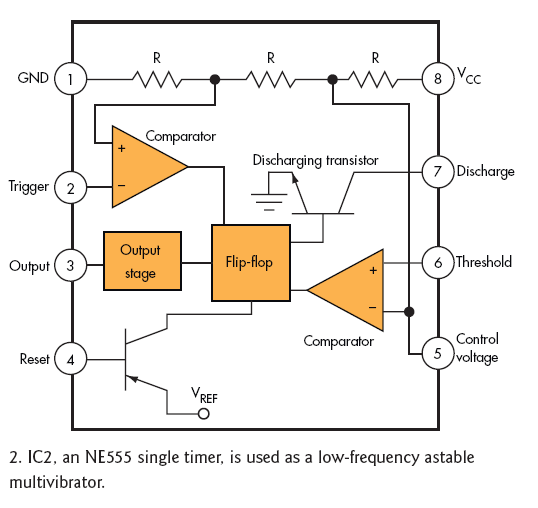
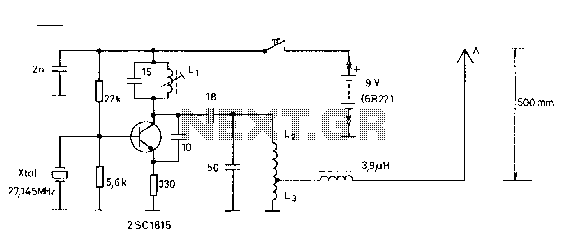
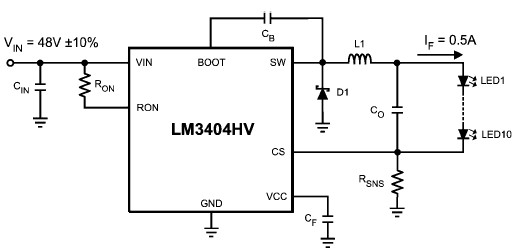
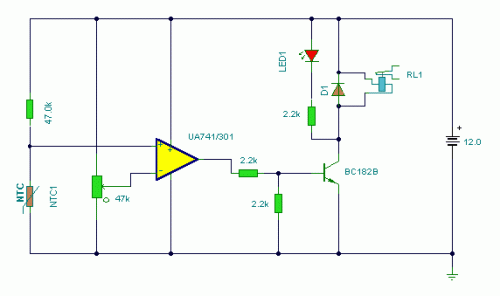
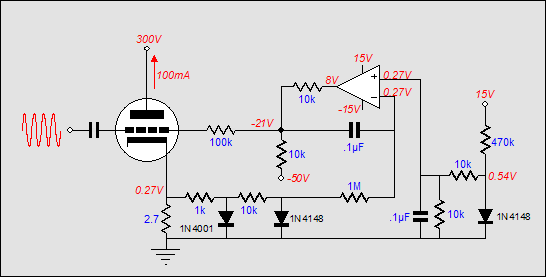
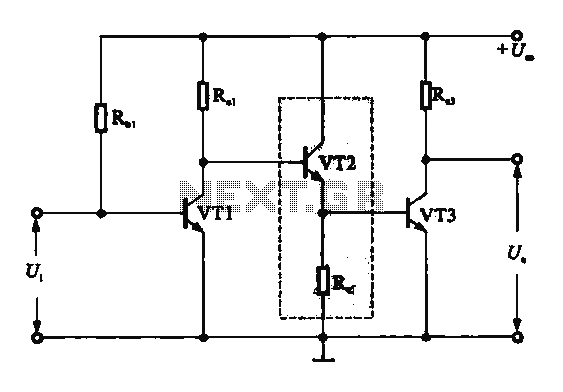
Remote Operated Spy Robot Circuit
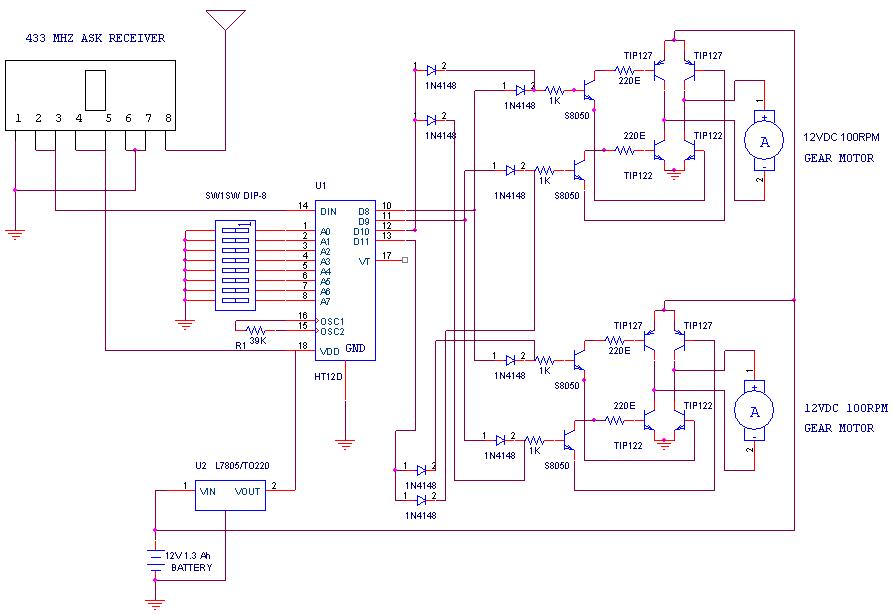
A remote-operated spy robot circuit can be controlled using a wireless remote controller. It captures audio and video information from the surroundings and transmits this data to a remote station via RF signals, with a maximum range of 125 meters, overcoming the limitations of infrared remote controllers. The robot consists of two main sections, which are detailed below. The circuit utilizes the HT 12E and HT 12D encoder and decoder, along with a 433MHz ASK transmitter and receiver for remote control. H-bridge circuits drive the motors, specifically two 12V DC/100RPM gear motors. The operation of the circuit is as follows: when a key on the remote controller is pressed, the HT 12E generates an 8-bit address and 4-bit data. DIP switches are used to set the address. The ASK transmitter then sends the 8-bit address and 4-bit data to the receiver, which is received by the ASK receiver. The HT 12D decoder decodes this data, enabling the appropriate output. The output signals generated control the H-bridge, thus rotating the motors. The 433MHz ASK transmitter and receiver are compact, ideal for applications requiring short-range RF remote controls. The transmitter module is approximately one-third the size of a standard postage stamp, allowing for easy placement within a small plastic enclosure. The transmitter outputs up to 8mW at 433.92MHz and accepts both linear and digital inputs, operating from 1.5 to 12 Volts DC, facilitating the construction of a miniature handheld RF transmitter. The 12V DC supply is sourced from a battery located within the robot. The camera has a receiver positioned at the remote station, with output signals in the form of audio and video. These signals can be directly connected to a TV receiver or computer via a tuner card.
The remote-operated spy robot circuit is designed for efficient surveillance applications, integrating audio and video capturing capabilities with robust wireless communication. The system architecture includes a microcontroller interfaced with the HT 12E encoder, which processes inputs from a remote control. The DIP switches allow for easy configuration of the device's unique address, ensuring that multiple units can operate in proximity without interference.
The 433MHz ASK transmitter and receiver modules are key components in this design, providing reliable communication over a distance of up to 125 meters. The transmitter's compact size and low power requirements make it suitable for portable applications, while the H-bridge motor driver circuit enables precise control of the two DC gear motors, allowing for smooth movement of the robot.
The integration of a camera allows for real-time audio and video streaming, enhancing the robot's functionality. The captured signals can be transmitted wirelessly to a remote monitoring station, where they can be processed and displayed using standard TV receivers or computers equipped with tuner cards. This capability makes the robot an effective tool for reconnaissance and surveillance tasks, providing users with critical information from a safe distance.
Overall, the design emphasizes modularity and ease of use, making it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike. The use of widely available components ensures that the circuit can be replicated and modified for various applications, further extending its utility in the field of remote surveillance technology.Here is a remote operated spy robot circuit which can be controlled by using a wireless remote controller. It can capture audio and video information`s from the surroundings and can be sent to a remote station through RF signals.
The maximum range is 125 meters. It overcomes the limited range of infrared remote controllers. This robot consists of mainly two sections. They are explained in detail below. The circuit uses HT 12E, HT 12D encoder and decoder. 433MHz ASK transmitter and receiver is used for the remote control. H-bridge circuits are used for driving motors. Two 12V DC/100RPM gear motors are used as drivers. The working of the circuit is as follows. When we are pressing any key in remote controller the HT 12E generate 8 bit address and 4 bit data. The DIP switches are used for setting the address. Then the ASK transmitter sends the 8 bit address and 4 bit data to the receiver Then the ASK receiver receives the 8 bit address and 4 bit data and HT 12D decoder decodes the data, thus enabling the appropriate output. Thus the output signals that are generated controls the H-bridge which then rotates the motors. The 433 MHZ ASK transmitter and receivers are extremely small, and are excellent for applications requiring short-range RF remote controls.
The transmitter module is only 1/3rd the size of a standard postage stamp, and can easily be placed inside a small plastic enclosure. The transmitter output is up to 8mW at 433. 92MHz. The transmitter accepts both linear and digital inputs and can operate from 1. 5 to 12 Volts-DC, and makes building a miniature hand-held RF transmitter very easy. The 433 MHZ ASK transmitters is approximately the size of a standard postage stamp The 12 Volt DC supply is taken from the battery placed in the robot.
The camera has a receiver, which is placed in the remote station. Its output signals are in the form of audio and video. These signals are directly connected to a TV receiver or a computer through a tuner card. 🔗 External reference
The remote-operated spy robot circuit is designed for efficient surveillance applications, integrating audio and video capturing capabilities with robust wireless communication. The system architecture includes a microcontroller interfaced with the HT 12E encoder, which processes inputs from a remote control. The DIP switches allow for easy configuration of the device's unique address, ensuring that multiple units can operate in proximity without interference.
The 433MHz ASK transmitter and receiver modules are key components in this design, providing reliable communication over a distance of up to 125 meters. The transmitter's compact size and low power requirements make it suitable for portable applications, while the H-bridge motor driver circuit enables precise control of the two DC gear motors, allowing for smooth movement of the robot.
The integration of a camera allows for real-time audio and video streaming, enhancing the robot's functionality. The captured signals can be transmitted wirelessly to a remote monitoring station, where they can be processed and displayed using standard TV receivers or computers equipped with tuner cards. This capability makes the robot an effective tool for reconnaissance and surveillance tasks, providing users with critical information from a safe distance.
Overall, the design emphasizes modularity and ease of use, making it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike. The use of widely available components ensures that the circuit can be replicated and modified for various applications, further extending its utility in the field of remote surveillance technology.Here is a remote operated spy robot circuit which can be controlled by using a wireless remote controller. It can capture audio and video information`s from the surroundings and can be sent to a remote station through RF signals.
The maximum range is 125 meters. It overcomes the limited range of infrared remote controllers. This robot consists of mainly two sections. They are explained in detail below. The circuit uses HT 12E, HT 12D encoder and decoder. 433MHz ASK transmitter and receiver is used for the remote control. H-bridge circuits are used for driving motors. Two 12V DC/100RPM gear motors are used as drivers. The working of the circuit is as follows. When we are pressing any key in remote controller the HT 12E generate 8 bit address and 4 bit data. The DIP switches are used for setting the address. Then the ASK transmitter sends the 8 bit address and 4 bit data to the receiver Then the ASK receiver receives the 8 bit address and 4 bit data and HT 12D decoder decodes the data, thus enabling the appropriate output. Thus the output signals that are generated controls the H-bridge which then rotates the motors. The 433 MHZ ASK transmitter and receivers are extremely small, and are excellent for applications requiring short-range RF remote controls.
The transmitter module is only 1/3rd the size of a standard postage stamp, and can easily be placed inside a small plastic enclosure. The transmitter output is up to 8mW at 433. 92MHz. The transmitter accepts both linear and digital inputs and can operate from 1. 5 to 12 Volts-DC, and makes building a miniature hand-held RF transmitter very easy. The 433 MHZ ASK transmitters is approximately the size of a standard postage stamp The 12 Volt DC supply is taken from the battery placed in the robot.
The camera has a receiver, which is placed in the remote station. Its output signals are in the form of audio and video. These signals are directly connected to a TV receiver or a computer through a tuner card. 🔗 External reference