Switch De-Bouncer Circuit
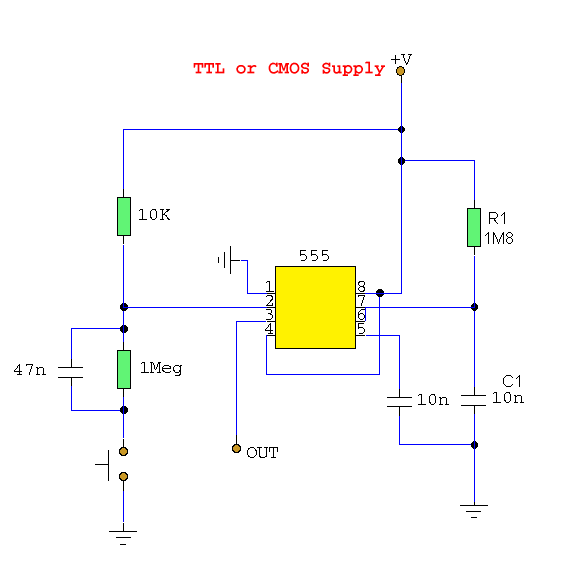
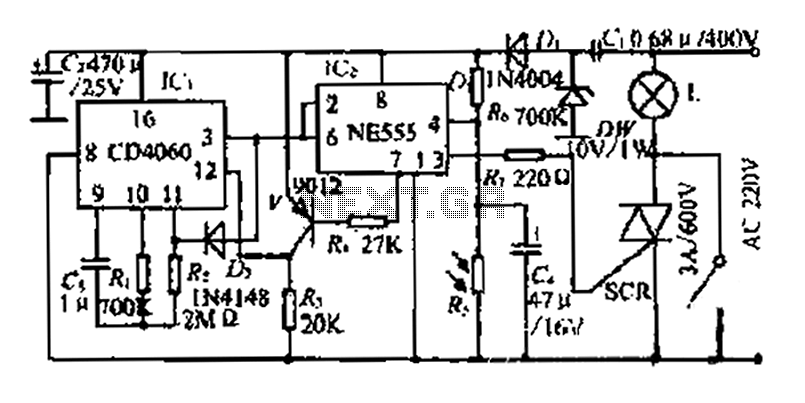
The 555 circuit can be re-triggered if the input is held low for a duration longer than the output pulse. To prevent this from occurring, an additional timing circuit has been incorporated, consisting of a 1 Megohm resistor and a 47nF capacitor. Typically, the 47nF capacitor discharges through the 1 Megohm resistor. When the switch is activated, the capacitor charges rapidly, generating a brief negative pulse to the 555 input. Once the capacitor reaches full charge, the voltage across the divider formed by the 10k and 1 Megohm resistors is inadequate to retrigger the monostable configuration. Releasing the switch allows for the quick discharge of the capacitor. The output from a 555 monostable is compatible with TTL and CMOS logic circuits.
The described 555 timer circuit operates in a monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to a triggering event. The additional timing circuit, comprising a 1 Megohm resistor and a 47nF capacitor, serves to mitigate the risk of unintended retriggering of the 555 timer. This is particularly important in applications where precise timing is critical, as it ensures that the timer output pulse duration remains stable and predictable.
Upon pressing the switch, the capacitor charges rapidly, creating a negative pulse at the input of the 555 timer. This pulse initiates the timer's output. The careful selection of the resistor and capacitor values is crucial; the 1 Megohm resistor provides a slow discharge path for the capacitor, while the 47nF capacitor determines the timing characteristics of the circuit. The voltage divider, consisting of the 10k and 1 Megohm resistors, plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the voltage at the input of the 555 timer remains below the retrigger threshold once the capacitor is fully charged.
When the switch is released, the capacitor discharges quickly through the 1 Megohm resistor, resetting the circuit and preparing it for the next triggering event. The output from the 555 timer can interface directly with TTL and CMOS logic circuits, making this configuration versatile for various digital applications. The design effectively balances responsiveness and stability, making it suitable for timing applications, pulse generation, and signal conditioning in electronic systems.The 555 circuit can be re-triggered if the input is held low longer than the output pulse. To prevent this happening, I have included a further timing circuit comprised of the 1Meg resistor and 47n capacitor. Normally, the 47n capacitor is discharged via the 1 Meg resistor. When the switch is pressed the capacitor quickly charges and provides a br ief negative pulse to the 555 input. When the capacitor is fully charged, the potential across the voltage divider formed by the 10k and 1Meg resistors is insufficient to retrigger the monostable. Releasing the switch quickly discharges the capacitor. The output of a 555 monostable is suitable for connecting to TTL and CMOS logic circuits. 🔗 External reference
The described 555 timer circuit operates in a monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to a triggering event. The additional timing circuit, comprising a 1 Megohm resistor and a 47nF capacitor, serves to mitigate the risk of unintended retriggering of the 555 timer. This is particularly important in applications where precise timing is critical, as it ensures that the timer output pulse duration remains stable and predictable.
Upon pressing the switch, the capacitor charges rapidly, creating a negative pulse at the input of the 555 timer. This pulse initiates the timer's output. The careful selection of the resistor and capacitor values is crucial; the 1 Megohm resistor provides a slow discharge path for the capacitor, while the 47nF capacitor determines the timing characteristics of the circuit. The voltage divider, consisting of the 10k and 1 Megohm resistors, plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the voltage at the input of the 555 timer remains below the retrigger threshold once the capacitor is fully charged.
When the switch is released, the capacitor discharges quickly through the 1 Megohm resistor, resetting the circuit and preparing it for the next triggering event. The output from the 555 timer can interface directly with TTL and CMOS logic circuits, making this configuration versatile for various digital applications. The design effectively balances responsiveness and stability, making it suitable for timing applications, pulse generation, and signal conditioning in electronic systems.The 555 circuit can be re-triggered if the input is held low longer than the output pulse. To prevent this happening, I have included a further timing circuit comprised of the 1Meg resistor and 47n capacitor. Normally, the 47n capacitor is discharged via the 1 Meg resistor. When the switch is pressed the capacitor quickly charges and provides a br ief negative pulse to the 555 input. When the capacitor is fully charged, the potential across the voltage divider formed by the 10k and 1Meg resistors is insufficient to retrigger the monostable. Releasing the switch quickly discharges the capacitor. The output of a 555 monostable is suitable for connecting to TTL and CMOS logic circuits. 🔗 External reference