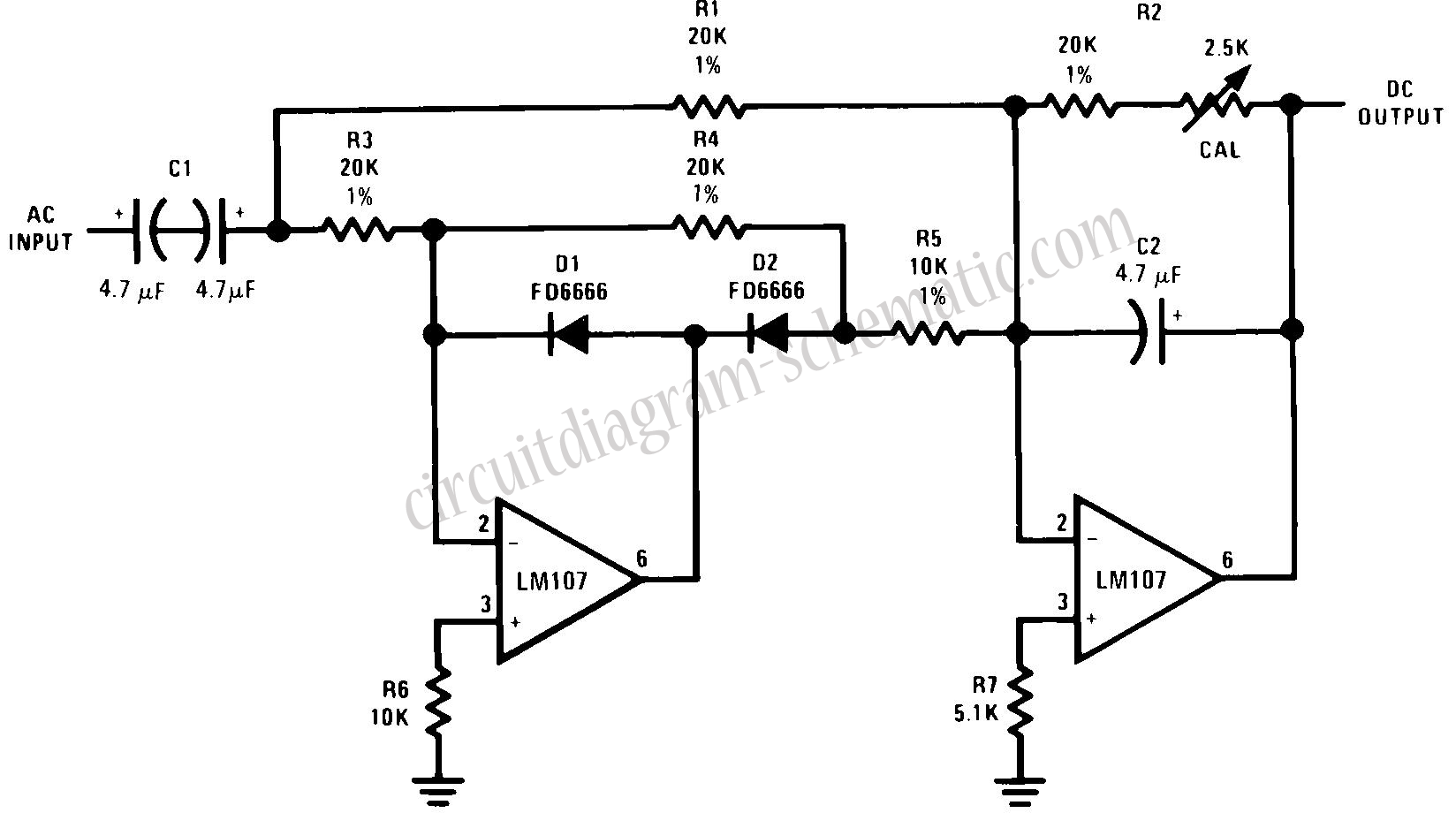
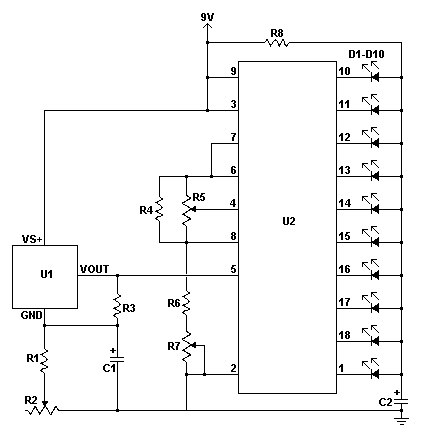
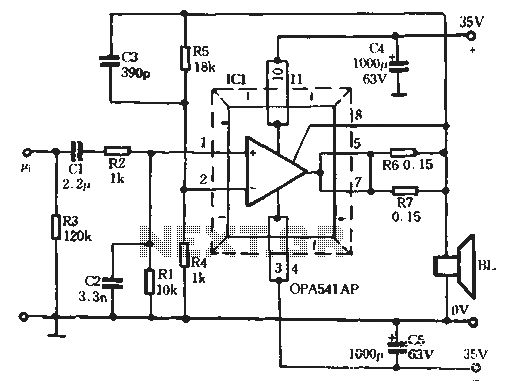
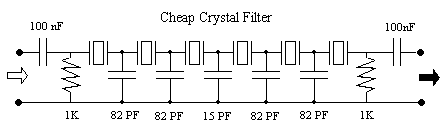
4 order filter with a single IC project PCB
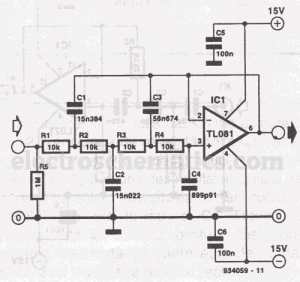
High-order circuit filters are typically designed using two or more cascaded sections. This fourth-order filter requires only one operational amplifier (OA) integrated circuit (IC), which helps achieve lower distortion and reduced intermodulation. The resistor values represent the load on the OA output, with the maximum load for the TL081 being 2k ohms. Resistors R1 to R4 create a 2.5k ohm impedance, meaning the external load should not be less than 10k ohms. The filter characteristic follows a Bessel polynomial. With the current component values, the -3dB frequency is set at 1kHz, and different frequencies can be achieved by altering the component values.
The described fourth-order filter circuit is structured to provide superior performance in applications requiring minimal phase distortion and a smooth frequency response. The use of a single operational amplifier (TL081) not only simplifies the design but also minimizes potential sources of distortion typically associated with multiple stages. The TL081 is a high-performance JFET-input operational amplifier, known for its low noise characteristics and wide bandwidth, making it suitable for audio and precision filtering applications.
The resistor network formed by R1 to R4 establishes a load impedance of 2.5k ohms at the output of the operational amplifier. This impedance is crucial as it defines how the circuit interacts with subsequent stages or loads, ensuring that the maximum load does not exceed the specified 2k ohms limit of the TL081. It is essential to maintain an external load of at least 10k ohms to prevent excessive loading on the operational amplifier, which could lead to performance degradation.
The filter's design employs a Bessel polynomial characteristic, which is particularly advantageous for applications requiring a maximally flat group delay. This characteristic ensures that the phase response of the filter is linear over the passband, making it ideal for audio and signal processing applications where time-domain fidelity is critical.
At the specified component values, the filter exhibits a -3dB cutoff frequency of 1kHz, indicating that signals at this frequency will be attenuated to half of their power level. By adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors within the circuit, various cutoff frequencies can be achieved, allowing for customization based on specific application requirements.
In conclusion, this fourth-order Bessel filter circuit is an effective solution for applications needing precise frequency response and low distortion, with the added flexibility of tuning to various frequencies through component value adjustments.Circuit Filters with high orders are designed usually with 2 or more cascaded sections. This order 4 filter need only one OA IC, so we can achieve lower distorsions, lower intermodulation Resistors values represent the load on the OA output, the maximum TL081 load is 2k ©. R1-R4 build a 2. 5k © impedance and so the external load cannot be low er than 10k ©. The filter characteristic is a Bessel polinome. With the actual components value, at -3dB the frequency is 1kHz. You can obtain different frequencies by changing the components value. 🔗 External reference
The described fourth-order filter circuit is structured to provide superior performance in applications requiring minimal phase distortion and a smooth frequency response. The use of a single operational amplifier (TL081) not only simplifies the design but also minimizes potential sources of distortion typically associated with multiple stages. The TL081 is a high-performance JFET-input operational amplifier, known for its low noise characteristics and wide bandwidth, making it suitable for audio and precision filtering applications.
The resistor network formed by R1 to R4 establishes a load impedance of 2.5k ohms at the output of the operational amplifier. This impedance is crucial as it defines how the circuit interacts with subsequent stages or loads, ensuring that the maximum load does not exceed the specified 2k ohms limit of the TL081. It is essential to maintain an external load of at least 10k ohms to prevent excessive loading on the operational amplifier, which could lead to performance degradation.
The filter's design employs a Bessel polynomial characteristic, which is particularly advantageous for applications requiring a maximally flat group delay. This characteristic ensures that the phase response of the filter is linear over the passband, making it ideal for audio and signal processing applications where time-domain fidelity is critical.
At the specified component values, the filter exhibits a -3dB cutoff frequency of 1kHz, indicating that signals at this frequency will be attenuated to half of their power level. By adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors within the circuit, various cutoff frequencies can be achieved, allowing for customization based on specific application requirements.
In conclusion, this fourth-order Bessel filter circuit is an effective solution for applications needing precise frequency response and low distortion, with the added flexibility of tuning to various frequencies through component value adjustments.Circuit Filters with high orders are designed usually with 2 or more cascaded sections. This order 4 filter need only one OA IC, so we can achieve lower distorsions, lower intermodulation Resistors values represent the load on the OA output, the maximum TL081 load is 2k ©. R1-R4 build a 2. 5k © impedance and so the external load cannot be low er than 10k ©. The filter characteristic is a Bessel polinome. With the actual components value, at -3dB the frequency is 1kHz. You can obtain different frequencies by changing the components value. 🔗 External reference