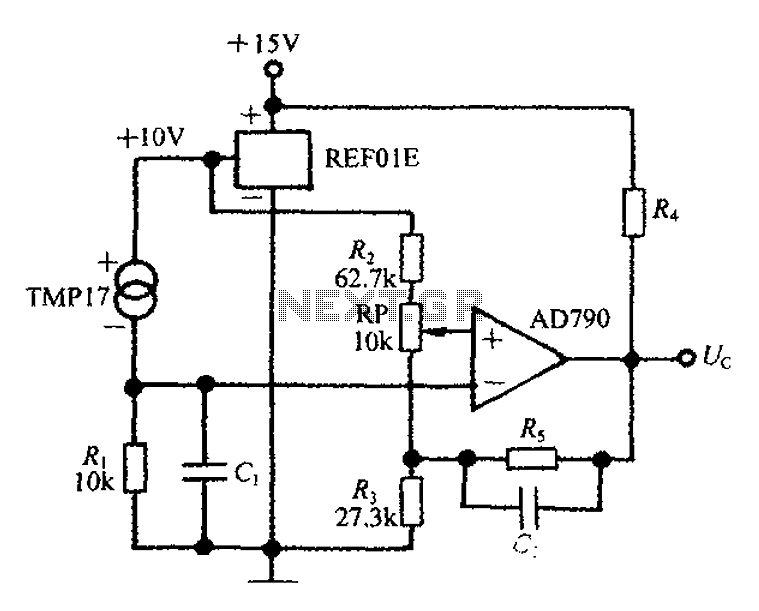
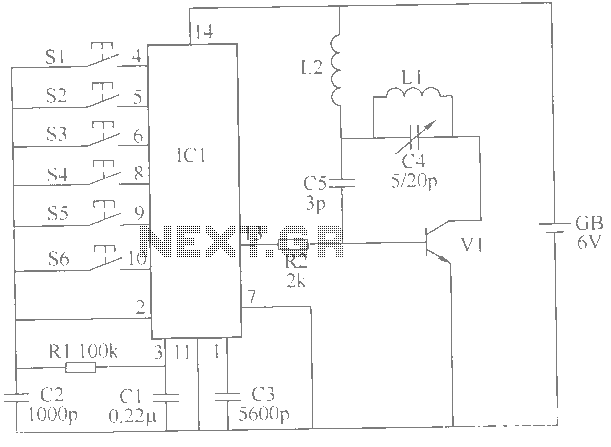
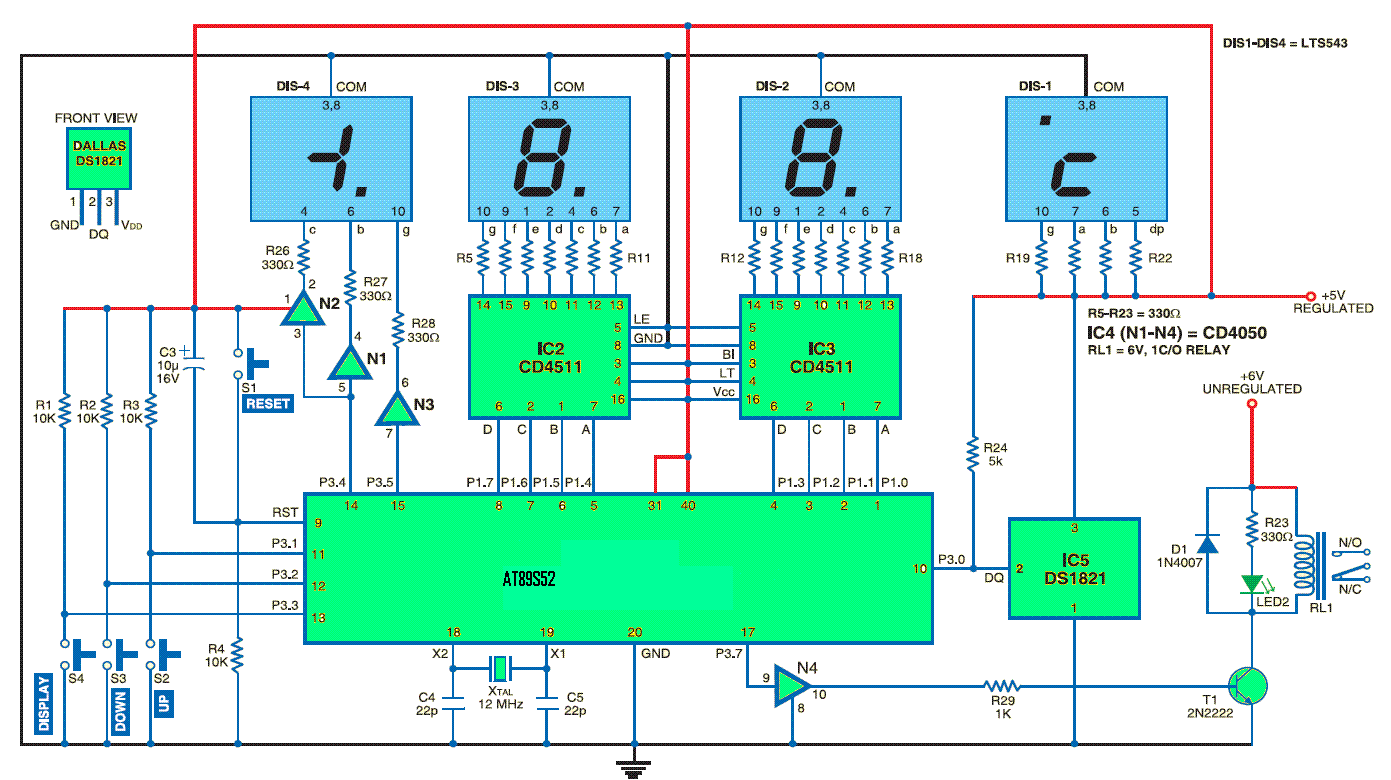
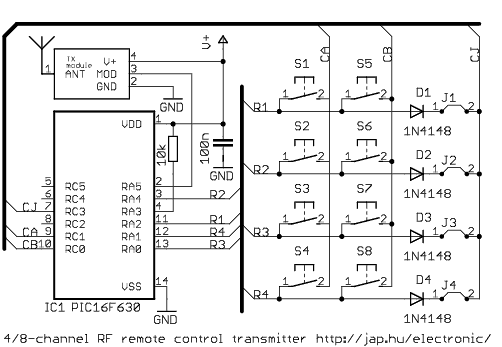
Radio control
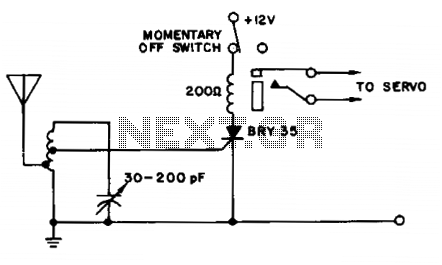
A simple and effective receiver for actuating garage doors, alarms, warning systems, etc. The SCR, which has a very low trigger current of 30 µA, requires an input power of only 30 µW to activate the relay. A high Q tuned antenna circuit ensures rejection of spurious signals. A whip or wire antenna is sufficient up to 100 feet from a low power transistor transmitter. A momentary-off switch resets the circuit.
This receiver circuit is designed for applications such as garage door operation, alarm activation, and warning systems, making it versatile for various automation needs. The core component of this design is a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR), which is notable for its low trigger current of 30 µA. This low trigger current allows the circuit to operate efficiently with minimal power consumption, requiring only 30 µW to activate the relay that controls the output devices.
The circuit employs a high Q tuned antenna circuit, which is crucial for filtering out unwanted signals and ensuring that the receiver only responds to the desired frequencies. The design can utilize either a whip antenna or a simple wire antenna, which can effectively receive signals from a low power transistor transmitter located up to 100 feet away. This range makes the system suitable for residential or light commercial use where such distances are common.
Additionally, the inclusion of a momentary-off switch provides a practical means to reset the circuit. This feature enhances user control over the system, allowing for easy reconfiguration or troubleshooting without the need for disconnecting power. Overall, the combination of low power requirements, effective signal filtering, and user-friendly reset functionality makes this receiver circuit a reliable choice for various remote actuation applications.A simple and effective receiver for actuating garage doors, alarms, warning systems, etc. The SCR, which has a very low trigger current 30 µ is typical—it requires an input power of only 30 juW to activate the relay. A high Q tuned antenna circuit assures rejection of spurious signals. A whip or wire antenna is adequate up to 100 feet from a low power transistor transmitter. A momentary-off switch resets the circuit. 🔗 External reference
This receiver circuit is designed for applications such as garage door operation, alarm activation, and warning systems, making it versatile for various automation needs. The core component of this design is a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR), which is notable for its low trigger current of 30 µA. This low trigger current allows the circuit to operate efficiently with minimal power consumption, requiring only 30 µW to activate the relay that controls the output devices.
The circuit employs a high Q tuned antenna circuit, which is crucial for filtering out unwanted signals and ensuring that the receiver only responds to the desired frequencies. The design can utilize either a whip antenna or a simple wire antenna, which can effectively receive signals from a low power transistor transmitter located up to 100 feet away. This range makes the system suitable for residential or light commercial use where such distances are common.
Additionally, the inclusion of a momentary-off switch provides a practical means to reset the circuit. This feature enhances user control over the system, allowing for easy reconfiguration or troubleshooting without the need for disconnecting power. Overall, the combination of low power requirements, effective signal filtering, and user-friendly reset functionality makes this receiver circuit a reliable choice for various remote actuation applications.A simple and effective receiver for actuating garage doors, alarms, warning systems, etc. The SCR, which has a very low trigger current 30 µ is typical—it requires an input power of only 30 juW to activate the relay. A high Q tuned antenna circuit assures rejection of spurious signals. A whip or wire antenna is adequate up to 100 feet from a low power transistor transmitter. A momentary-off switch resets the circuit. 🔗 External reference