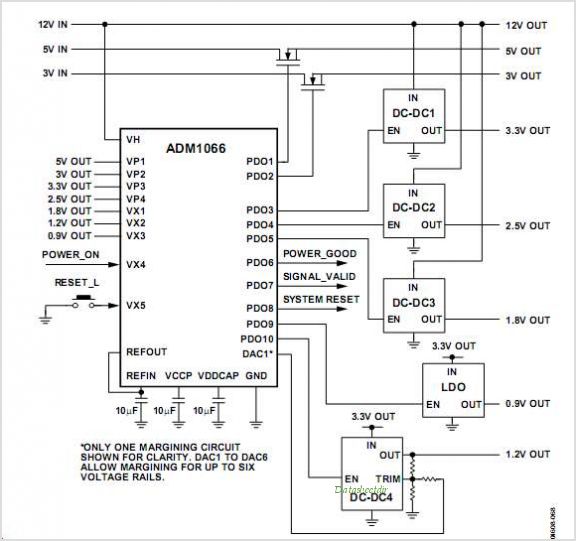
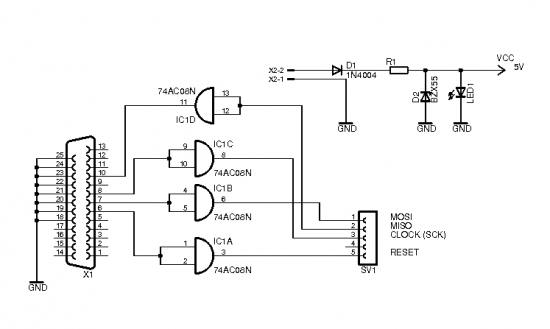
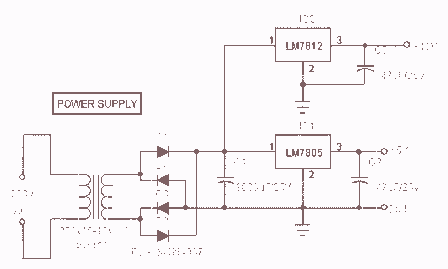
Remote Control Transmitter Circuit
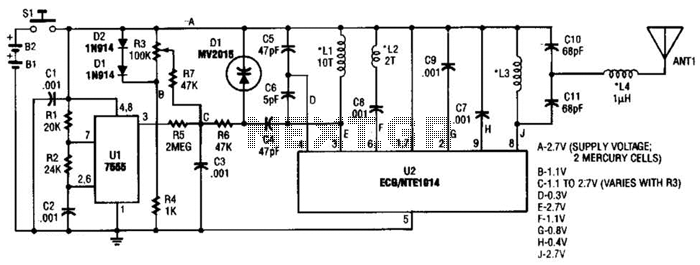
This transmitter can be utilized for multiple applications. An INS8048L microprocessor produces various codes based on keypad inputs. These codes are modulated onto a 40-kHz carrier frequency. Additionally, Q1 drives infrared LEDs LED1 and LED2.
The transmitter circuit primarily consists of the INS8048L microprocessor, which serves as the central processing unit. It interprets the signals from a keypad interface, generating specific codes that correspond to the keys pressed. The microprocessor is programmed to handle various functions, allowing for flexibility in application, such as remote controls or data transmission.
The generated codes are then modulated onto a 40-kHz carrier frequency, which is essential for efficient transmission of signals over infrared light. Modulation is crucial as it allows the codes to be embedded within the carrier wave, making them suitable for infrared communication.
The output stage of the transmitter includes two infrared light-emitting diodes (LEDs), LED1 and LED2, which are driven by a transistor Q1. This transistor acts as a switch, controlling the current flow to the LEDs based on the signals generated by the microprocessor. The use of two LEDs can enhance the transmission range and reliability, as they can work in tandem to emit a stronger infrared signal.
In summary, this transmitter circuit leverages the INS8048L microprocessor for code generation, employs modulation for effective signal transmission, and utilizes infrared LEDs to facilitate communication. This design is suitable for various applications requiring wireless data transmission through infrared signals. This transmitter can be used for a variety of purposes. An INS8048L microprocessor generates various codes depending on keypad presses. The codes are modulated on a 40-kHz carrier. Ql drives IR LEDs LED1 and LED2. 🔗 External reference
The transmitter circuit primarily consists of the INS8048L microprocessor, which serves as the central processing unit. It interprets the signals from a keypad interface, generating specific codes that correspond to the keys pressed. The microprocessor is programmed to handle various functions, allowing for flexibility in application, such as remote controls or data transmission.
The generated codes are then modulated onto a 40-kHz carrier frequency, which is essential for efficient transmission of signals over infrared light. Modulation is crucial as it allows the codes to be embedded within the carrier wave, making them suitable for infrared communication.
The output stage of the transmitter includes two infrared light-emitting diodes (LEDs), LED1 and LED2, which are driven by a transistor Q1. This transistor acts as a switch, controlling the current flow to the LEDs based on the signals generated by the microprocessor. The use of two LEDs can enhance the transmission range and reliability, as they can work in tandem to emit a stronger infrared signal.
In summary, this transmitter circuit leverages the INS8048L microprocessor for code generation, employs modulation for effective signal transmission, and utilizes infrared LEDs to facilitate communication. This design is suitable for various applications requiring wireless data transmission through infrared signals. This transmitter can be used for a variety of purposes. An INS8048L microprocessor generates various codes depending on keypad presses. The codes are modulated on a 40-kHz carrier. Ql drives IR LEDs LED1 and LED2. 🔗 External reference