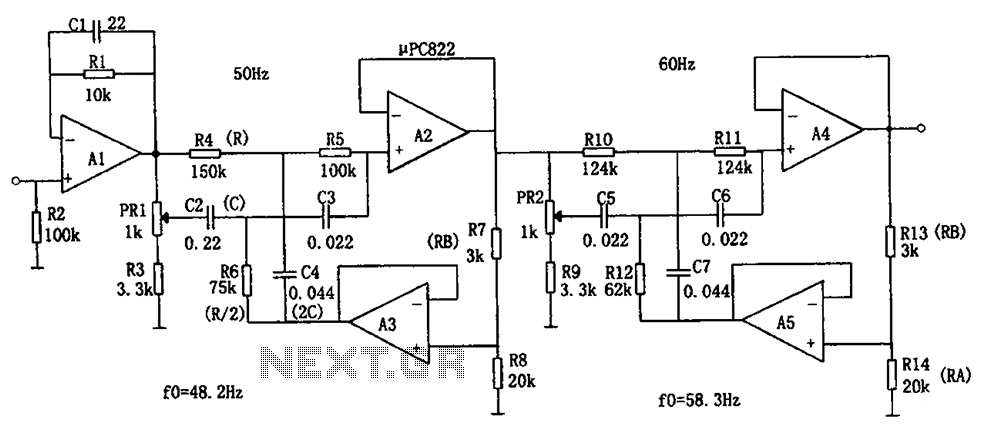
Rejection filter
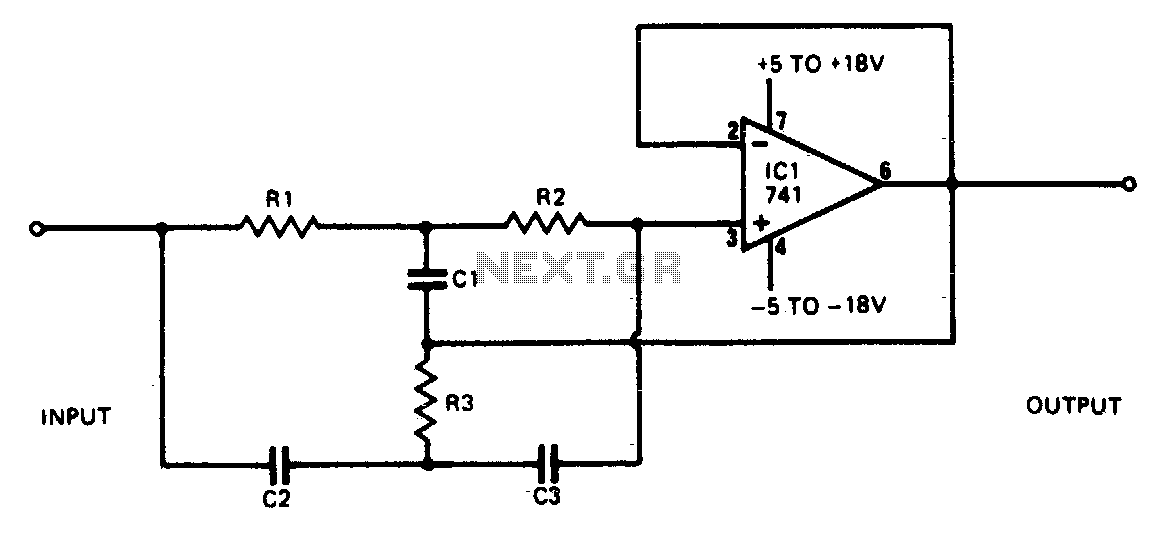
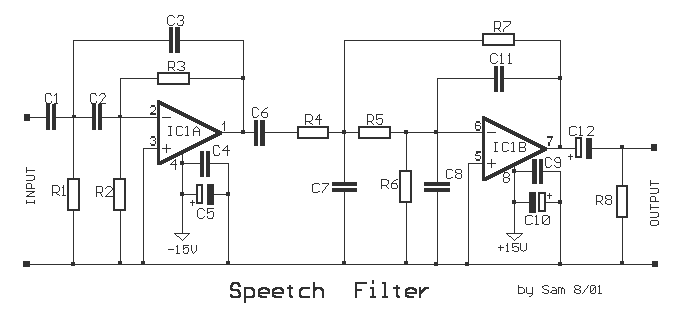
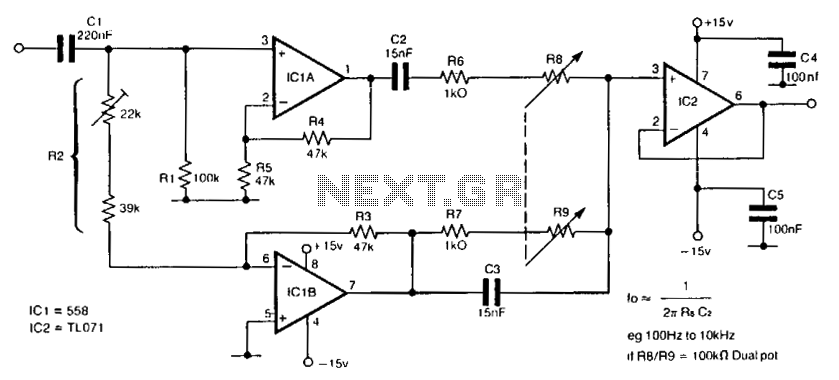
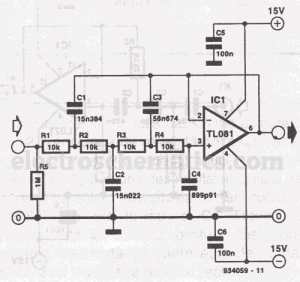
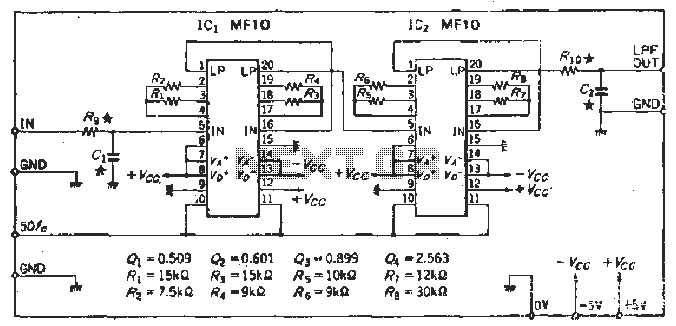
This narrowband filter utilizing the 741 operational amplifier can achieve a rejection level of up to 60 dB. By employing resistors with a value of 100 K ohms and capacitors of 320 pF, the circuit effectively rejects frequencies at 50 Hz. Frequencies ranging from 1 Hz to 10 kHz can be rejected by selecting components based on the specified formula. To attain rejections exceeding 40 dB, it is recommended that resistors be matched to 0% tolerance and capacitors to 1% tolerance.
The described narrowband filter circuit is designed around the 741 operational amplifier, which is a versatile and widely used component in analog electronics. The filter's primary function is to attenuate unwanted frequencies while allowing desired signals to pass through. In this configuration, the 741 op-amp is used in a specific arrangement that enhances its filtering capabilities.
The filter's design involves careful selection of passive components—resistors and capacitors—that determine its frequency response. The stated values of 100 K ohms for resistors and 320 pF for capacitors suggest a configuration that is optimized for rejecting the 50 Hz frequency, which is often associated with power line noise and other low-frequency interference.
The performance of the filter is quantified by its rejection ratio, which can reach up to 60 dB, indicating a significant attenuation of unwanted signals. The formula referenced for component selection is crucial for tuning the filter's performance across the broader range of 1 Hz to 10 kHz. This flexibility allows the filter to be adapted for various applications, including audio processing, signal conditioning, and noise reduction.
To ensure optimal performance, particularly for achieving rejections greater than 40 dB, component tolerances must be strictly adhered to. Resistors should be matched to 0% tolerance to minimize variations that could affect the filter's frequency response, while capacitors should be selected with a 1% tolerance to maintain consistent capacitance values. This precision in component selection is essential for high-performance filtering applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, this narrowband filter circuit exemplifies the practical application of operational amplifiers in electronic design, showcasing how careful component selection and configuration can lead to effective signal processing solutions.This narrowband filter using the 741 operational amplifier can provide up to 60 dB of rejection. With resistors equal to 100 K and capacitors equal to 320 pF, the circuit will reject 50 Hz. Frequencies within the range 1 Hz to 10 kHz may be rejected by selecting components in accordance with the formula To obtain rejections better than 40 dB, resistors should be matched to 0% and capacitors to 1%. 🔗 External reference
The described narrowband filter circuit is designed around the 741 operational amplifier, which is a versatile and widely used component in analog electronics. The filter's primary function is to attenuate unwanted frequencies while allowing desired signals to pass through. In this configuration, the 741 op-amp is used in a specific arrangement that enhances its filtering capabilities.
The filter's design involves careful selection of passive components—resistors and capacitors—that determine its frequency response. The stated values of 100 K ohms for resistors and 320 pF for capacitors suggest a configuration that is optimized for rejecting the 50 Hz frequency, which is often associated with power line noise and other low-frequency interference.
The performance of the filter is quantified by its rejection ratio, which can reach up to 60 dB, indicating a significant attenuation of unwanted signals. The formula referenced for component selection is crucial for tuning the filter's performance across the broader range of 1 Hz to 10 kHz. This flexibility allows the filter to be adapted for various applications, including audio processing, signal conditioning, and noise reduction.
To ensure optimal performance, particularly for achieving rejections greater than 40 dB, component tolerances must be strictly adhered to. Resistors should be matched to 0% tolerance to minimize variations that could affect the filter's frequency response, while capacitors should be selected with a 1% tolerance to maintain consistent capacitance values. This precision in component selection is essential for high-performance filtering applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, this narrowband filter circuit exemplifies the practical application of operational amplifiers in electronic design, showcasing how careful component selection and configuration can lead to effective signal processing solutions.This narrowband filter using the 741 operational amplifier can provide up to 60 dB of rejection. With resistors equal to 100 K and capacitors equal to 320 pF, the circuit will reject 50 Hz. Frequencies within the range 1 Hz to 10 kHz may be rejected by selecting components in accordance with the formula To obtain rejections better than 40 dB, resistors should be matched to 0% and capacitors to 1%. 🔗 External reference