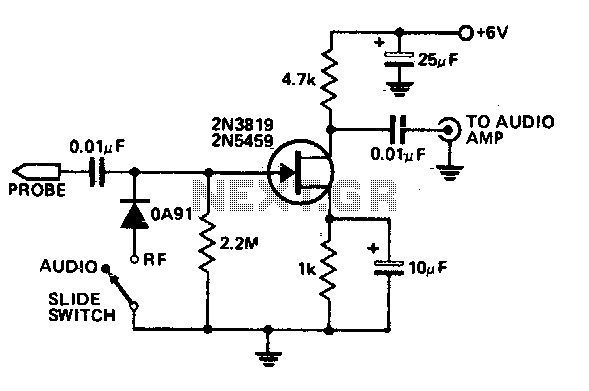
audio notch filter
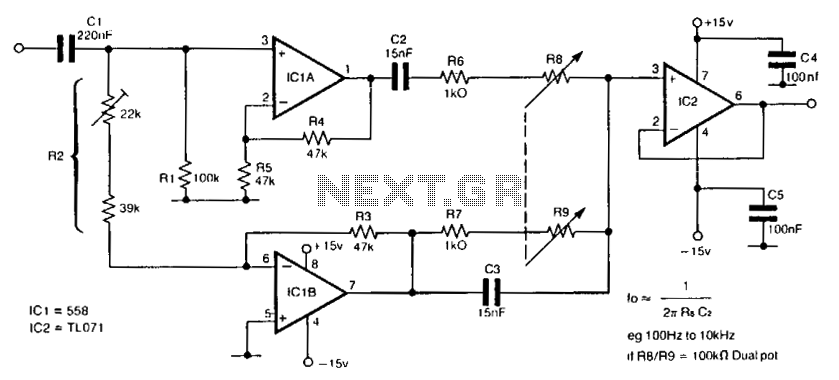
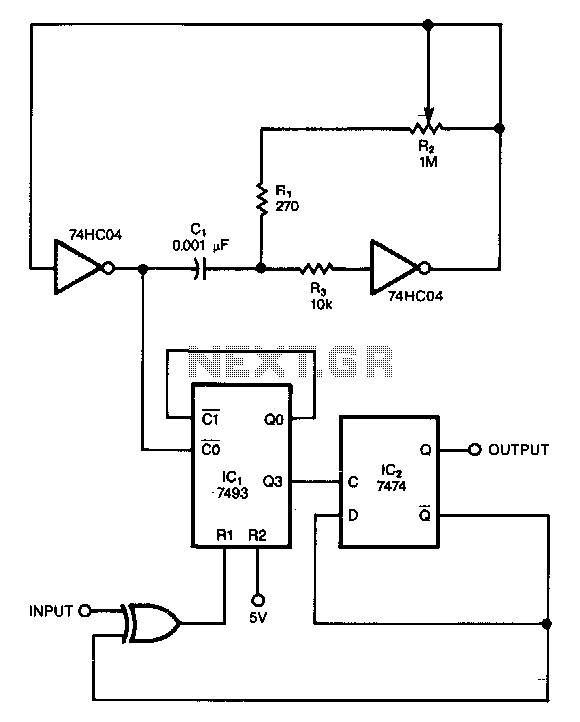
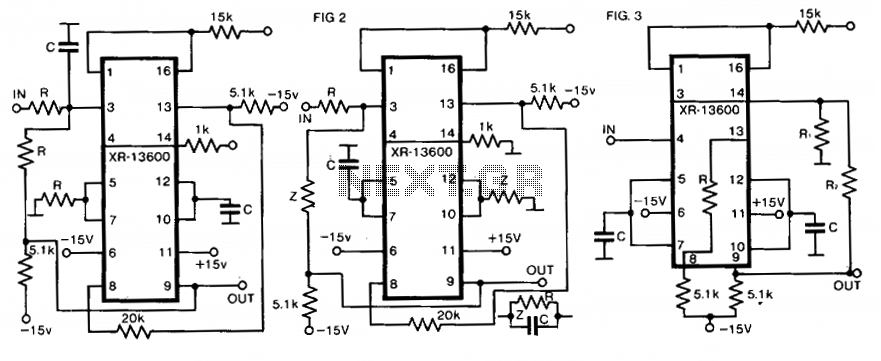
The circuit utilizes a single dual-ganged potentiometer to achieve tuning across a broad spectrum, potentially covering the entire audio range in a single adjustment. The underlying principle is based on the Wien bridge configuration, which is supplied with anti-phase inputs. It is recommended to buffer the output using a field-effect transistor (FET) input operational amplifier, especially when employing a high-value potentiometer. An operational amplifier featuring differential outputs, such as the MC1445, can serve as an alternative to the driver integrated circuits (ICs). Additionally, resistor R2 can be designed to be trimmable for the purpose of optimizing the notch.
The described circuit employs a Wien bridge oscillator configuration, which is recognized for its low distortion and stable frequency characteristics, making it suitable for audio applications. The dual-ganged potentiometer serves as a tuning mechanism, allowing the user to adjust the frequency response of the circuit with precision. By utilizing anti-phase inputs, the circuit ensures that the oscillation remains stable and minimizes any potential drift that may occur during operation.
In this design, the output stage is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal. The use of a FET input operational amplifier is advantageous due to its high input impedance, which prevents loading effects that could alter the performance of the circuit when a high-value potentiometer is employed. The buffering action of the op-amp isolates the Wien bridge oscillator from subsequent stages, ensuring that the output signal remains faithful to the input.
The option to use an operational amplifier with differential outputs, such as the MC1445, provides flexibility in the design, allowing for improved signal handling and noise rejection. This can be particularly beneficial in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) may be present.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a trimmable resistor R2 enhances the circuit's performance by allowing fine-tuning of the notch frequency. This capability is essential for applications requiring precise filtering, such as in audio equalization or noise reduction systems. By adjusting R2, the user can optimize the notch depth and bandwidth, tailoring the circuit to specific requirements.
Overall, this circuit design presents an efficient solution for audio tuning applications, leveraging the stability of the Wien bridge oscillator while providing user-friendly adjustment capabilities through the dual-ganged potentiometer and trimmable resistor.The circuit requires only one dual-ganged potentiometer to tune over a wide range; if necessary over the entire audio range in one sweep. The principle used is that of the Wien bridge, fed from anti-phase inputs. The output should be buffered as shown with a FET input op amp, particularly if a high value pot is used.
An op amp with differential outputs (eg., MC1445) may be used in place of the driver ICS. R2 may be made trimmable to optimize the notch. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a Wien bridge oscillator configuration, which is recognized for its low distortion and stable frequency characteristics, making it suitable for audio applications. The dual-ganged potentiometer serves as a tuning mechanism, allowing the user to adjust the frequency response of the circuit with precision. By utilizing anti-phase inputs, the circuit ensures that the oscillation remains stable and minimizes any potential drift that may occur during operation.
In this design, the output stage is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal. The use of a FET input operational amplifier is advantageous due to its high input impedance, which prevents loading effects that could alter the performance of the circuit when a high-value potentiometer is employed. The buffering action of the op-amp isolates the Wien bridge oscillator from subsequent stages, ensuring that the output signal remains faithful to the input.
The option to use an operational amplifier with differential outputs, such as the MC1445, provides flexibility in the design, allowing for improved signal handling and noise rejection. This can be particularly beneficial in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) may be present.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a trimmable resistor R2 enhances the circuit's performance by allowing fine-tuning of the notch frequency. This capability is essential for applications requiring precise filtering, such as in audio equalization or noise reduction systems. By adjusting R2, the user can optimize the notch depth and bandwidth, tailoring the circuit to specific requirements.
Overall, this circuit design presents an efficient solution for audio tuning applications, leveraging the stability of the Wien bridge oscillator while providing user-friendly adjustment capabilities through the dual-ganged potentiometer and trimmable resistor.The circuit requires only one dual-ganged potentiometer to tune over a wide range; if necessary over the entire audio range in one sweep. The principle used is that of the Wien bridge, fed from anti-phase inputs. The output should be buffered as shown with a FET input op amp, particularly if a high value pot is used.
An op amp with differential outputs (eg., MC1445) may be used in place of the driver ICS. R2 may be made trimmable to optimize the notch. 🔗 External reference