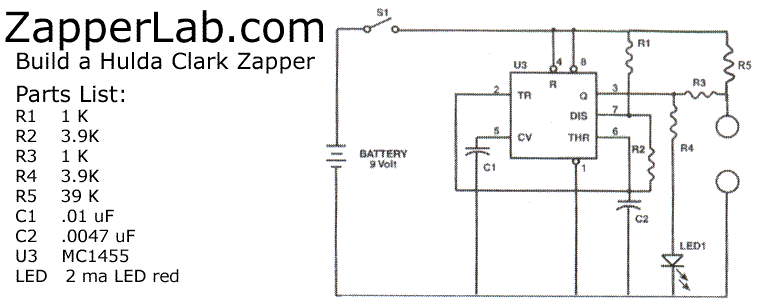
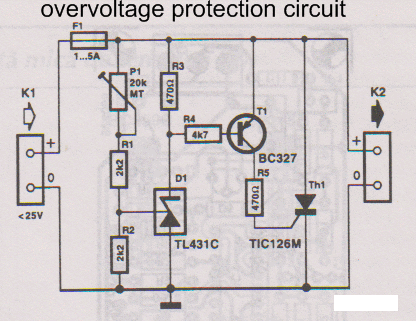
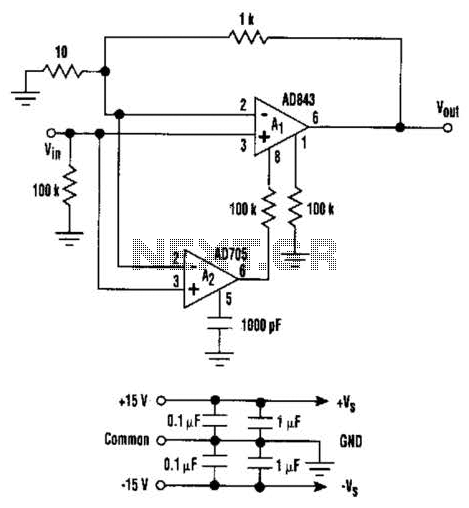
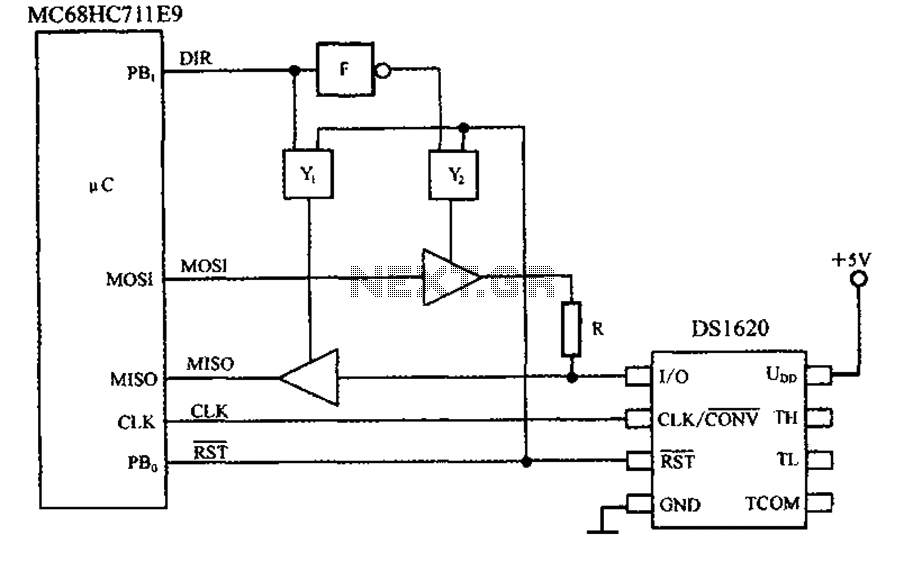
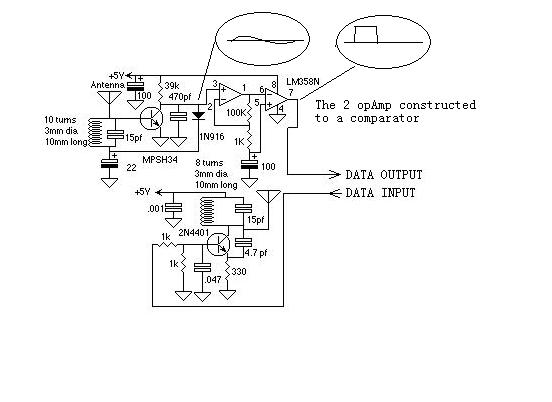
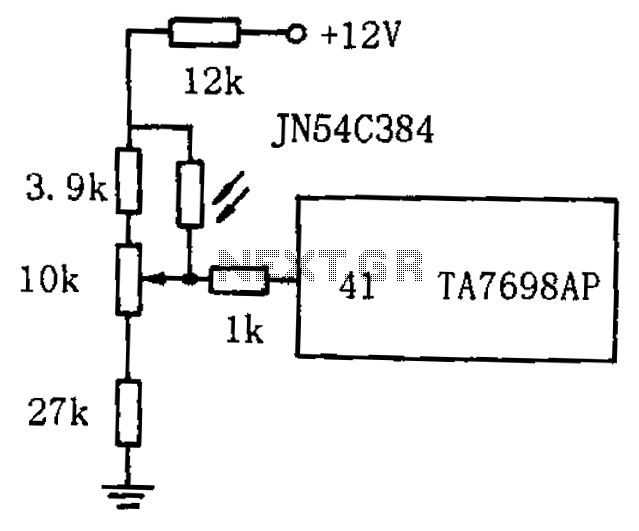
Remote temperature sensing circuit diagrams
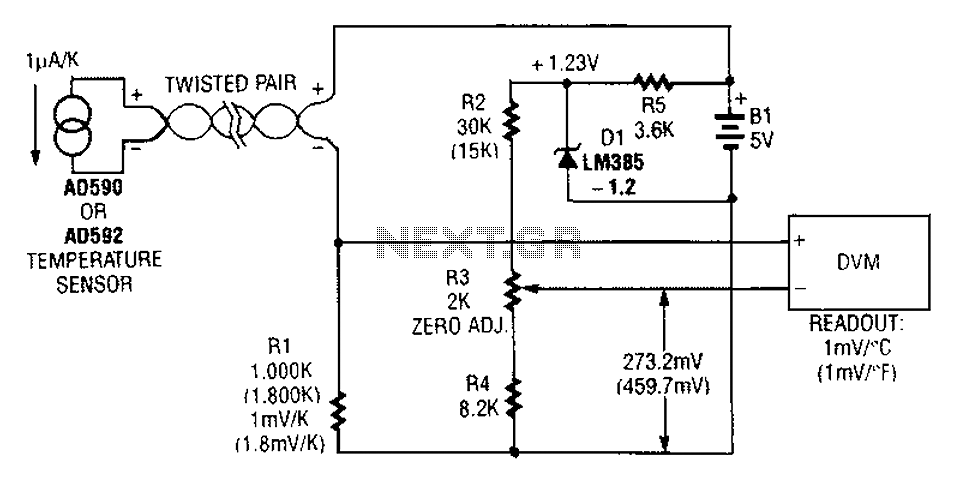
An AD590 or AD592 can be utilized in a transmission line for temperature data transmission. The circuit generates a value of 1 mV per degree Fahrenheit.
The AD590 and AD592 are precision temperature sensors that output a voltage proportional to the absolute temperature. The output voltage of 1 mV/°F indicates that for every degree Fahrenheit change in temperature, the output signal will vary by 1 millivolt. This linear relationship makes these sensors suitable for applications requiring accurate temperature measurement and transmission over long distances.
In a typical application, the AD590 or AD592 can be connected in a circuit configuration that includes a power supply, a signal conditioning module, and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital processing. The power supply provides the necessary operating voltage for the sensor, typically in the range of 4 to 30 volts. The output from the sensor can be fed into an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured for signal amplification, if necessary, to enhance the signal strength for transmission.
The transmission line can be designed using twisted pair or coaxial cables to minimize signal degradation due to electromagnetic interference. Proper termination and impedance matching are critical to ensure signal integrity, particularly over long distances. The use of differential signaling can further enhance noise immunity and improve the quality of the transmitted data.
In summary, the AD590 and AD592 provide a reliable means of temperature data transmission, with a straightforward output that can be easily interfaced with other electronic components for further processing and analysis.A AD590 or AD592 can easily in a transmission line temperature data transmission. The circuit generates a value 1mV/(or is 1mV/F using the values in brackets).
The AD590 and AD592 are precision temperature sensors that output a voltage proportional to the absolute temperature. The output voltage of 1 mV/°F indicates that for every degree Fahrenheit change in temperature, the output signal will vary by 1 millivolt. This linear relationship makes these sensors suitable for applications requiring accurate temperature measurement and transmission over long distances.
In a typical application, the AD590 or AD592 can be connected in a circuit configuration that includes a power supply, a signal conditioning module, and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital processing. The power supply provides the necessary operating voltage for the sensor, typically in the range of 4 to 30 volts. The output from the sensor can be fed into an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured for signal amplification, if necessary, to enhance the signal strength for transmission.
The transmission line can be designed using twisted pair or coaxial cables to minimize signal degradation due to electromagnetic interference. Proper termination and impedance matching are critical to ensure signal integrity, particularly over long distances. The use of differential signaling can further enhance noise immunity and improve the quality of the transmitted data.
In summary, the AD590 and AD592 provide a reliable means of temperature data transmission, with a straightforward output that can be easily interfaced with other electronic components for further processing and analysis.A AD590 or AD592 can easily in a transmission line temperature data transmission. The circuit generates a value 1mV/(or is 1mV/F using the values in brackets).