repair microcontroller circuit
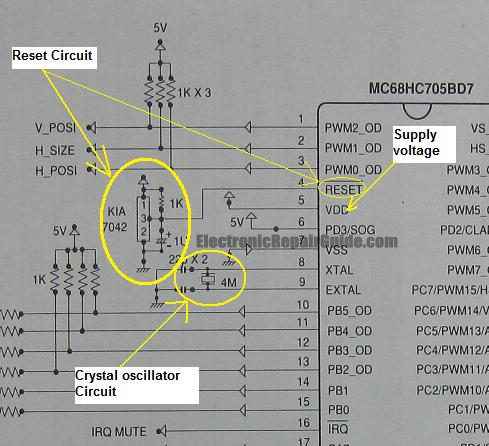
The difference between these two ICs. A microcontroller is a specialized type of microprocessor designed to be self-sufficient and cost-effective, while a microprocessor is typically intended for general-purpose use, such as in personal computers (PCs). The microcontroller integrates several useful functions into a single IC package. These functions include a main CPU core, ROM/EPROM/EEPROM/FLASH, RAM, and various accessory functions (such as timers and I/O controllers) all integrated into one chip. In contrast, a microprocessor IC generally consists solely of the CPU core, although modern versions may include some accessory components, like cache memory. Microcontroller ICs are commonly found in consumer electronics, including monitors, televisions, automobiles, washing machines, office machines, toys, and appliances. In the early 1990s and prior, many analog monitors did not incorporate a microcontroller circuit; their functions were managed by variable resistors. For example, if a monitor's brightness was problematic, tracing the fault from the variable resistor on the front panel was straightforward. This method could also be applied to other circuits, such as the pincushion circuit, horizontal size circuit, and vertical size circuit. However, with the introduction of digital monitors utilizing microcontroller circuits, fault-finding became more complex and could not follow the same methodology as with analog monitors. Below are some frequently asked questions from colleagues:
Question 1: If a microprocessor requires 5 volts to operate and the supply voltage is insufficient, such as 4.2 volts or 3 volts, how does this affect the overall performance of the microprocessor?
Answer: Yes, it will either fail to function entirely (showing input signals but no output) or operate intermittently. Therefore, when inquiries arise regarding unusual issues in electronic equipment under repair, checking the supply voltage is essential. Ensuring the supply voltage meets specifications is critical. Intermittently means that the equipment may sometimes work and sometimes not; even if operational, it might suddenly shut down and restart. For monitors, the OSD (On-Screen Display) may appear unexpectedly, causing various display issues.
Answer: The only option is to trace backward from each pin of the microprocessor until locating a voltage regulator IC, such as the 7805, or any other relevant part number that may be found through internet searches. The microcontroller pin should connect to one of the legs of the voltage regulator IC. Some designs do not utilize a voltage regulator but instead employ transistor circuits, where the voltage is sourced from the output of a switch-mode power supply.
Answer: Certainly, not only will the microprocessor fail to operate (resulting in the equipment ceasing to function), but it may also cause intermittent problems similar to other electronic components. If a scope is used to test the crystal pins and no sine wave is detected, there is a high probability that the crystal itself is faulty, or the microcontroller IC or associated components may be at fault. An intermittent crystal in a monitor (LCD or CRT) could lead to the OSD (On-Screen Display) appearing unexpectedly after use.
Microcontrollers and microprocessors serve distinct roles within electronic systems, with microcontrollers being integral to embedded applications due to their compact integration of essential components. Their design allows for efficient control and management of various functions, making them suitable for a wide array of applications, from household appliances to automotive systems. The evolution from analog to digital systems has necessitated a shift in diagnostic approaches, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying architecture of these components for effective troubleshooting and repair.The different between these two IC`s. A Microcontroller is a specialized form of Microprocessor that is created to be self-sufficient and cost-effective, where a Microprocessor is typically designed to be general purpose use like in a Personal Computer (PC). The Microcontroller is the integration of a number of useful functions into a single IC package. These functions are: A Microcontroller generally has the main CPU core, ROM/EPROM/EEPROM/FLASH, RAM and some accessory functions (like timers and I/O controllers) all integrated into one chip. Microprocessor IC is generally just the CPU core itself, although nowadays it might have some accessory parts also integrated to the same chip (for example cache memory).
Microcontrollers IC`s are frequently found in consumer electronics like Monitors, Televisions, in automobiles, washing machine, office machines, toys, appliances and etc. I still could recall during the early 90`s and before, many of the Analog Monitors that I repaired does not have the microcontroller circuit.
The functions of the Monitors were all controlled by variable resistors. Let say if the Monitor brightness have problem we just have to follow the brightness control starting from the variable resistor in the front panel and trace it backward and it was very easy to locate the fault. You can use this method to trace on other circuit as well like the Pincushion circuit, Horizontal size circuit, Vertical Size circuit and etc.
However when the newer type of Monitors (Digital Monitors) that use the Microcontroller circuit came into the market I have problem in finding those fault and you can`t follow the way that you used in finding fault in an Analog Monitors. Below I cover some of the most frequently asked questions from fellow members: Question 1: Assuming a Microprocessor need 5 volt to run and if the supply voltage is not sufficient like 4.
2 volt or 3 volt and etc, does it affect the overall performance of the Microprocessor Answer: Yes definitely, it will either do not work at all (have input signal but no output signal) or working intermittently. That is why whenever I have email that asked me about weird problems in the electronic equipment that they are repairing I always asked them to check on the supply voltage.
Make sure that the supply voltage is within the spec. Intermittently means the equipment sometimes could work and sometimes don`t and even if the equipment is working then out of sudden the equipment could shutdown and restart again and if you repair Monitors, the OSD (On screen Display) could appear on it own and creating lots of weird problem to the display and etc. Answer: The only choice you have is to trace backward from each pins of the microprocessor till you found a voltage regulator IC with the part number of 7805 or any other new part number that you need to check it out from internet search.
The Microcontroller pin should lead you to one of the leg of the voltage regulator IC. Some do not use voltage regulator but uses transistors circuit where the source of voltage was taken from the output of switch mode power supply. Answer: Certainly- Not only it will not work (causing the equipment to stop working) but also could cause intermittent problem too just like any other electronic components.
If using scope to test on the CRYSTAL pins and you did not get the sine wave chances is very high the CRYSTAL it self have problem or it could be the Microcontroller IC or corresponding components fault. An intermittent Crystal in Monitor (LCD or CRT) could cause the OSD (On Screen Display) to suddenly appear after usi
🔗 External reference
Question 1: If a microprocessor requires 5 volts to operate and the supply voltage is insufficient, such as 4.2 volts or 3 volts, how does this affect the overall performance of the microprocessor?
Answer: Yes, it will either fail to function entirely (showing input signals but no output) or operate intermittently. Therefore, when inquiries arise regarding unusual issues in electronic equipment under repair, checking the supply voltage is essential. Ensuring the supply voltage meets specifications is critical. Intermittently means that the equipment may sometimes work and sometimes not; even if operational, it might suddenly shut down and restart. For monitors, the OSD (On-Screen Display) may appear unexpectedly, causing various display issues.
Answer: The only option is to trace backward from each pin of the microprocessor until locating a voltage regulator IC, such as the 7805, or any other relevant part number that may be found through internet searches. The microcontroller pin should connect to one of the legs of the voltage regulator IC. Some designs do not utilize a voltage regulator but instead employ transistor circuits, where the voltage is sourced from the output of a switch-mode power supply.
Answer: Certainly, not only will the microprocessor fail to operate (resulting in the equipment ceasing to function), but it may also cause intermittent problems similar to other electronic components. If a scope is used to test the crystal pins and no sine wave is detected, there is a high probability that the crystal itself is faulty, or the microcontroller IC or associated components may be at fault. An intermittent crystal in a monitor (LCD or CRT) could lead to the OSD (On-Screen Display) appearing unexpectedly after use.
Microcontrollers and microprocessors serve distinct roles within electronic systems, with microcontrollers being integral to embedded applications due to their compact integration of essential components. Their design allows for efficient control and management of various functions, making them suitable for a wide array of applications, from household appliances to automotive systems. The evolution from analog to digital systems has necessitated a shift in diagnostic approaches, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying architecture of these components for effective troubleshooting and repair.The different between these two IC`s. A Microcontroller is a specialized form of Microprocessor that is created to be self-sufficient and cost-effective, where a Microprocessor is typically designed to be general purpose use like in a Personal Computer (PC). The Microcontroller is the integration of a number of useful functions into a single IC package. These functions are: A Microcontroller generally has the main CPU core, ROM/EPROM/EEPROM/FLASH, RAM and some accessory functions (like timers and I/O controllers) all integrated into one chip. Microprocessor IC is generally just the CPU core itself, although nowadays it might have some accessory parts also integrated to the same chip (for example cache memory).
Microcontrollers IC`s are frequently found in consumer electronics like Monitors, Televisions, in automobiles, washing machine, office machines, toys, appliances and etc. I still could recall during the early 90`s and before, many of the Analog Monitors that I repaired does not have the microcontroller circuit.
The functions of the Monitors were all controlled by variable resistors. Let say if the Monitor brightness have problem we just have to follow the brightness control starting from the variable resistor in the front panel and trace it backward and it was very easy to locate the fault. You can use this method to trace on other circuit as well like the Pincushion circuit, Horizontal size circuit, Vertical Size circuit and etc.
However when the newer type of Monitors (Digital Monitors) that use the Microcontroller circuit came into the market I have problem in finding those fault and you can`t follow the way that you used in finding fault in an Analog Monitors. Below I cover some of the most frequently asked questions from fellow members: Question 1: Assuming a Microprocessor need 5 volt to run and if the supply voltage is not sufficient like 4.
2 volt or 3 volt and etc, does it affect the overall performance of the Microprocessor Answer: Yes definitely, it will either do not work at all (have input signal but no output signal) or working intermittently. That is why whenever I have email that asked me about weird problems in the electronic equipment that they are repairing I always asked them to check on the supply voltage.
Make sure that the supply voltage is within the spec. Intermittently means the equipment sometimes could work and sometimes don`t and even if the equipment is working then out of sudden the equipment could shutdown and restart again and if you repair Monitors, the OSD (On screen Display) could appear on it own and creating lots of weird problem to the display and etc. Answer: The only choice you have is to trace backward from each pins of the microprocessor till you found a voltage regulator IC with the part number of 7805 or any other new part number that you need to check it out from internet search.
The Microcontroller pin should lead you to one of the leg of the voltage regulator IC. Some do not use voltage regulator but uses transistors circuit where the source of voltage was taken from the output of switch mode power supply. Answer: Certainly- Not only it will not work (causing the equipment to stop working) but also could cause intermittent problem too just like any other electronic components.
If using scope to test on the CRYSTAL pins and you did not get the sine wave chances is very high the CRYSTAL it self have problem or it could be the Microcontroller IC or corresponding components fault. An intermittent Crystal in Monitor (LCD or CRT) could cause the OSD (On Screen Display) to suddenly appear after usi
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713