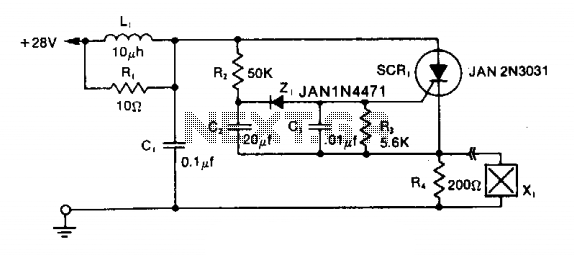
Recording Level Meter Circuit
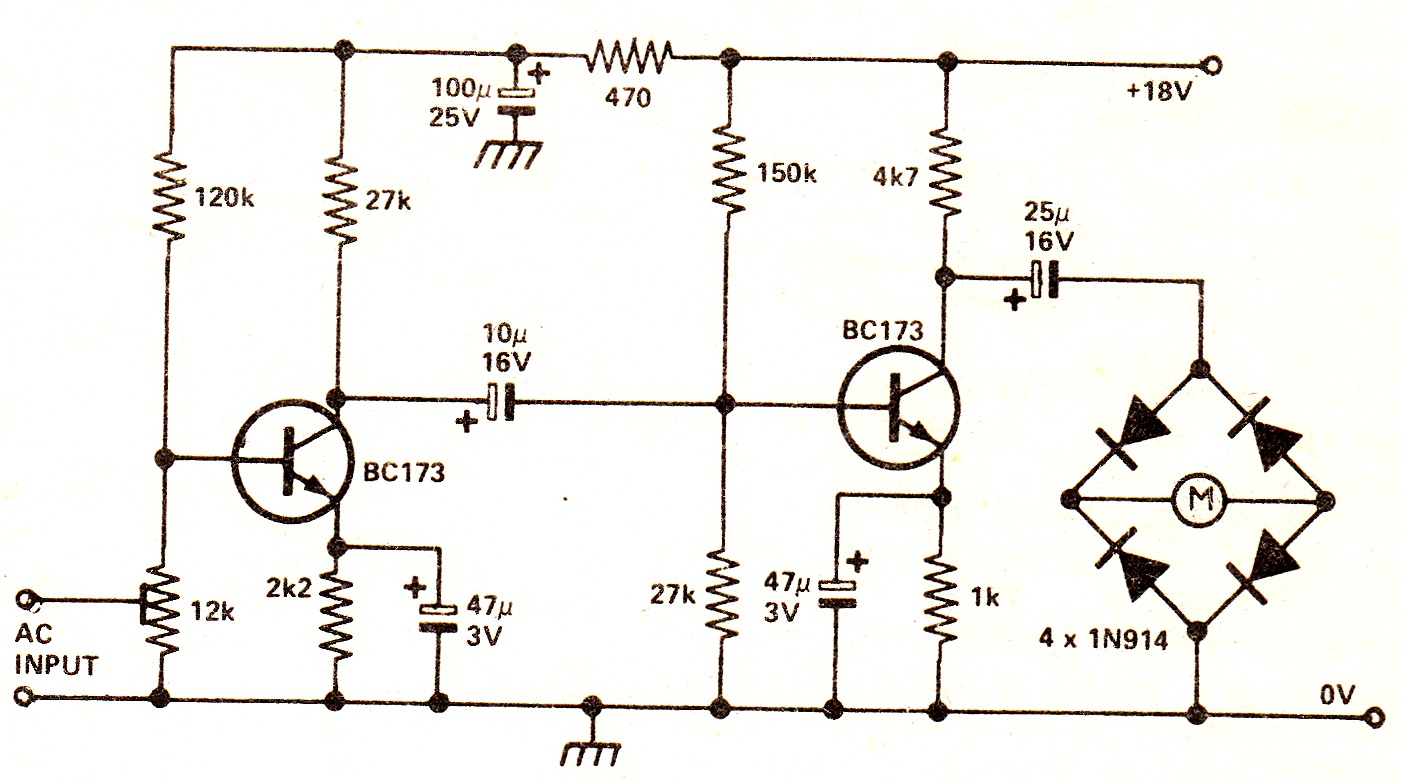
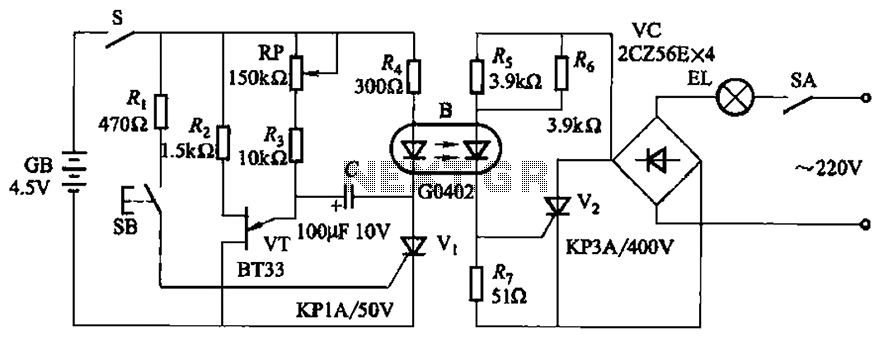
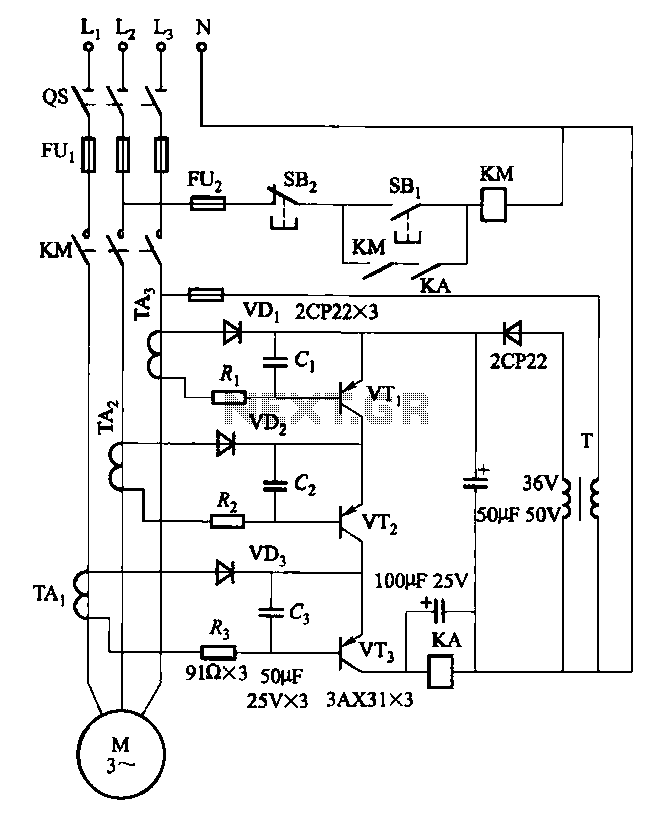
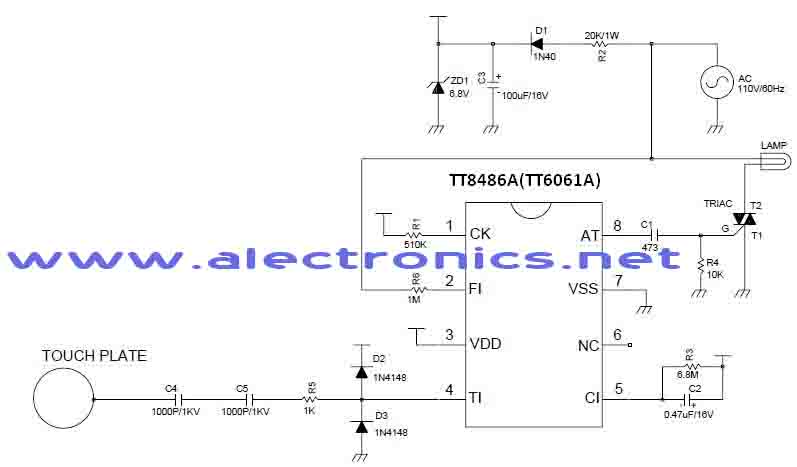
The circuit illustrates a two-stage voltage amplifier that drives a recording level meter. An AC signal input is amplified and rectified, with the resulting DC voltage displayed on the meter. This circuit is compatible with tape recorders or audio mixers and should be connected to an early point in the pre-amplifier stage. The current consumption in a no-signal state is 2.8 mA. The 12 kΩ preset provides a range of sensitivity adjustments. The meter can be any general-purpose type.
The described circuit employs a two-stage voltage amplification process to enhance an AC signal before it is converted to a DC voltage for display on a level meter. The first stage typically consists of a transistor or operational amplifier configured for voltage gain, while the second stage further amplifies the signal to ensure adequate drive capability for the meter.
The rectification stage is crucial as it converts the amplified AC signal into a DC voltage. This is often achieved using a diode bridge rectifier, which allows the circuit to respond to both positive and negative halves of the AC waveform, ensuring that the meter reflects the true level of the input signal.
The choice of a general-purpose meter provides flexibility, allowing for various applications within audio systems. The circuit's design facilitates integration with tape recorders or audio mixers, making it suitable for monitoring audio levels during recording or mixing processes.
The current consumption of 2.8 mA in a no-signal state indicates efficient power usage, essential for battery-operated devices or low-power applications. The inclusion of a 12 kΩ preset resistor enhances the circuit's versatility, enabling users to adjust sensitivity according to their specific requirements, which is particularly beneficial when working with different types of audio signals or varying input levels.
Overall, this circuit design is a practical solution for audio level monitoring, combining effective amplification and rectification while maintaining low power consumption and adaptability for various audio applications.The circuit shows a two ”stage voltage amplifier driving a recording level meter. The AC signal input is amplified, rectified, and the resultant DC voltage shown on the meter. The circuit can be used with a tape recorder or audio mixer and should be fed from a point early in the pre-amp. Current consumption in a no-signal state is 2. 8mA. The 12K preset gives a variation in sensitivity. The meter can be any general purpose type. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a two-stage voltage amplification process to enhance an AC signal before it is converted to a DC voltage for display on a level meter. The first stage typically consists of a transistor or operational amplifier configured for voltage gain, while the second stage further amplifies the signal to ensure adequate drive capability for the meter.
The rectification stage is crucial as it converts the amplified AC signal into a DC voltage. This is often achieved using a diode bridge rectifier, which allows the circuit to respond to both positive and negative halves of the AC waveform, ensuring that the meter reflects the true level of the input signal.
The choice of a general-purpose meter provides flexibility, allowing for various applications within audio systems. The circuit's design facilitates integration with tape recorders or audio mixers, making it suitable for monitoring audio levels during recording or mixing processes.
The current consumption of 2.8 mA in a no-signal state indicates efficient power usage, essential for battery-operated devices or low-power applications. The inclusion of a 12 kΩ preset resistor enhances the circuit's versatility, enabling users to adjust sensitivity according to their specific requirements, which is particularly beneficial when working with different types of audio signals or varying input levels.
Overall, this circuit design is a practical solution for audio level monitoring, combining effective amplification and rectification while maintaining low power consumption and adaptability for various audio applications.The circuit shows a two ”stage voltage amplifier driving a recording level meter. The AC signal input is amplified, rectified, and the resultant DC voltage shown on the meter. The circuit can be used with a tape recorder or audio mixer and should be fed from a point early in the pre-amp. Current consumption in a no-signal state is 2. 8mA. The 12K preset gives a variation in sensitivity. The meter can be any general purpose type. 🔗 External reference